By Stan Paul
It started as a conversation about democracy and why some countries enjoy a higher quality of life than others, and it culminated in the release of a groundbreaking analysis of more than 130 governments around the world.
The 2022 Berggruen Governance Index, unveiled June 1 during a gathering at UCLA’s Kerckhoff Grand Salon, found a dramatic drop in the quality of government and quality of democracy in the United States over the past 20 years.
At the same time, several African nations showed measurable improvements in their provision of public goods like education, health care and environmental protection.
The collaborative project of UCLA Luskin and the Los Angeles-based Berggruen Institute is now available online on the index’s website as a report, plus links that allow researchers to search and sort the data for themselves.
“We had this fundamental concern that governance itself was poorly understood,” said Dawn Nakagawa, executive vice president of the Berggruen Institute, recalling the origins of the index during a “chaotic and concerning time” for democracy in the U.S. and other parts of the world.
The index was compiled by researchers from UCLA Luskin and the Hertie School in Berlin. It draws on data from sources that included the United Nations, statistical offices and research institutes from 2000 through 2019.
“And these have been a really consequential 20 years for democracy,” said Nakagawa, who spoke during the launch event, as did UCLA Luskin Dean Gary Segura.
Leading the day’s discussion was principal investigator Helmut Anheier, UCLA adjunct professor of social welfare and former president of the Hertie School in Germany, along with Markus Lang, a researcher at the Hertie School and the University of Heidelberg in Germany.
Anheier noted that although research and literature on governance have existed for some time, it has focused on various singular aspects of governance or democracy. He and his co-authors took a different, multipronged approach to understanding governance.
“We say governance is finding the balance among three components,” Anheier said.
The researchers scored selected national governments on an array of individual measures, grouping findings into three overarching categories:
- Quality of democracy, which is based on the effectiveness of checks and balances between branches of government, and officials’ accountability to voters and society.
- Quality of government, which considers governments’ abilities to generate revenue, function administratively and execute policies.
- Quality of life, which considers governments’ ability to provide social, economic and environmental public goods.
“Rather than saying there is one number that represents governance performance, we see a lot of insight that had been gained by looking at the tension and relationship among these components, and that is expressed by something we call the governance triangle,” Anheier said.
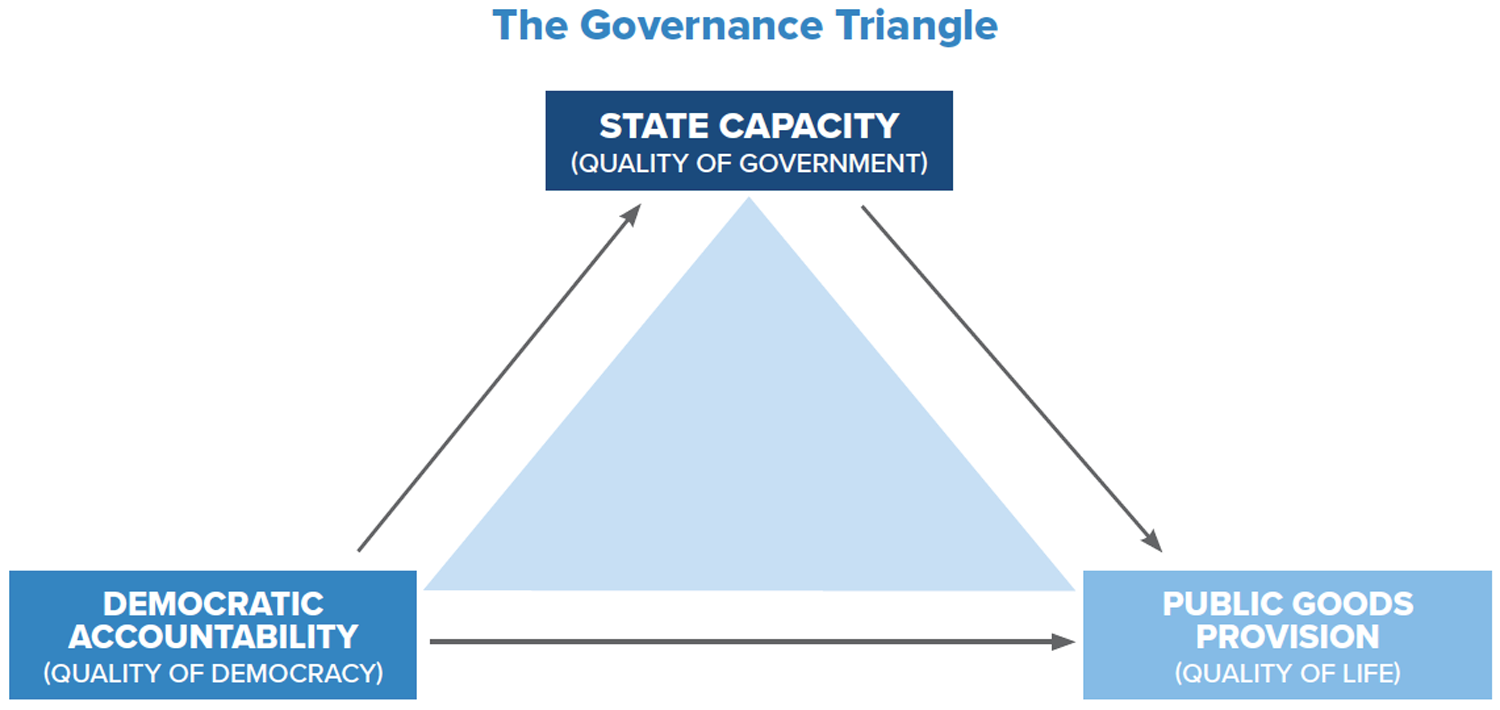
The rankings evaluate quality of government, quality of democracy and quality of life measures, which the researchers call the “governance triangle.”
