Briefing Seeks Solutions to Latino Doctor Shortfall UCLA Latino Policy and Politics Initiative’s gathering of medical professionals, policy analysts and advocates looks at underlying causes and why the impact is keenly felt in California
By Gabriela Solis
Although Latinos comprise the largest ethnic group in California, Latino doctors in the state are in short supply, according to recent research from the UCLA Latino Policy and Politics Initiative (LPPI).
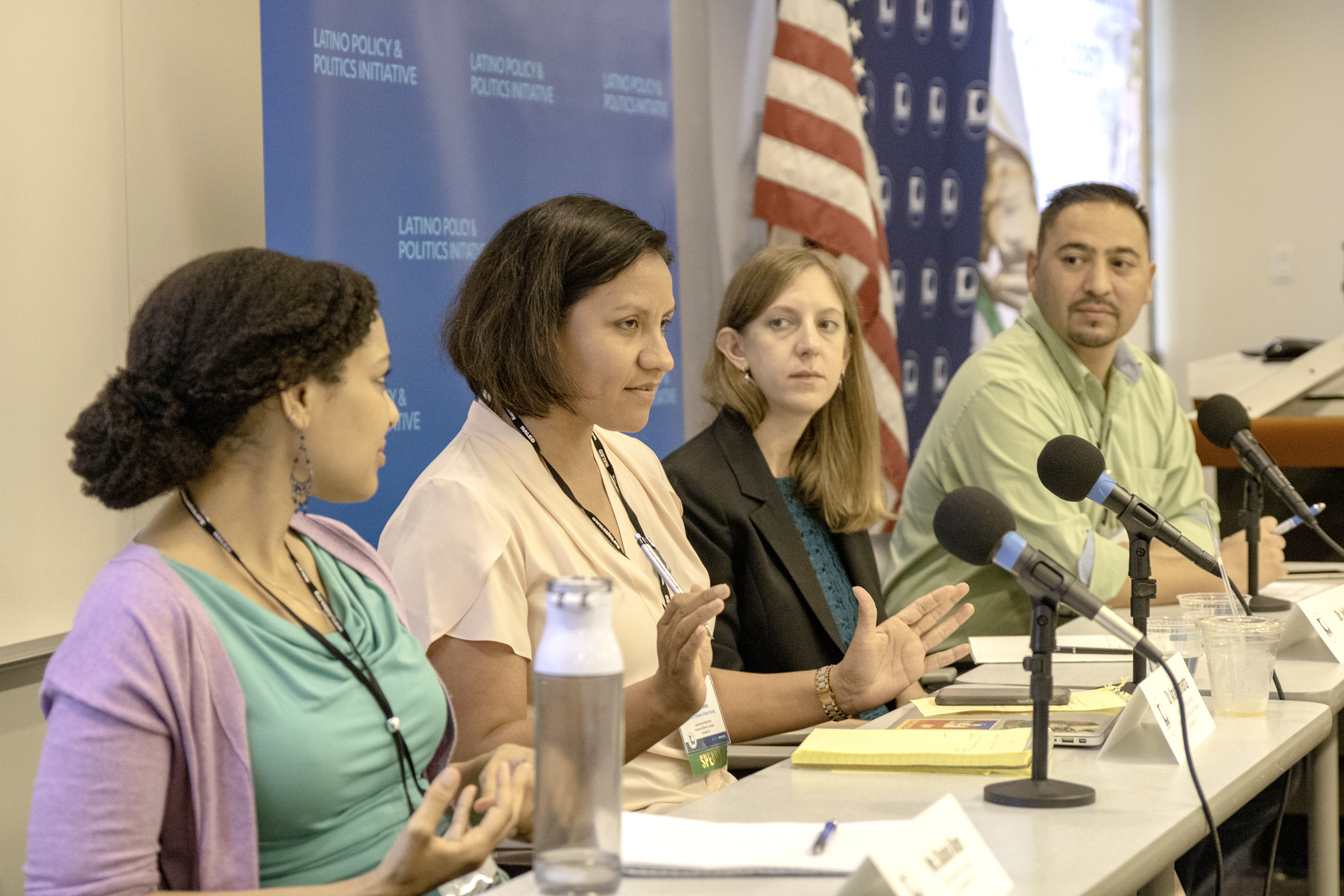
On Jan. 15, 2019, the UCLA Luskin-based think tank co-hosted a discussion in Oakland that brought together doctors, medical practitioners, academics and advocates to discuss California’s Latino physician shortage.
“California has an alarmingly low rate of Latino doctors. There are 46 Latino doctors for every 100,000 Latino Californians,” said LPPI Executive Director Sonja Diaz, citing data derived from the U.S. Census Bureau’s 2015 American Community Survey. “In contrast, there are 405.7 non-Hispanic white physicians for every 100,000 non-Hispanic white Californians.”
Diaz led the discussion co-hosted by the Latino Coalition for a Healthy California (LCHC) and the Greenlining Institute, which is based in Oakland.
“We graduate about 110 Latino medical doctors every year. If we continue forward, it will take almost five centuries to close the gap,” noted Diaz. That data from the Association of American Medical Colleges is included in the LPPI report, “5 Centuries to Reach Parity: An Analysis of How Long It Will Take to Address California’s Latino Physician Shortage,” which was produced under the guidance of LPPI faculty expert David Hayes Bautista, a distinguished professor at the UCLA David Geffen School of Medicine.
Joining Diaz in debate and discussion were Jeffrey Reynoso, executive director, Latino Coalition for a Healthy California; Arturo Vargas Bustamante, associate professor of health policy and management at the UCLA Fielding School of Public Health and public policy at UCLA Luskin; Carmela Castellano-Garcia, president and chief executive officer, California Primary Care Association; Berenice Núñez Constant, vice president, government relations, AltaMed Health Services Corporation; and Carmen Estrada, MD candidate at the UC Davis School of Medicine.
The wide-reaching conversation focused on the shortage’s effects on California’s economy, the needs of medical providers and the shortcomings within higher education that contribute to the shortfall.

Medical student Carmen Estrada of UC Davis
Estrada spoke about her personal experience of being one of the limited number of Latinos currently pursuing a medical degree. Estrada’s first-hand experiences traced her personal journey to medical school from a California State University and the lack of outreach that she said created unnecessary challenges in her career choice.
Núñez Constant shared that although her organization, AltaMed, is constantly looking for Latino physicians, “The supply is just not there.” She also highlighted the difficulty of retaining a Latino physician in such a competitive job market.
Vargas Bustamante’s research supported Núñez Constant’s comments on workforce recruitment. Bustamante said he has found a substantial pipeline problem for Latinos in their transition from high school to college and their transition from college to medical school. Based on his interviews with Latino pre-med students, medical school applicants, Latino medical students and recently graduated Latino physicians, Vargas Bustamante said students who may have an interest in the field often feel discouraged by the lack of investment to recruit and retain Latino students. Many then choose another career.
The panel agreed that this complex issue requires a strategic collaboration of California policymakers, medical providers and academia to form solutions.
But, said California State Assemblyman Robert “Rob” Bonta, expressing his support, “I think we have some wonderful opportunities.” Bonta, a Democrat whose California District 18 includes Oakland, Alameda and San Leandro, serves on a number of legislative committees, including the Health Committee. “Your timing couldn’t be better in terms of uplifting and raising the issue. This is something I’d be proud to work on, and I think it needs to be worked on.”
To learn about California’s Latino physician shortage, visit latino.ucla.edu/health.
View additional photos on Flickr.