Government Leaders, Scholars Discuss Policy Solutions During UCLA Luskin Summit Congresswoman Karen Bass opens the inaugural convening of a research-informed, cross-sector conference about issues facing the region
By Les Dunseith
Elected officials, scholars, civic leaders, and difference-makers in the nonprofit and philanthropic spheres came together April 24 to learn the results of the annual Quality of Life Index and discuss policy issues during a half-day conference put together by the UCLA Luskin School of Public Affairs.
Congresswoman Karen Bass provided the morning’s keynote address for “Luskin Summit 2019: Livable L.A.,” an event that also kicked off the 25th anniversary celebration at the Luskin School.
Bass opened the conference by jokingly telling more than 300 people in attendance at the UCLA Luskin Conference Center that she “wanted to tell you about what we are doing in D.C. because, if you watch some TV news, you have no idea what we are doing in D.C.”
Bass has served in the U.S. House of Representatives since 2011. She said that “Democrats and Republicans actually do work together” in the nation’s capital.
“We don’t hate each other,” Bass said, smiling broadly. “Our accomplishments unfortunately don’t sustain media attention. So you might hear that we passed legislation on something like gun control … and then somebody tweets, and that’s all you hear about for the next several hours.”
The congresswoman’s remarks set a cooperative tone for the inaugural Luskin Summit, which focused on finding solutions through research and policy change. The conference emphasized a Los Angeles perspective during breakout sessions moderated by UCLA faculty members that focused on issues such as public mobility, climate change, housing and criminal justice.
Providing a framework for those discussions was the unveiling of the fourth Quality of Life Index, a project at UCLA Luskin that is supported by The California Endowment under the direction of longtime Los Angeles political stalwart Zev Yaroslavsky, director of the Los Angeles Initiative. The survey asks county residents to rate their quality of life in a range of categories and to answer questions about important issues facing them and the region.
“The cost of living, and particularly the cost of housing, is the single biggest drag on the rating that residents ultimately give to their quality of life in Los Angeles,” Yaroslavsky told Luskin Summit attendees. “The unmistakable takeaway from this project continues to be the crippling impact of the cost of living in Los Angeles County, punctuated by the extraordinary cost of housing.”
