Casting Youth Justice in a Different Light Experts at UCLA Luskin Social Welfare event laud recent moves to divert more youth from the criminal justice system and into programs that help them transform their lives
By Les Dunseith
On March 13, 2018, UCLA Luskin Social Welfare hosted an event that featured two panels of experts in youth justice engaged in critical conversations about efforts to intercede on behalf of troubled young people before they become entangled in a corrections system that often perpetuates a cycle of crime and punishment.
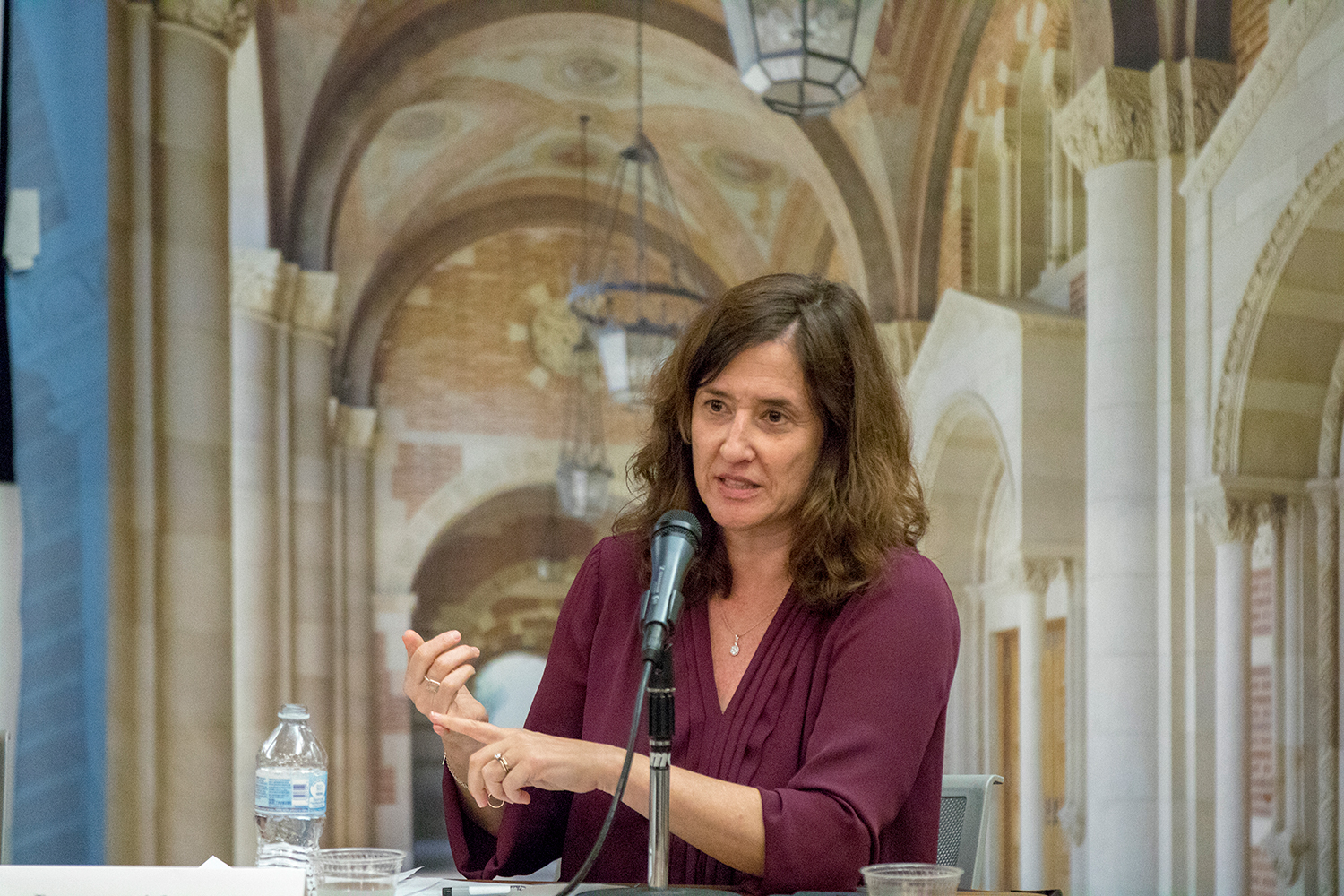
The event was organized by Professor Laura Abrams, chair of UCLA Luskin Social Welfare, building on themes outlined in her recent book co-authored with Diane Terry BA ’01 MSW ’04 Ph.D. ’12, who is a senior research associate at Loyola Marymount University: “Everyday Desistance: The Transition to Adulthood Among Formerly Incarcerated Youth.”