“It really does break open the black box of governance, looks inside, and allows us to see these three very important components interact,” Nakagawa said.
A major finding was the dramatic drop in the quality of government and quality of democracy in the United States, which was the only Western power with a declining score in those categories. The U.S. quality of life score improved, but only slightly.
Additional findings:
- Although the U.S. score for quality of government remains far above the global average, its decline on that measure since 2000 was one of the world’s largest, on par with declines in Haiti, Hong Kong and Hungary.
- The 10 countries with the greatest improvements in quality of life measures all are in Africa. However, as a whole, Africa still ranks well below other regions in terms of quality of life factors.
- Quality of democracy scores retreated in several Asian nations, including in Bangladesh, China, India, the Philippines and Thailand. Many nations in the Americas also saw declines in those measures.
The day’s program also included a discussion of democracy, public policy and global challenges featuring UCLA experts. Moderated by Anheier, the panel featured Steve Zipperstein, an attorney and lecturer in global studies at UCLA; Veronica Herrera, an associate professor of urban planning who studies political development in the Global South; Cesi Cruz, an assistant professor whose research intersects political science and economics; and Zachary Steinert-Threlkeld, an assistant professor of public policy focusing on subnational conflict, statistics and advanced data analysis.
Closing comments were provided by Michael Storper, distinguished professor of regional and international development in urban planning at UCLA Luskin, and Andrew Apter, a professor of history and anthropology at UCLA.
“One of the most important indicators of successful research is … surprising results,” said Apter, who complimented his longtime colleague Anheier on fulfilling that ideal.
Storper, who also serves as director of Global Public Affairs at UCLA Luskin, took a comparative view of the results. Democracy in the United States is very different from the federal governments in nations such as France and Germany that fared better in the analysis.
“European governmental setups are really different than what we have here in the United States,” he said. Several European countries have more modern constitutions, he noted, than the older, more rigid U.S. constitution.
“The index is going to allow us … to do more and more of this, I would say, comparative, evolutionary thinking,” Storper said. “Thanks for doing this work and actually bringing it to UCLA.”
UCLA produces and disseminates the index thanks to a $3 million gift from the Berggruen Institute. Researchers plan to publish the next Berggruen Governance Index in 2024. In the meantime, they will present the work at key institutions in the U.S., Europe and elsewhere, culminating in an international conference hosted on campus by UCLA Luskin on Oct. 10-11.
View photos from the launch event on Flickr:

Watch a recording of the launch event on Vimeo:




