By George Foulsham
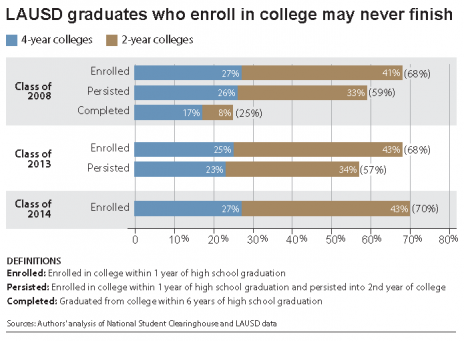
In the first comprehensive analysis of college enrollment of Los Angeles Unified School District graduates, UCLA and Claremont Graduate University researchers show that 70 percent of high school graduates enrolled in either two- or four-year colleges, but only 25 percent of graduates went on to earn a college degree within six years.
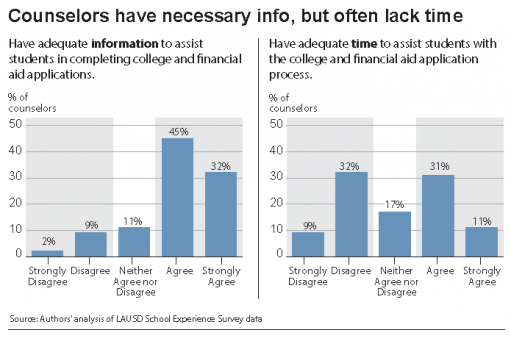
A separate, parallel study that focused on college readiness revealed that while over 75 percent of high school counselors say they have adequate information to help students complete college and financial aid applications, less than half (42 percent) said they have enough time to provide students with the assistance they need.
Both studies were co-directed by Meredith Phillips, associate professor of public policy and sociology at the UCLA Luskin School of Public Affairs, and Kyo Yamashiro, associate professor of education at Claremont Graduate University. Carrie Miller, a doctoral candidate at UCLA, co-authored the report on college readiness supports; Thomas Jacobson, a Luskin Master of Public Policy graduate and incoming doctoral student at UCLA, co-authored the report on college enrollment. Phillips, Yamashiro, Miller and Jacobson are all research collaborators with the Los Angeles Education Research Institute (LAERI), a nonprofit research organization engaged in a research-practice partnership with L.A. Unified. The studies were funded by a grant from the College Futures Foundation to UCLA and LAERI.
“In the first report, we analyze data on college enrollment, persistence and completion from the National Student Clearinghouse and L.A. Unified data on students’ high school performance, and ethnic and socioeconomic backgrounds, to provide the first detailed description of graduates’ postsecondary outcomes,” Phillips said. “In the second report, we examine the prevalence of college readiness supports throughout the school district. We hope these reports, taken together, contribute to a broader conversation about preparing L.A. Unified students for their post-secondary options and how the Los Angeles community can work together to ensure that more students enroll in college and complete a four-year degree.”
Enrollment Numbers
The analysis examines college-going outcomes for district graduates who had passed critical milestones for enrollment within one year (class of 2014), persistence into a second year (class of 2013), and completion within six years (class of 2008).
Among the key findings:
- Seventy percent of 2014 L.A. Unified students enrolled in college within one year of high school graduation; college enrollment rates were similar for the classes of 2008 and 2013.
- Most college attendees persisted into a second year of college.
- However, only 25 percent of 2008 graduates had earned a college degree within six years of high school graduation (by 2014). More than two-thirds were four-year degrees.
The researchers also found that L.A. Unified graduates were more likely to enroll in two-year than four-year colleges. Most of the 2008, 2013 and 2014 graduates enrolled in public colleges and universities in California. About 8 percent of the class of 2014 enrolled in “very selective” four-year universities such as UCLA, UC Berkeley, Stanford and USC, or “selective” four-year colleges such as Loyola Marymount University, UC Irvine, UC Santa Cruz and San Diego State University.
The study also revealed disparities based on gender and ethnicity:
- College enrollment, persistence and completion rates were lower for Filipino American, African American and Latino graduates than for white and Asian American graduates.
- Female graduates were more likely than their male classmates to enroll in, persist in and complete college.
- Gender disparities were especially stark for Filipino American, African American and Latino male graduates, who were roughly one-third less likely to enroll or persist in four-year colleges than their female classmates of the same ethnicity.
According to the researchers, improving L.A. Unified students’ academic preparation is essential for ensuring that more graduates start and complete college, and must begin earlier than high school. In addition, striving to ensure that all District students complete their A-G course requirements with at least a C is critical for students’ immediate enrollment after high school in a public, four-year college.
“This report provides a first look at L.A. Unified graduates’ pathways to and through college,” UCLA co-author Jacobson said. “It will be important to continue to track these college-going outcomes in upcoming years to understand students’ successes and challenges as they progress through college, and to learn about how college outcomes change for future graduate cohorts.”
L.A. Unified officials say the study’s recommendations align with the district’s new and ongoing efforts to ensure that students develop the skills and mindset to thrive in college and the workforce.
“The LAERI goals serve as the framework for an array of strategies we are implementing to address the needs of students, families and schools,” said Frances Gipson, the District’s chief academic officer. “We are passionate about continuing our work to foster a college-going climate in our schools and to strengthen our college planning and academic supports as we provide more robust counseling services for our students.”
“We look forward to continuing our partnership with LAERI to learn more about promising strategies for increasing our students’ college readiness,” Gipson said.
Preparation for College
The college readiness study explores the prevalence of support for high school students in L.A. Unified. The data analyzed for this report include survey data from school staff and students in more than 90 percent of the district’s traditional high schools and 76 external service providers, as well as data collected during interviews with district and school staff.
Although more than 75 percent of counselors said they have adequate information to assist students with the college application and financial aid process, less than half said they have enough time to provide students with the individualized college application assistance they need. And counselors at 75 percent of schools report that some students at their schools are not getting the help they need.
Other key findings:
- Counselors cite large caseloads and competing demands on their time as barriers to helping students with the college application and financial aid process. Counselors spend nearly the same amount of time coordinating academic testing and performing non-counseling activities as they do advising students about college and financial aid.
- Nearly all schools offer college readiness support but students still need more help with the college application, financial aid and college enrollment process. About one-fifth of 12th graders in the survey said they didn’t feel that adults at their school had helped them learn the details of getting into college.
- Most L.A. Unified schools rely on external service providers to help them provide college application, financial aid and college enrollment assistance. At more than two-thirds of schools, counselors report that both school and external staff provide college application (66 percent) and financial aid (75 percent) help.
Learning more about disparities among students in their access to college readiness support is an important next step for improving college-going among L.A. Unified graduates, according to the study.