The housing affordability crisis was echoed throughout the event and in the days that followed as Yaroslavsky explained details of the survey in coverage by news outlets such as the Los Angeles Times, local radio news programs, and broadcast television reports by the local affiliates for NBC and ABC.
The coverage by KABC (also known as ABC7 Los Angeles) included segments on daily news broadcasts and a follow-up discussion with Yaroslavsky scheduled to air May 26 on the station’s weekly public affairs program, “Eyewitness Newsmakers.” That program is hosted by Adrienne Alpert, a general assignment reporter at ABC7 who served as the moderator for the Luskin Summit.
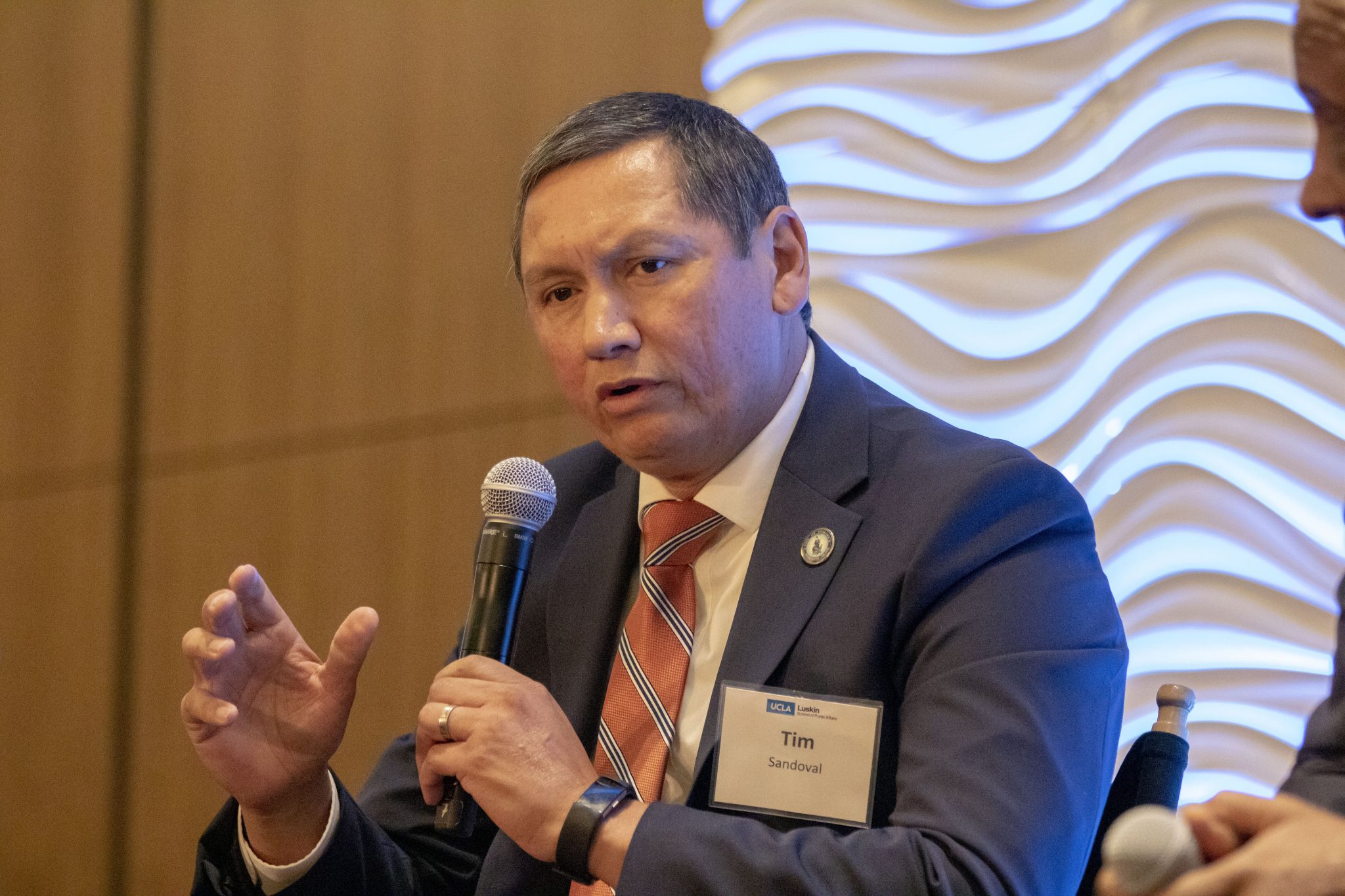
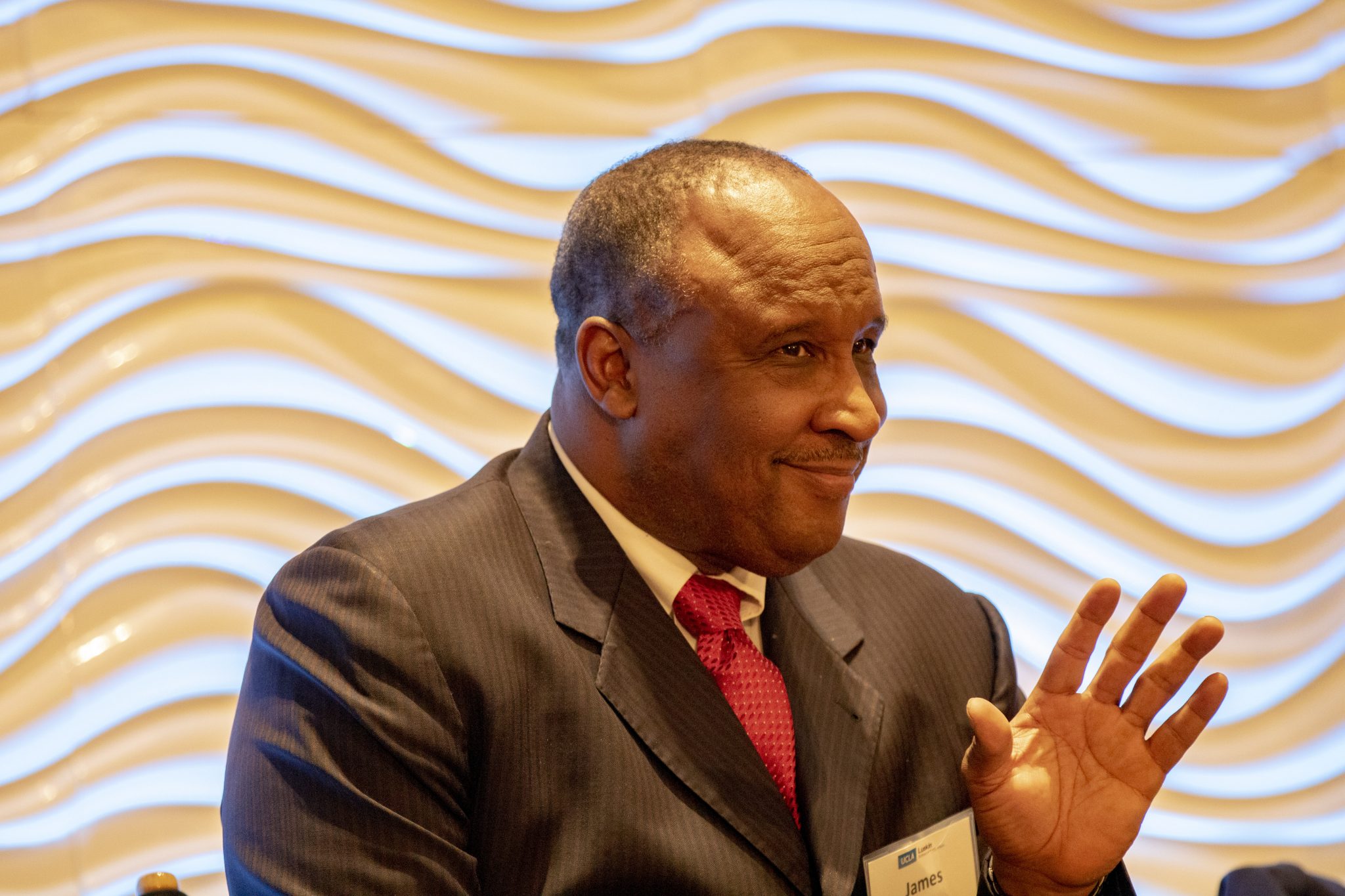
Alpert also hosted a panel discussion that closed the conference, during which mayors of four cities in Los Angeles County — Emily Gabel-Luddy of Burbank, Thomas Small of Culver City, James Butts of Inglewood and Tim Sandoval of Pomona — spoke frankly about the challenges their cities face in dealing with issues such as the rising cost of housing and its potential to lead to displacement of low-income residents.
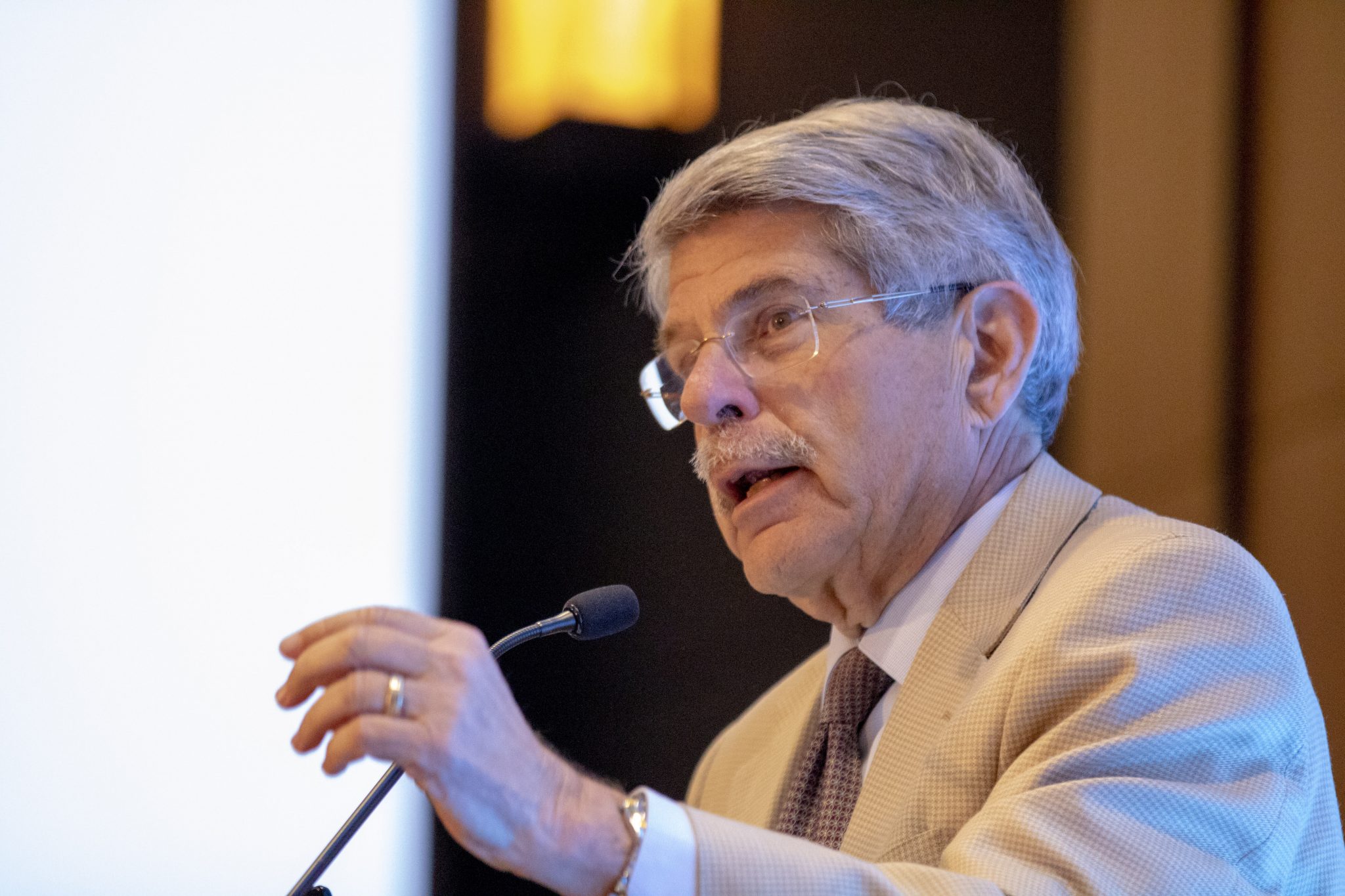
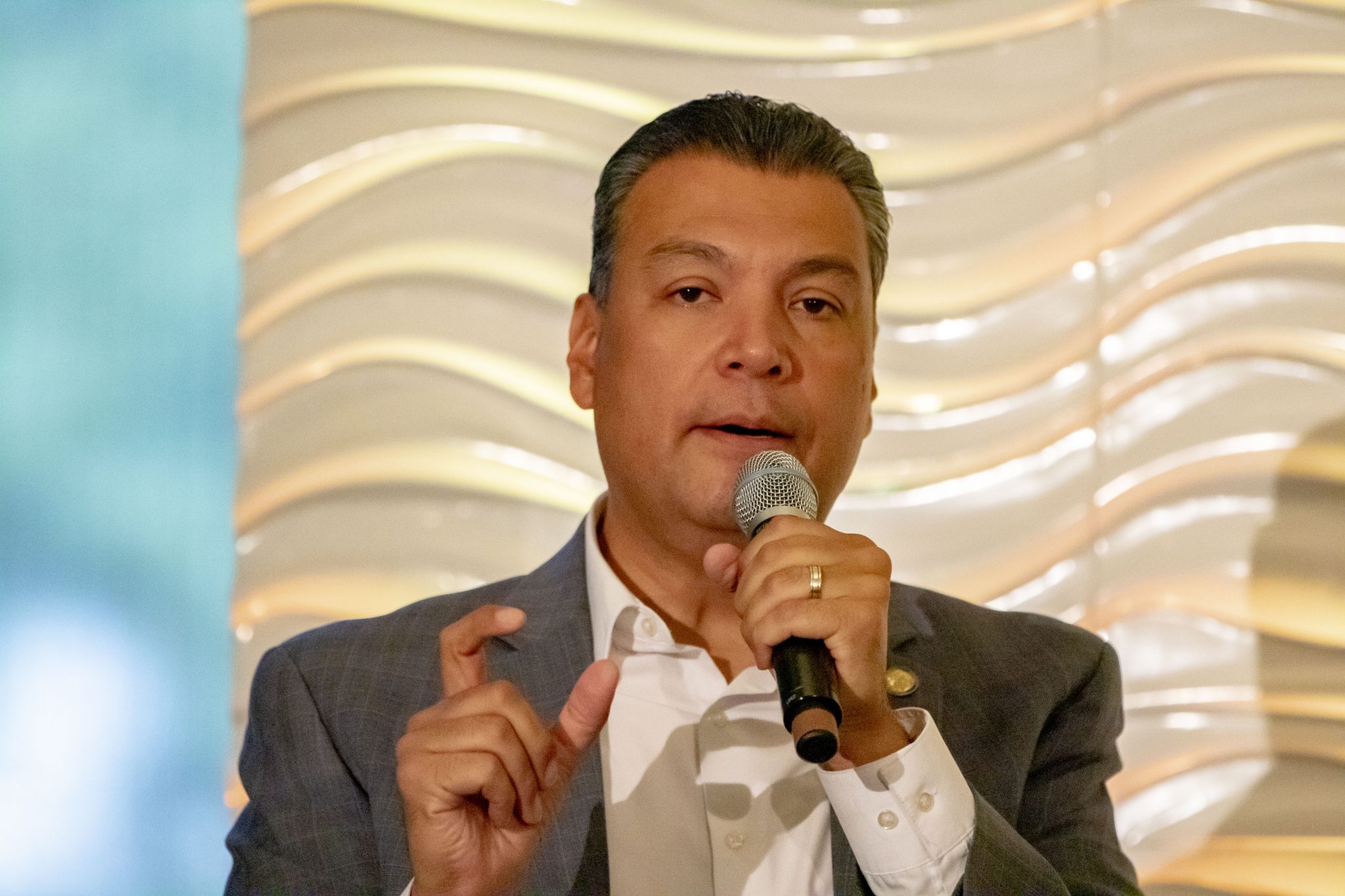