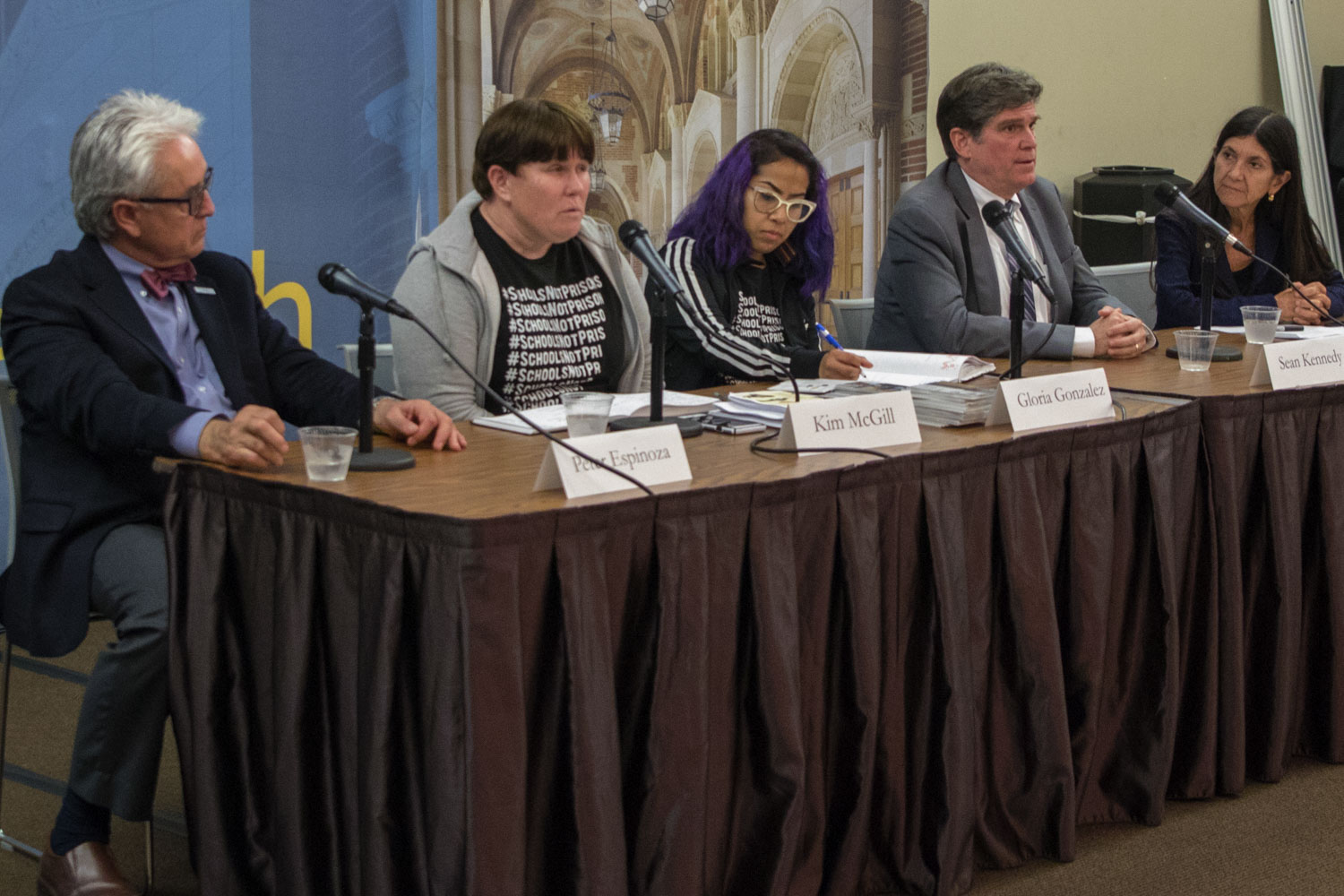
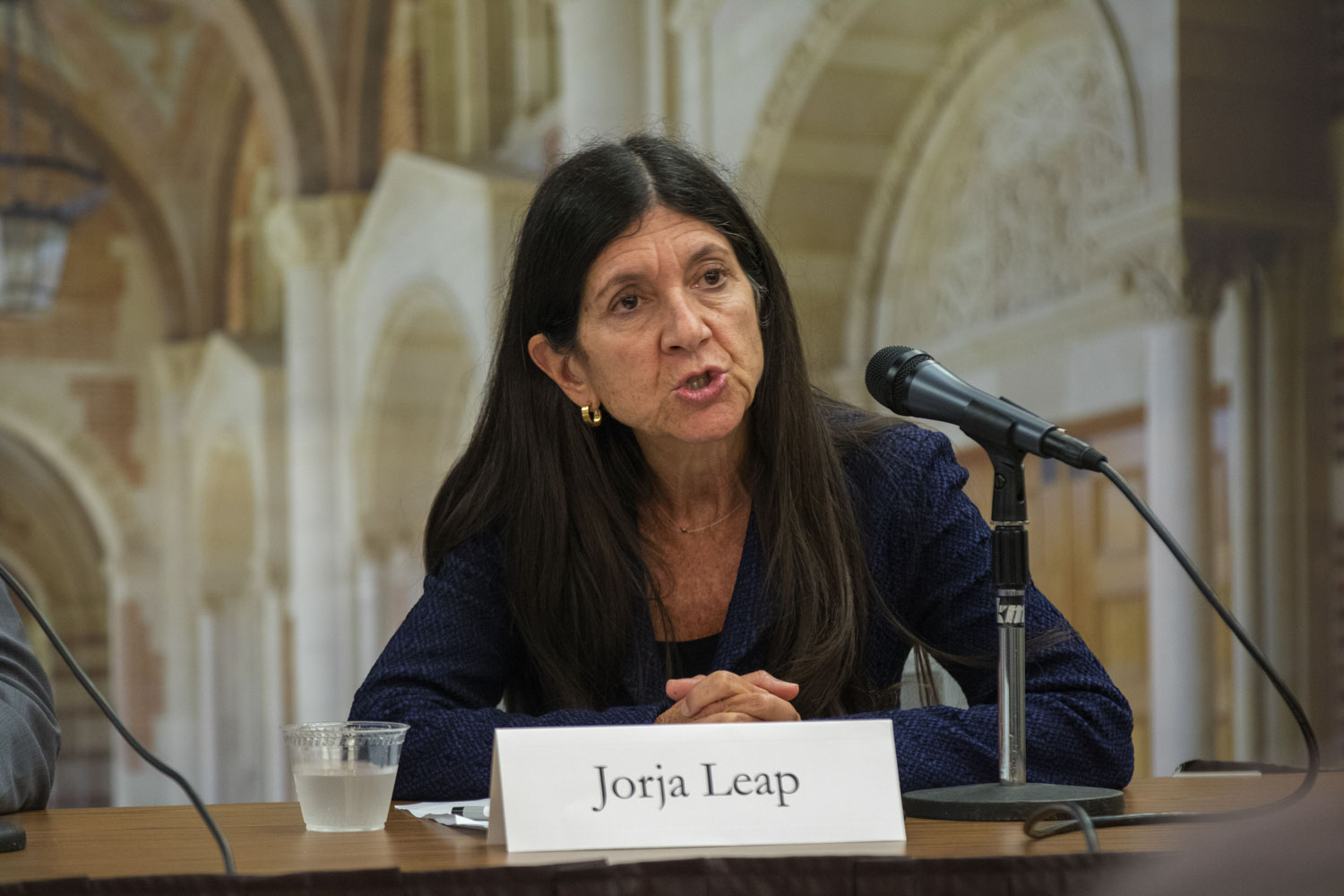
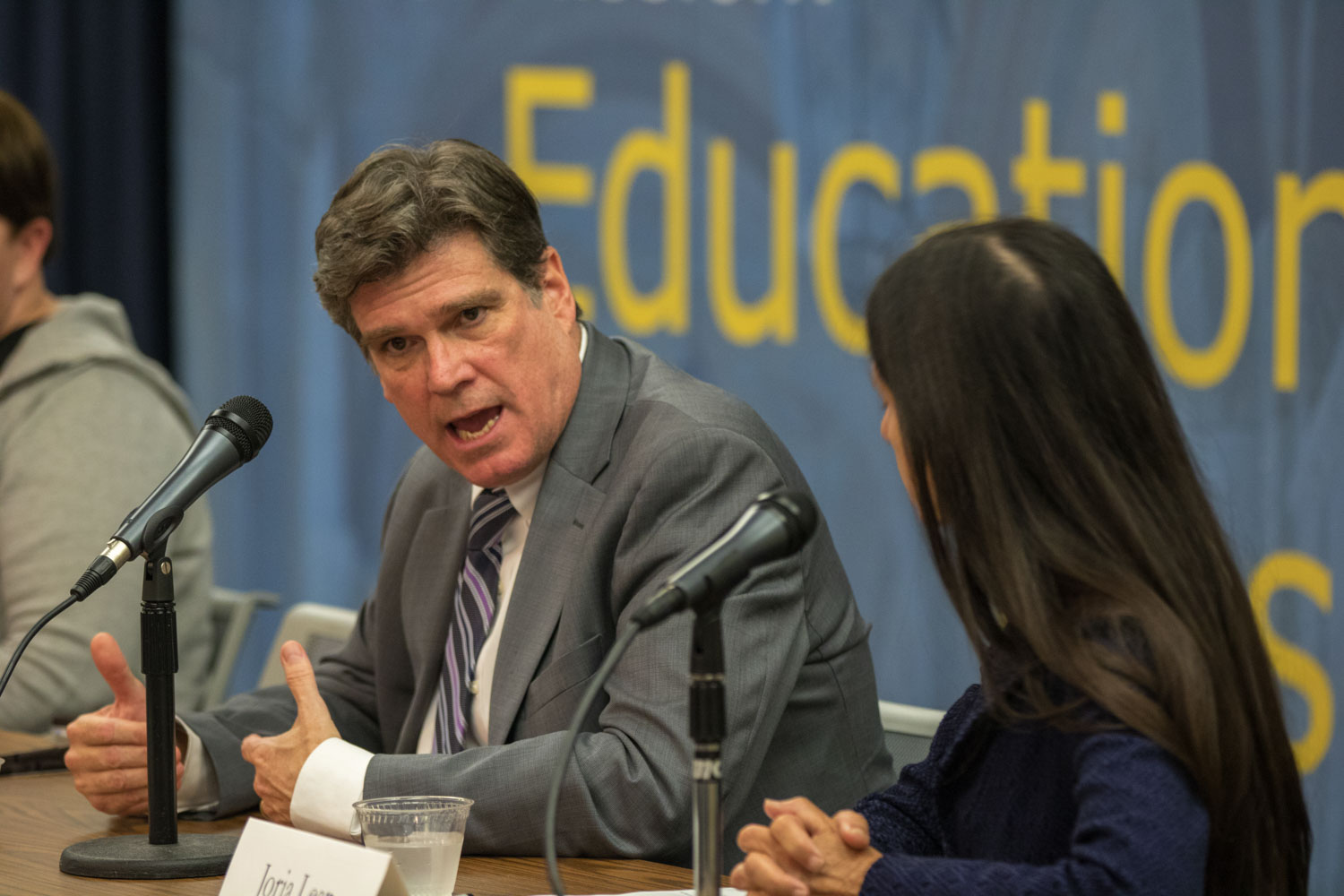