Researchers on the UCLA-LAERI LAUSD study include Meredith Phillips, front, associate professor of public policy and sociology at UCLA; and, back row, from left, Kyo Yamashiro, associate professor of education at Claremont Graduate University; Thomas Jacobson, a Luskin Master of Public Policy graduate and incoming doctoral student at UCLA; and Carrie Miller, a doctoral candidate at UCLA.
The researchers offer several recommendations for increasing schools’ capacity to meet students’ college counseling needs, including clarifying a common set of college counseling expectations by grade level, diversifying the type of school staff responsible for specific aspects of college counseling assistance, incorporating key college application tasks into required academic coursework, and providing professional development specific to college counseling tasks.
The researchers concluded that the district could maximize the effectiveness of existing partnerships with external service providers by:
- providing counselors and other school staff who connect schools and students to external providers with additional support to develop and maintain these partnerships;
- asking external service providers to contribute to a common information system to aid individual schools or the district in determining which students are and are not receiving sufficient help; and
- evaluating the effectiveness of the college-related services that students receive from external providers.
“This report is a first step toward understanding the college readiness resources available to LAUSD students,” UCLA co-author Miller said. “While we find that nearly all schools offer a range of college readiness resources, identifying the extent of these services — the proportion of students served and the intensity of the services they receive — is essential for more effectively targeting school and district resources.”
Phillips said that LAERI will continue its collaboration with L.A. Unified by gathering additional data on college counseling resources available to students and the relationship between those resources and whether and where students enroll in college.
“Our partnership with LAERI and this research informed our approach to the state’s College Readiness Block Grant,” said Gipson, of L.A. Unified. “Through this research, Phillips and Yamashiro’s team developed a counselor section of our annual staff survey, which provided the first districtwide data on college readiness resources. Additionally, these initial data have provided a foundation for the college readiness professional development resources we are developing for schools.”
“We’re very excited to present the first detailed overviews of LAUSD graduates’ postsecondary outcomes and college readiness supports,” Yamashiro said. “As we build on this research partnership work, we look forward to continuing to collaborate with the district to get a better understanding of elementary and middle school predictors of college readiness and success, identifying schools that are doing an especially good job of preparing their students for college, and helping the district identify the most effective practices and interventions for improving college access.”
Click below to download the full reports in PDF format.

“College Going in LAUSD: An Analysis of College Enrollment, Persistence, and Completion Patterns”

“College Readiness Supports In LAUSD High Schools: A First Look”