California Secretary of State Alex Padilla, a former colleague of Yaroslavsky on the Los Angeles City Council, was also in attendance at the conference. Padilla engaged in a lively exchange about election security and voter registration efforts with UCLA Luskin Dean Gary Segura during a lunch meeting of panelists, faculty members and sponsors that took place immediately after the summit.
Segura also provided remarks during the morning session, introducing Bass and giving attendees a preview of the day to follow.
“Today you will hear from a series of dedicated public officials who understand that as great as our nation is, it can be better,” Segura said. “And they are taking action to make our country and our city more effective, more innovative, more fair and more inclusive.”
During her remarks, Bass offered her perspective on the recently released investigation by special counsel Robert Mueller into Russian interference in the 2016 presidential election.
“One thing that is a responsibility by the Constitution for Congress — we are supposed to provide oversight and investigation of the administration,” Bass said. “Most of the time it’s not that controversial, and you don’t really hear about it. But it’s made to be super-controversial now because we are in a hyper-partisan situation.”
The bitter partisanship prevalent in Washington today does have a positive aspect, she said, in that Americans seem to be paying closer attention to government and political issues.
“I am hoping that this trauma that we have collectively gone through will lead to a change in our American culture,” Bass said, “because as a culture we tend not to be involved politically.”
Bass said that more people seem to have a deeper understanding of political actions related to “immigration, the Muslim ban, the environment — all the kind of negative things that this administration has done,” said Bass, a Democrat who has been critical of many Trump administration policies. “I think he has sparked a new level of awareness and involvement, where we are working across our silos. I think, ultimately, we can take advantage of this period and bring about transformative change.”
The idea of initiating transformative change was a popular notion among many attendees at the Luskin Summit, as was the focus on making Los Angeles a more livable place.
“I can’t think of a better topic than how to make our city more livable and touch on all of these different aspects of life and the built environment and our environment in Los Angeles,” said Nurit Katz MPP/MBA ’08, the chief sustainability officer at UCLA.
Wendy Greuel BA ’83 is a former Los Angeles city controller and past president of the Los Angeles City Council. She noted that the research presented during the Luskin Summit was timely and focused “on issues that matter to Los Angeles, but also to this country and this world.”
