By Les Dunseith
Residents of Los Angeles County have been deeply affected by the COVID-19 crisis, with significant numbers citing the pandemic’s adverse impact on their finances, health and children’s education, according to UCLA’s sixth annual Quality of Life Index.
“A year ago we speculated about how resilient our region would be in the year to follow,” said Zev Yaroslavsky, director of the Los Angeles Initiative at the UCLA Luskin School of Public Affairs, who oversees the index. “We now know that Los Angeles County has demonstrated robust resilience, but a significant toll has been exacted on our residents by the tumultuous events. Many of our residents — especially younger ones — are anxious, angry and steadily losing hope about their future in Los Angeles.”
This year’s Quality of Life Index, or QLI, was based on interviews with 1,434 county residents over a 20-day period beginning on March 3, just as vaccinations were beginning to fuel optimism about a possible return to more normal life. Last year’s survey, conducted in the earliest stages of the pandemic, found high levels of anxiety about the possible impacts of COVID-19. Twelve months later, respondents said many of those fears had come to pass:
- More than half of those surveyed (54%) reported that they or a close family member or friend had tested positive for the coronavirus.
- Forty percent said their income went down because of the pandemic, with 22% saying it dropped “a lot” and 18% reporting “some” decline. Roughly 1 in 5 (18%) said they had lost their job at some point during the COVID-19 crisis.
- Three-quarters of parents (76%) with school-age children felt their kids had been “substantially hurt, either academically or socially,” by pandemic-related distance learning and quarantine experiences.
 In addition, nearly a fifth (17%) of all respondents reported that their income declined “a lot” in the past year and that they also suffered at least two specific negative impacts, such as a job loss, a wage or salary reduction, a decline in work hours or difficulty paying their rent or mortgage. This group was disproportionately composed of women under age 50, single people, renters, those without college degrees and those with household incomes of less than $60,000.
In addition, nearly a fifth (17%) of all respondents reported that their income declined “a lot” in the past year and that they also suffered at least two specific negative impacts, such as a job loss, a wage or salary reduction, a decline in work hours or difficulty paying their rent or mortgage. This group was disproportionately composed of women under age 50, single people, renters, those without college degrees and those with household incomes of less than $60,000.
“These are among the most vulnerable individuals living in our county,” Yaroslavsky said.
The QLI, a joint project of the UCLA Luskin Los Angeles Initiative and The California Endowment with major funding provided by Meyer and Renee Luskin, asks a cross-section of Los Angeles County residents each year to rate their quality of life in nine categories and 40 subcategories. Full results of this year’s survey were made available April 19 as part of UCLA’s Luskin Summit, which is taking place virtually.
Mirroring last year’s result, this year’s overall quality-of-life rating held steady at 58 (on a scale of 10 to 100), which is slightly more positive than negative. But researchers noted that marked changes emerged among specific racial and ethnic groups, especially with younger residents.
Younger Angelenos: Sinking optimism, tempered by race
Reflecting a trend seen in recent QLI surveys, the county’s younger population — those between the ages of 18 and 49 — rated their quality of life lower than older residents, and the pandemic seems to have exacerbated that disparity.
“The varied manifestations of COVID-19,” Yaroslavsky said, “fell most heavily on the shoulders of younger county residents.”
In particular, researchers observed a growing belief by younger Angelenos that the cost of living in the region is threatening their ability to make ends meet, get ahead or gain some sort of financial security.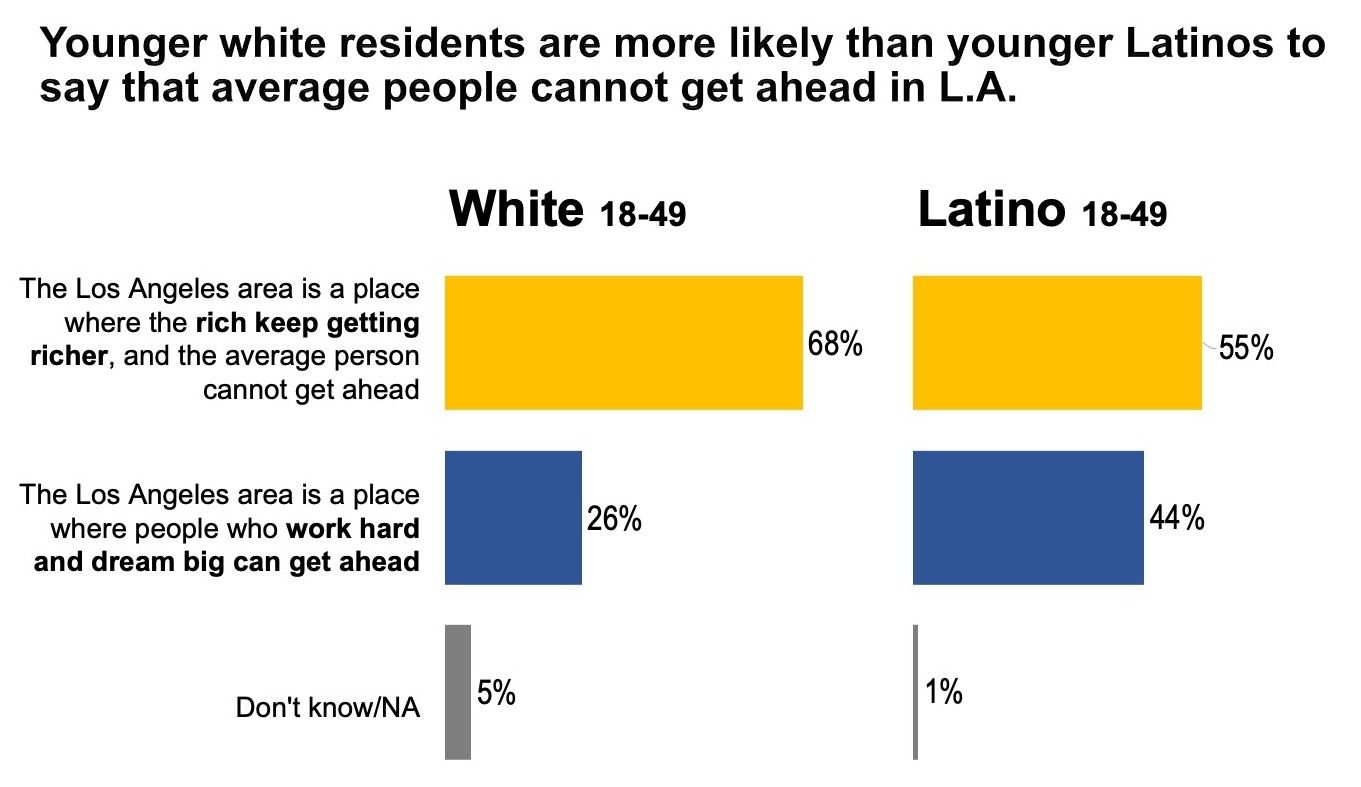 Yet even among this demographic, the survey revealed a distinct divergence in views between Latinos and whites, the two largest racial/ethnic groups in the county. While they have faced demonstrably harder challenges in the region, Latino residents overall were more positive about their quality of life than whites — and this was particularly pronounced among younger residents.
Yet even among this demographic, the survey revealed a distinct divergence in views between Latinos and whites, the two largest racial/ethnic groups in the county. While they have faced demonstrably harder challenges in the region, Latino residents overall were more positive about their quality of life than whites — and this was particularly pronounced among younger residents.
“Repeatedly, younger Latinos are more positive about their own conditions and express greater approval and positivity toward the variety of public officials and governmental entities that affect their lives,” said Paul Maslin, a public opinion and polling expert with Fairbank, Maslin, Maullin, Metz & Associates (FM3 Research) who has overseen the QLI survey process since 2016. “Among younger white residents in Los Angeles County, a greater sense of frustration and even bitterness is apparent.”
The survey uncovered a number of noteworthy differences in these two groups’ views of the pandemic, public officials and the opportunities available in the region:
- Younger white residents were evenly split over whether the handling of the pandemic had been fair or unfair to “people like them” (48% vs. 49%), whereas younger Latinos reported that it had been fair to them by a 2-to-1 margin (65% vs. 33%).
- About two-thirds (68%) of younger whites believe the Los Angeles area is a place where the rich get richer and the average person can’t get ahead, compared with only 55% of younger Latinos.
- Younger Latinos had more favorable views of Los Angeles Mayor Eric Garcetti (57%) and Gov. Gavin Newsom (53%) than younger whites, 57% of whom had unfavorable views of Garcetti and 62% unfavorable views of Newsom.
- Younger white residents rated the response to the pandemic — across all levels of government — much more harshly than younger Latinos. Only about a third of whites approved of the response of federal, state and county governments and local school districts. Latinos’ ratings of approval were at least 20 points higher for every level of government and for local school districts.
- However, in terms of paying their rent, more younger Latinos (43%) reported falling behind than did young whites (31%).
The 2021 QLI: Resilience and change
While this year’s quality-of-life rating remained at 58 overall, reflecting a remarkable resilience among county residents, several significant shifts within the nine major categories that make up the survey tell a different story.
This was most noticeable in the education category, where the satisfaction rating of respondents with children in public schools dropped from 58 last year to 52 this year, one of the most dramatic one-year declines in any category in the QLI’s history.
Satisfaction ratings for public safety also fell over the past year, from 64 to 60, influenced significantly by a growing concern over violent crime. And respondents’ rating of the quality of their neighborhoods dropped from 71 to 68.
On the other hand, satisfaction with transportation and traffic rose from 53 to 56, which researchers attribute to a significant reduction in commuter traffic caused by pandemic-related workplace shutdowns.
With regard to the workplace, 57% of employed respondents said they currently work from home or split time between home and their place of work. As to the future, 77% said they would prefer a mix of working from home and their workplace when the pandemic ends, with just 16% wanting to “almost always work at home.”
The 2021 UCLA Luskin Quality of Life Index is based on interviews with a random sample of residents conducted in both English and Spanish, with a margin of error of plus or minus 2.6%. The QLI was prepared in partnership with the public opinion research firm Fairbank, Maslin, Maullin, Metz & Associates (FM3 Research). The full reports for 2021 and previous years are posted online by the UCLA Lewis Center for Regional Policy Studies.


