Amplifying the Voice of Latinos on Policy Issues Latino Policy & Politics Initiative at UCLA Luskin School will fill a critical research gap and provide a think tank around political, social and economic issues
By Les Dunseith
A new initiative underway at the Luskin School of Public Affairs will take advantage of the immense research expertise at UCLA to fill a critical gap in research and policy analysis related to issues that impact Latinos and other communities of color in California and across the country.
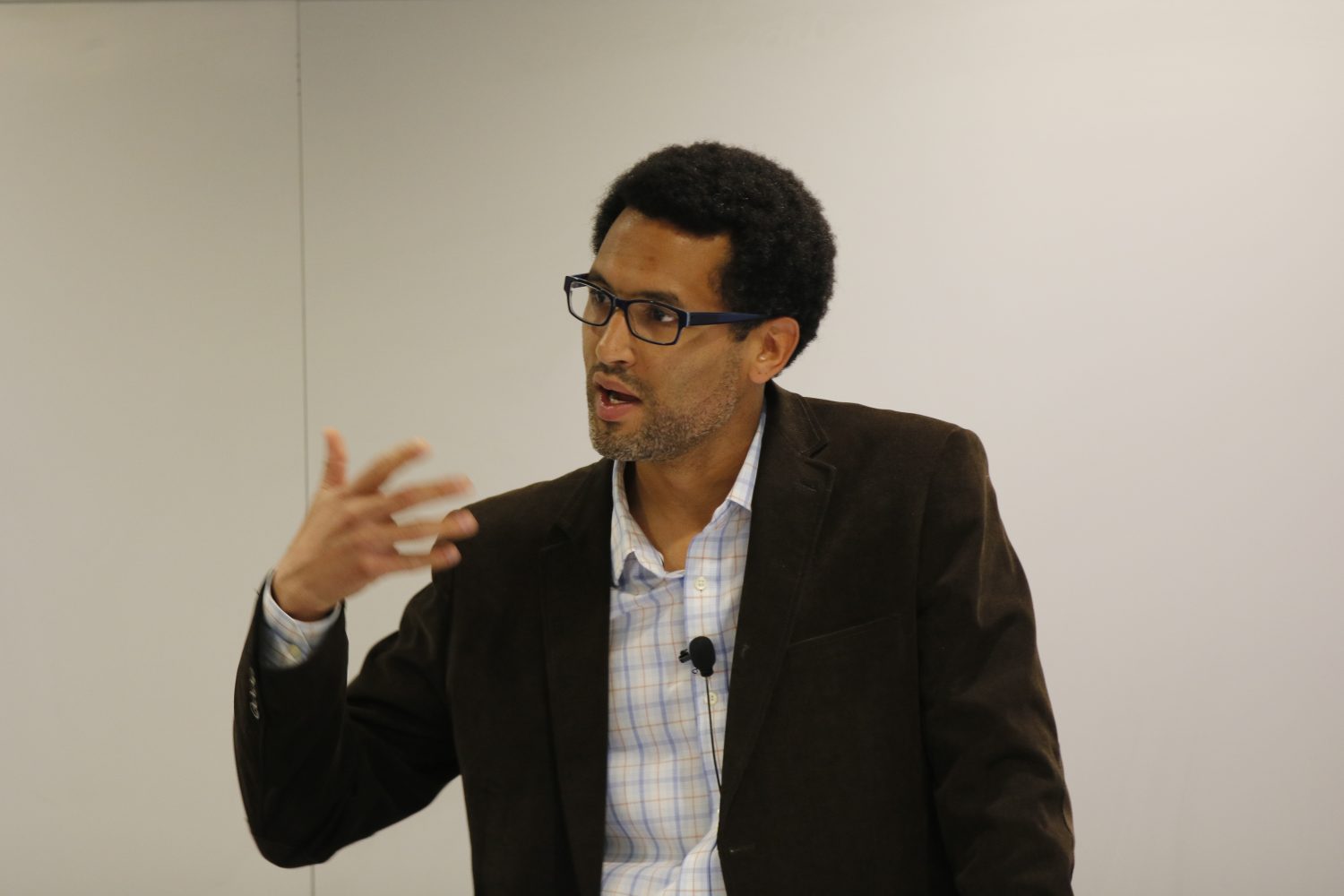
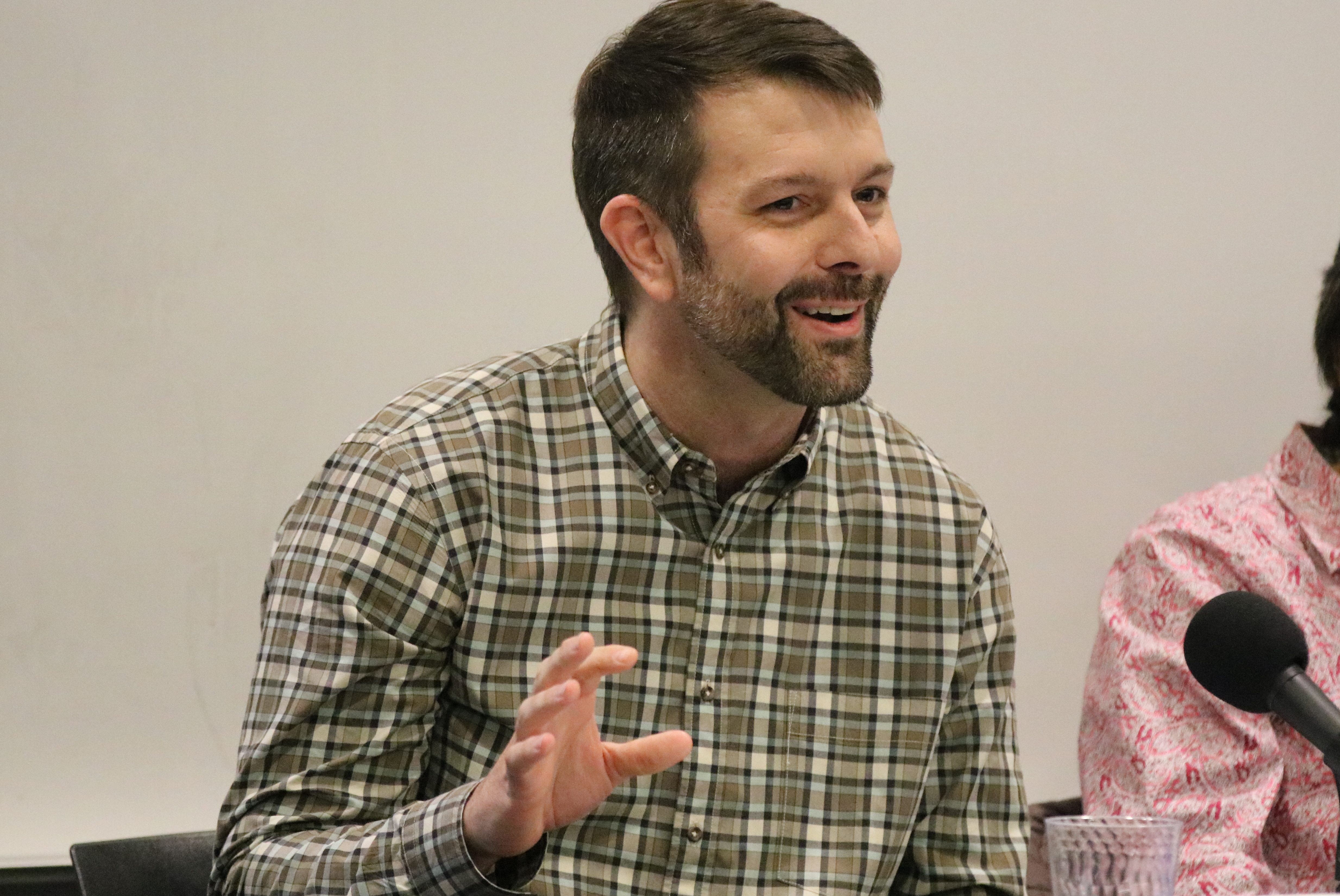
The Latino Policy & Politics Initiative (LPPI) will be “a comprehensive think tank around political, social and economic issues faced by California’s plurality population,” said UCLA Luskin Dean Gary Segura about the new effort, which also received startup funding from the Division of Social Sciences. Matt Barreto, professor of political science and Chicana/o Studies, co-founded the project with Segura in February 2017.
Founding Director Sonja Diaz came aboard in March and has spearheaded meetings with scholars, community organizations, public officials, staff members from governmental agencies, and potential funding partners to formalize the initiative and secure its place among the various research centers at UCLA.

“People on this campus are supportive and willing to partner.”
—Sonja Diaz
“One of the things that I have personally been so impressed with is that people on this campus are supportive and willing to partner,” said Diaz, who earned a Master of Public Policy degree at UCLA Luskin in 2010 before going on to receive her law degree from UC Berkeley. “They see the value of supporting LPPI as a meeting place, as an organization and as a foundation to build upon.”
Scholars from across campus have already come aboard, including professors from schools and departments such as Medicine, Business, Health Policy and Management, History and Law.
“We stand here on the shoulders of individual researchers, scholars, students and their centers to actually start having a convergence and a meeting place,” Diaz said about the role of LPPI in uniting Latino-focused research efforts so that studies can be found and shared more easily among interested parties. “We have more than 16 people already in place to produce rapid-response and evidence-tested research on domestic policy issue areas.”
