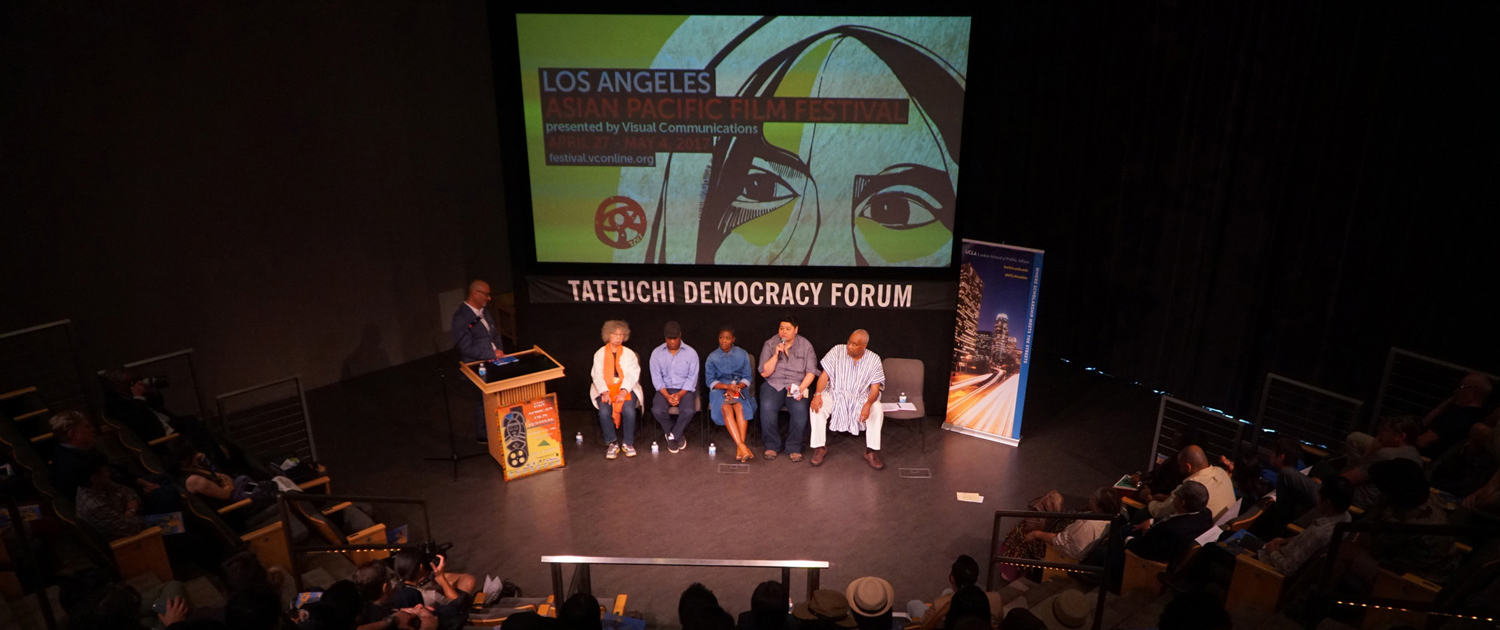
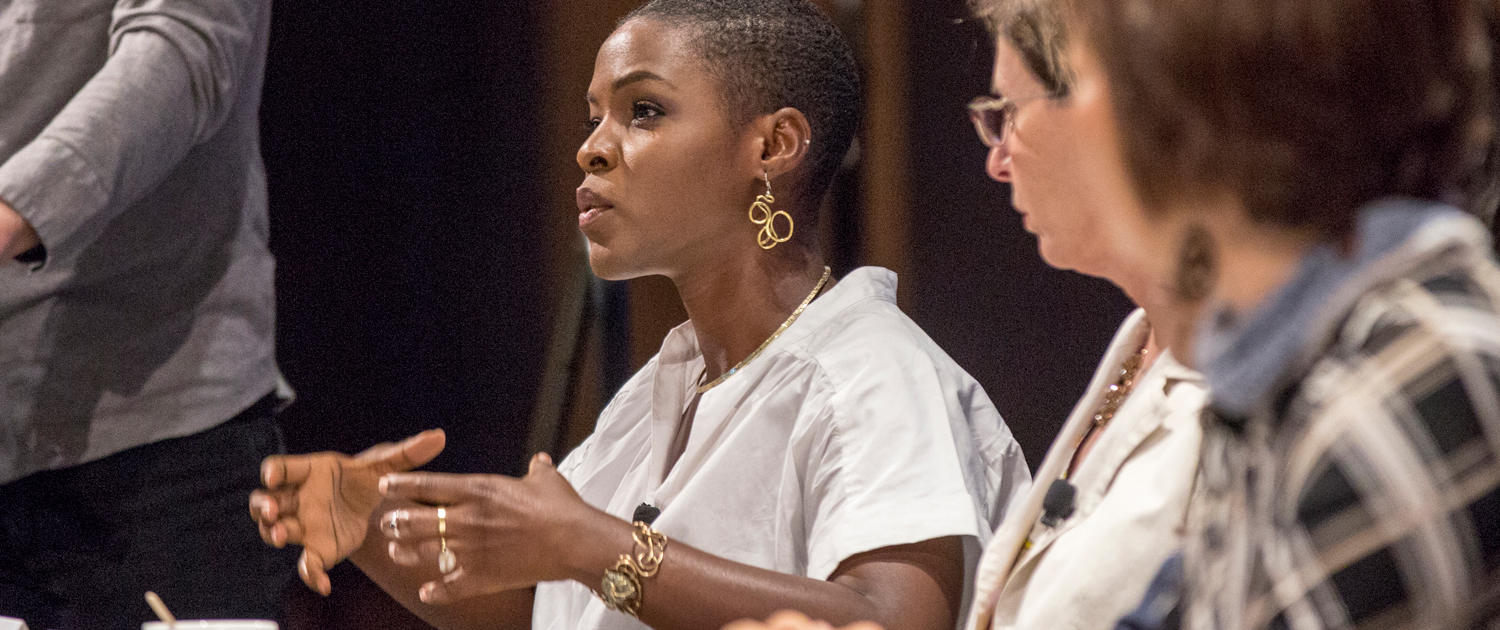Progress and Equity: It Takes a Village During a panel discussion on policymaking in the Trump era, local leaders advocate for targeted community action rather than relying solely on mass protests
By Aaron Julian
Determination and the call to purposeful action were primary themes at UCLA Luskin during “Equitable Policymaking Under a Trump Administration,” which featured local leaders whose work presses for the rights of minority and underrepresented groups in the greater Los Angeles community and beyond.
“The work we are doing now is more important than ever before. If there is a bright light [of the Trump election], it is that a lot of people have been mobilized to do something,” said panelist Fred Ali, president and CEO of the Weingart Foundation.
Furthering Ali’s point, Romel Pascual, executive director of CicLAvia, shared the message imparted to his staff the day after the election of President Trump. “Our work is so much more important than ever before. Because what we do is we bring people together,” he said.
Sonja Diaz MPP ’10, founding director of the Latino Policy and Politics Initiative at the UCLA Luskin School of Public Affairs, was the moderator of the May 11, 2017, event and discussion. The Equitable Policy Symposium was hosted by Policy Professionals for Diversity and Equity, co-chaired by Emma K. Watson and Jessica Noel, second-year students in the Master of Public Policy program.
Diaz directed the conversation with questions about how to ensure that the rights of minority communities are protected and how each panelist’s work has changed in the wake of the presidential election. A sense of community, paired with organized mass mobilization, was the panelists’ unanimous response.
Funmilola Fagbamila, activist-in-residence for the Institute on Inequality and Democracy at UCLA Luskin and arts and culture director for Black Lives Matter Los Angeles, pressed that the work of an activist has not changed, instead it has become more amplified. Fagbamila also noted that the same protesting and organizational techniques employed by Black Lives Matter were being used nationwide in resistance to the election’s outcome.
“Be willing to have conversations with folks in your own communities who don’t get it,” emphasized Fagbamila. “We need numbers, and in order to get numbers … we have to be willing to be in communication with each other.”
Immigration reform was a pillar of Trump’s presidential campaign, and Los Angeles has been a battleground site in the wake of executive actions by the president.