Greuel served as the chair of the UCLA Luskin Advisory Board committee that helped plan the Luskin Summit. “I think that UCLA Luskin is at the forefront of really focusing on issues that matter and being able to give us real-life solutions and address the challenges,” she said.
Another UCLA Luskin Advisory Board member is Stephen Cheung BA ’00 MSW ’07, who is president of the World Trade Center Los Angeles and executive vice president at the L.A. County Economic Development Corporation.
“I think anything that has to do with sustainability and the growth of Los Angeles as a whole is very important to the economic vitality of this region,” Cheung said as the event got underway. “So this summit and all the information that’s going to be provided will really set a roadmap in terms of what we need to do, addressing public policies in terms of creating new opportunities for our companies here.”
Jackie Guevarra, executive director of the Quality and Productivity Commission of the L.A. County Board of Supervisors, said she attended the Luskin Summit because of her interest in the issues under discussion, including housing affordability.
“Homelessness is a big issue that L.A. County is tackling right now,” Guevarra said. “That is an issue that touches all of us. … The more that we have that conversation, the more people we can get to the same way of thinking about how to address the need — so that maybe we can all say, ‘Yes, we need affordable housing, and it’s OK for it to be here in my community.’”
Misch Anderson is a community activist with the Pasadena Complete Streets Coalition, a volunteer organization created in 2013 after a series of fatal crashes involving cars, pedestrians and cyclists.
“I was feeling like my activism put me in touch with such a small, kind of silo-ized community mindset, and I really want to break out of that and connect with people on a larger level,” said Anderson about her reason for attending the summit. “I just wanted to get some inspiration.”
Her takeaway from the summit?
“The idea that we need cultural change, essentially. I think the realities of globalism should be forcing us as individuals to think more widely, more as a larger group, and not be so xenophobic,” Anderson said. “I keep hearing about cultural change [at the summit] and thinking about what can I do — what can each of us do.”
Among the UCLA students in attendance was Tam Guy, a second-year Urban Planning Ph.D. candidate who is studying equity in the city, which encompasses housing, transportation and environmental design.
“One thing that interested me about this summit in particular is that they’re bringing in people from outside academia to talk about the issues, people who are actually on the ground dealing with policy day-to-day,” Guy noted.
The Luskin Summit drew a large crowd to the UCLA campus, and several hundred people watched a live stream of selected presentations. It drew interest near and far. A prime example was a group seated together near the back of the vast ballroom during the opening session — high school students from New Zealand!
The youths had been traveling up and down the West Coast with Joanna Speed, international coordinator with Crimson Education, a college admissions consulting service that exposes teens to potential careers and educational opportunities abroad. Coincidentally, the group scheduled its campus tour of UCLA for April 24. When they saw that the summit was happening that day, they asked to attend.
“It’s been an incredible experience for them,” Speed said.
Mary Braswell and Stan Paul also contributed to this story.
—
View additional photos from the UCLA Luskin Summit
Watch videos recorded during the event:
- Opening remarks by U.S. Rep. Karen Bass, plus an overview of the Quality of Life Index by Zev Yaroslavsky and other presentations
- Breakout session titled “Dealing With Disruption: From Public Transit to Public Mobility”
- Breakout session titled “A Housing-Oriented Look at Understanding Rising L.A. Inequality”
- Closing discussion moderated by Adrienne Alpert of ABC7 and featuring Mayor Emily Gabel-Luddy of Burbank, Mayor Thomas Small or Culver City, Mayor James Butts of Inglewood and Mayor Tim Sandoval of Pomona









































 Jobs supported by California Climate Investments are diverse and cut across many different industries and economic sectors, ranging from the manufacture of clean vehicles to the restoration of degraded wetlands, according to the study.
Jobs supported by California Climate Investments are diverse and cut across many different industries and economic sectors, ranging from the manufacture of clean vehicles to the restoration of degraded wetlands, according to the study.










 Those students, now Luskin alumni, spent 2016-17 working on a variety of projects related to urgent human needs, such as:
Those students, now Luskin alumni, spent 2016-17 working on a variety of projects related to urgent human needs, such as: