The Problems and Possibilities of Parking Highlights of the latest issue of the Lewis Center’s ACCESS magazine
By John A. Mathews
The UCLA Luskin School of Public Affairs brings you a special edition of ACCESS dedicated to the most controversial topic in transportation: parking. Parking invokes immediate emotional responses. We experience joy when a stranger gives us his or her parking spot and rage when someone steals a space we waited 20 minutes for. And what better thrill is there than running to your car to feed the meter just in time to avoid a ticket?
The issues surrounding parking, however, go beyond our immediate reactions. Parking takes up valuable space that could go to better use. It can cause congestion and inflict additional costs on people who can’t even afford to own cars. But parking can also bring social benefits to a community. In this issue, ACCESS explores the good, the bad and the ugly of parking.
Parking as far as the eye can see
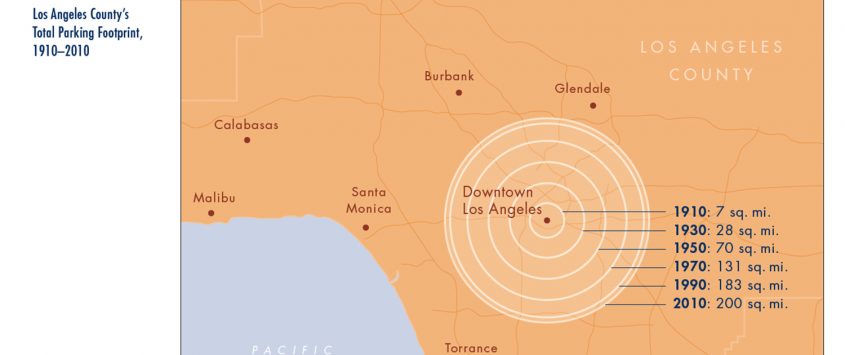
Whether you’re building a bar, a hair salon, or a zoo, you will have to build parking spaces to go with it. Now, after decades of development under excessive minimum parking requirements, parking dominates our cities. But how much parking is there really?
In their article, “Do Cities Have Too Much Parking?” Andrew Fraser, Mikhail Chester, Juan Matute and Ram Pendyala explore the distribution of parking in Los Angeles County and how the county’s parking infrastructure evolved over time. The authors found that, as of 2010, Los Angeles County had 18.6 million parking spaces. This amounts to more than 200 square miles of parking, or 14 percent of the county’s incorporated land area. So now the question is: Do we really need all of this parking?
Fraser is a postdoctoral researcher in Civil, Environmental and Sustainable Engineering at Arizona State University. Chester is associate professor in Civil, Environmental and Sustainable Engineering at Arizona State University. Matute is associate director of the Lewis Center and the Institute of Transportation Studies at UCLA’s Luskin School of Public Affairs. Pendyala is a professor of Civil, Environmental and Sustainable Engineering at Arizona State University.
Keeping people from cruising
One possible solution to cruising for parking comes in the form of performance-based pricing, where the rate at the parking meter changes based on demand. The theory is that, with the right price, there will always be one or two empty spaces for drivers to park. Drivers can then park sooner instead of cruising for parking over longer distances, causing additional congestion. But do performance-based pricing programs actually help reduce cruising?
In “Cruising for Parking: Lessons from San Francisco,” Adam Millard-Ball, Rachel Weinberger and Robert Hampshire evaluate whether SFpark, San Francisco’s performance-based pricing initiative, actually reduced cruising. By simulating parking occupancy using parking sensor data, block length, and the probability that a block is full, the authors were able to conclude that SFpark did indeed work. The average cruising distance fell by 50 percent, but people don’t cruise as far as they think.
Millard-Ball is assistant professor in the Environmental Studies Department at UC Santa Cruz. Weinberger is a transportation consultant based in New York City. Hampshire is assistant research professor in the Transportation Research Group at the University of Michigan.
Parking theories versus parking practice
The idea is simple: Charge more for parking and you should get more open parking spaces. Charge less for parking and parking spaces should fill up. But does this theory play out in the real world?
In their article, “Market-Priced Parking in Theory and Practice,” Michael Manville and Daniel Chatman evaluate how San Francisco’s market-priced parking program affected parking occupancy and cruising. They found that, when parking prices rose on a block, the block’s “average occupancy rate” for parking fell. The problem, however, is that drivers look for vacant parking spaces, not average occupancy rates. The longer the time included in average parking occupancy rates, the more misleading they can be.
Manville is assistant professor in the Department of Urban Planning at UCLA’s Luskin School of Public Affairs. Chatman is associate professor in the Department of City and Regional Planning at the UC Berkeley.
Making do with less
When you’re in a crowded parking lot trying to get in some holiday shopping, you might think there’s not enough parking. But if you drive around that same parking lot after hours, you can see the vast waste of space that occurs daily.
In his latest article, “Parking Management for Smart Growth,” Rick Willson asks how we can transition from too much parking to a more efficient use of a smaller parking supply. He argues that transportation demand management can reduce parking demand by encouraging drivers to carpool, walk, bike, or take public transit. Parking management strategies can further reduce the number of parking spaces needed through increased space efficiency. The use of sensors and sophisticated pricing meters can ensure open parking spots and help drivers find them.
Willson is professor of Urban and Regional Planning at Cal Poly Pomona, and a Fellow of the American Institute of Certified Planners.
London changes its parking requirements
Do we build so much parking because it’s needed or because it’s required? Parking theorists say that the market would provide fewer parking spaces if parking requirements did not exist. The evidence of this has been inconclusive, however, until now.
In his article, “From Parking Minimums to Parking Maximums in London,” Zhan Guo evaluates what happened after London reversed its parking requirements in 2004. The city removed the previous minimum parking requirements and instead adopted new maximum requirements for all metropolitan developments. What’s interesting is that the new maximum parking limits were often lower than the previous minimum requirements. What’s even more interesting is that most developments provided far less than the maximum limit allowed. This means that, with the previous minimum parking requirements, London was requiring far more parking than the market demanded.
Guo is associate professor of Urban Planning and Transportation Policy at the Wagner School of Public Service, New York University.
Parking: the new beachfront property
Many commercial areas have implemented Parking Benefit Districts that spend meter revenue for public services in the metered areas. But can Parking Benefit Districts work in purely residential neighborhoods as well?
In his article, “Parking Benefit Districts,” Donald Shoup argues that a residential Parking Benefit District can manage on-street parking and provide a neighborhood with revenue to clean and repair sidewalks, plant trees, and remove grime from subway stations. He also argues that residential Parking Benefit Districts can help unbundle the cost of parking from the cost of housing to create more affordable housing. If cities manage their curb parking as valuable real estate, they can stop subsidizing cars, congestion, pollution, and carbon emissions, and instead provide better public services and more affordable housing.
Shoup is editor of ACCESS and Distinguished Professor of Urban Planning in UCLA’s Luskin School of Public Affairs.









Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!