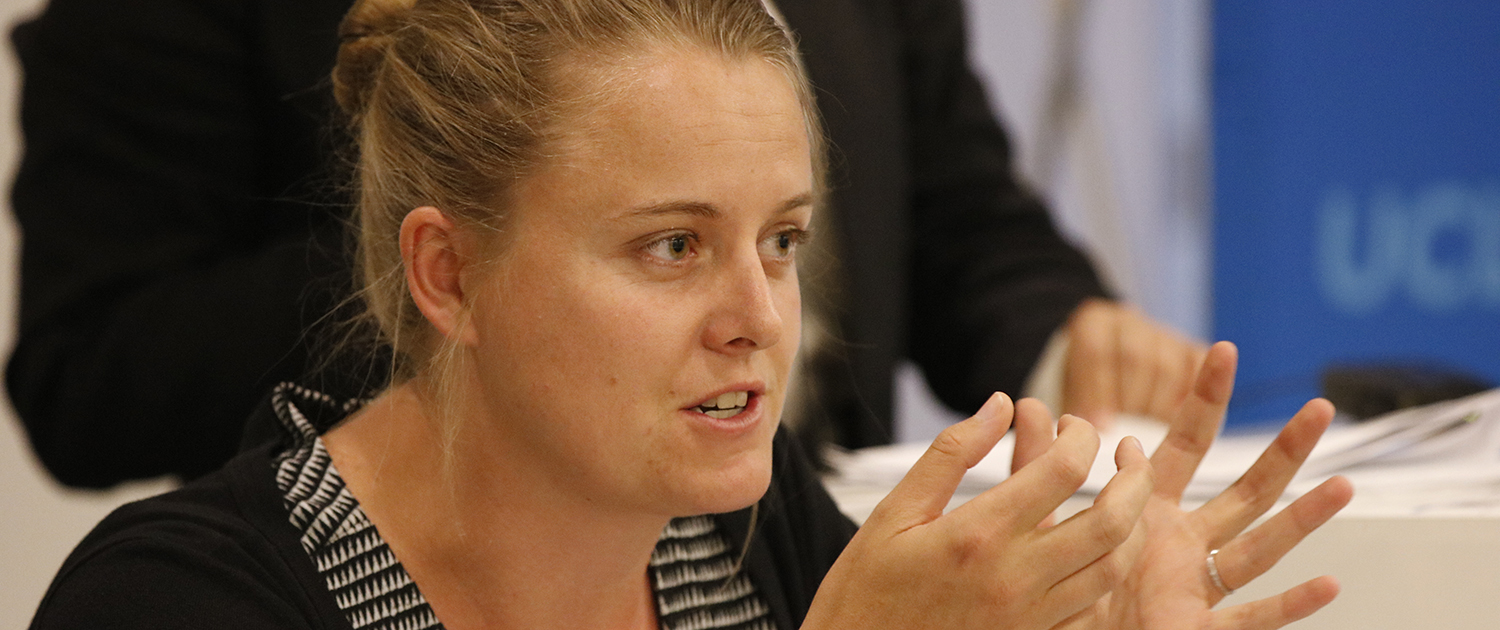

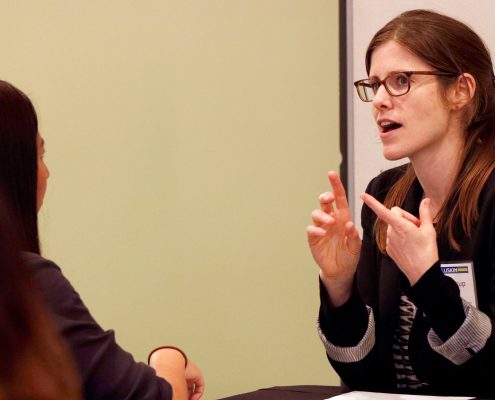
Jordan Cunnings of the Public Counsel’s Immigrant’s Rights Project discusses the communal effort and work of countless activists since the election. Photo by Les Dunseith
Jordan Cunnings, an Equal Justice Works fellow for the Public Counsel’s Immigrant’s Rights Project, gave her perspective on the local reaction, including spontaneous protests. “Everyone came… It was very powerful to see everyone coalesce,” Cunnings said about protests at LAX that followed the first of the Trump administration’s immigration bans. The communal effort and work of countless activists has made a difference, she said.
The LGBTQ community has also been impacted, said Lorri L. Jean, CEO of the Los Angeles LGBT Center. She has led the Los Angeles LGBT Center through an era of “unprecedented growth,” which has significantly increased the center’s ability to serve the Los Angeles community.
Jean noted an evolving strategy since the election. “Marching is great, gathering is great… but that is not enough,” she said. While resisting legislation and initiatives proposed by the Trump administration, the center has also been active in allying with groups such as labor to push for positive change.
Panelists said positive change can have different meanings, ranging from effective reform to making communities safer to spreading awareness of socioeconomic disparities between ethnic and social groups in areas such as imprisonment and poverty.
“Resources should go into places that influence people into coming together and not just straight to putting a cop on the street,” Pascual insisted. More policing does not necessarily build community or safety, he said.
Torie Osborn, principal deputy for policy and strategy for Supervisor Sheila Kuehl of the L.A. County Board of Supervisors, noted that the Affordable Care Act had added coverage for the mentally ill and people with drug addictions. A repeal of the ACA, and the aid that came with it, would negatively impact many people with the greatest need, she said, including the homeless and those recently released from prisons.
“We have got to look at the unlikely allies who we do not think will be under our tent,” Pascual said about the need to be resourceful. “The takeaway I have gotten from my experiences is to build a big tent.”
During a Q&A that followed the panel discussion, topics included weighing the relationship between safer communities and gentrification, and the current state of the two-party political system in the United States.