Segura, himself a professor of public policy and Chicana/o studies, said that the University of California — particularly UCLA — is an ideal home for the enterprise. LPPI will develop new research, as well as assist existing faculty research projects and provide direct support for the community, centered around policy issues of vital importance to Latinos.
“The city of Los Angeles is the second-largest Spanish speaking city on the planet — after Mexico City, and significantly ahead of Buenos Aires and Madrid,” Segura explained. “If you are going to study what is happening to Latinos in the United States, you begin in Los Angeles, and your next stop is California.”
Barreto noted that Latinos have been the largest minority group in the U.S. since 2001, and the Latino percentage of the population continues to grow, particularly in California. “Yet, there is a significant gap between the diversity of our state and the institutional representation of Latinos in Sacramento, as well as in the UC system,” he said. “Through this initiative, we hope to increase policy-relevant research on Latinos in California and the country as a whole.”
Basing LPPI at UCLA not only makes sense geographically, it makes sense organizationally, Segura said.
“UCLA has a very strong Department of Chicano/a Studies. It has a very strong Chicano Studies Research Center. And the Luskin School of Public Affairs is UCLA’s — and I would argue the University of California’s — best voice on questions of human service and human need,” Segura said. “The concentration of Latino academics here makes UCLA the right place for LPPI. It’s where it should exist.”

“The concentration of Latino academics here makes UCLA the right place for LPPI.”
—Gary Segura
Although LPPI is still in the organizational phase of its evolution, Diaz noted that its leaders have “already connected with, met with, and partnered with more than 50 community-based organizations, both nationally and at the state level.”
Segura, Barreto and Diaz continue to meet with potential funding partners, including a host of state and federal foundations, and recently completed a trip to Sacramento to engage with members of the California Legislature. The visit served a dual purpose, simultaneously letting elected officials know about LPPI and giving the leadership team an opportunity to ascertain the needs of elected officials in terms of the policymaking demands of the populations that they represent.
“One of the things that we learned is that state government does no demographic research as a matter of form,” Diaz said. “It means that policy is not always best-tailored to the needs of communities of color. We know there is an opportunity there — a need for this type of research.”
To fill that need, LPPI will be launching new research projects to be completed by internal staff members, often working with postdoctoral candidates and graduate assistants. Those projects will afford students an opportunity to get hands-on training and will forge partnerships that Diaz sees continuing beyond graduation as former UCLA students take their places in government life.
“One of the things that is unique about LPPI is that it’s action-oriented,” she explained. “It’s not enough to just produce the research and produce the evidence, but we will actually put it into the hands of people who can go ahead and integrate it into their own proposals.”
The ability to respond quickly to issues of concern among Latinos is a vital aspect of the new initiative. “It’s no secret that a majority of Latinos felt disrespected and under attack by Donald Trump during the presidential campaign,” Barreto said. “It is more important now than ever before to have an objective, research-based approach to policy and politics, to understand the Latino experience in this country, and to make sure that policymakers at all levels of government — from president of the school board to president of the United States — understand that Latinos contribute equally to our communities and expect to have equal input into, and equal outputs, from the political system.”
Diaz sees LPPI becoming a go-to source of information on Latino policy issues at City Hall, in Sacramento and for people nationwide. Segura concurs, noting that he has launched an effort to hire additional faculty members at UCLA Luskin who will add new areas of expertise to the cadre of faculty members across the campus who are already actively pursuing important policy or social issue research.
Segura’s ultimate goal for the Latino Policy & Politics Initiative?
“We will be doing something in the world to improve the lives of the people that we study,” he said, “which, really, is why we do it.”


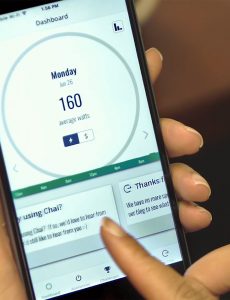 The UCLA researchers have partnered with a clean technology company named Chai Energy. “Chai developed a free smartphone application that displays your home daily electricity consumption and provides you with tips on how to better manage your electricity bill,” DeShazo said. This could include knowing when it makes financial sense to replace an old appliance, or simply what time to use it based on electricity prices. Chai has also developed a gateway device that establishes communication between a participant’s smartphone and the smart-meter already installed in his house, allowing users to see real-time energy consumption by individual household appliances.
The UCLA researchers have partnered with a clean technology company named Chai Energy. “Chai developed a free smartphone application that displays your home daily electricity consumption and provides you with tips on how to better manage your electricity bill,” DeShazo said. This could include knowing when it makes financial sense to replace an old appliance, or simply what time to use it based on electricity prices. Chai has also developed a gateway device that establishes communication between a participant’s smartphone and the smart-meter already installed in his house, allowing users to see real-time energy consumption by individual household appliances.