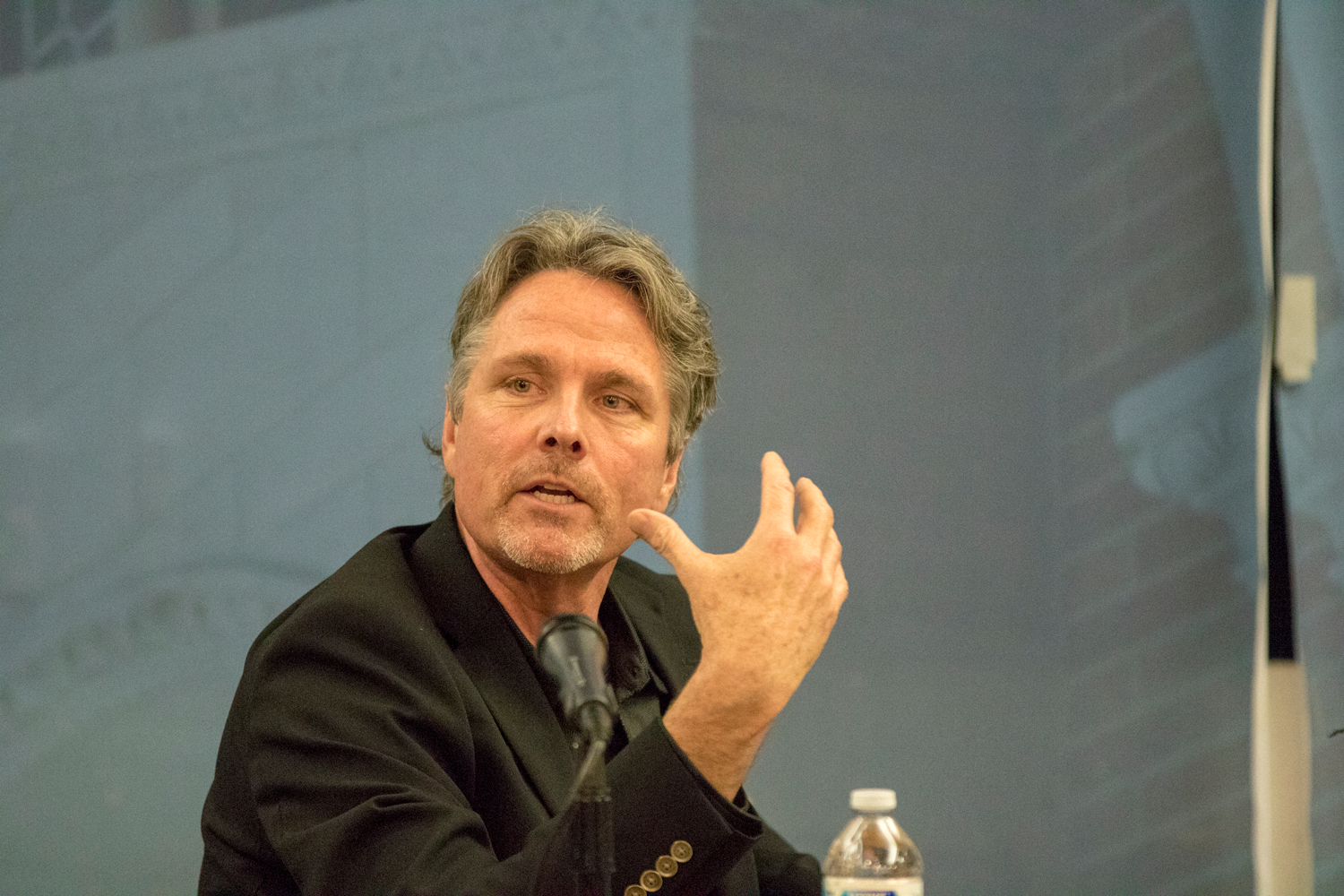
The first panel was moderated by Jorja Leap MSW ’80 PhD ’89, an adjunct professor of social welfare. It focused on diversion, a process that enables young people in contact with the justice system to bypass formal prosecution if they meet specific criteria and successfully complete a program that fits their potential needs (such as restorative justice and counseling).
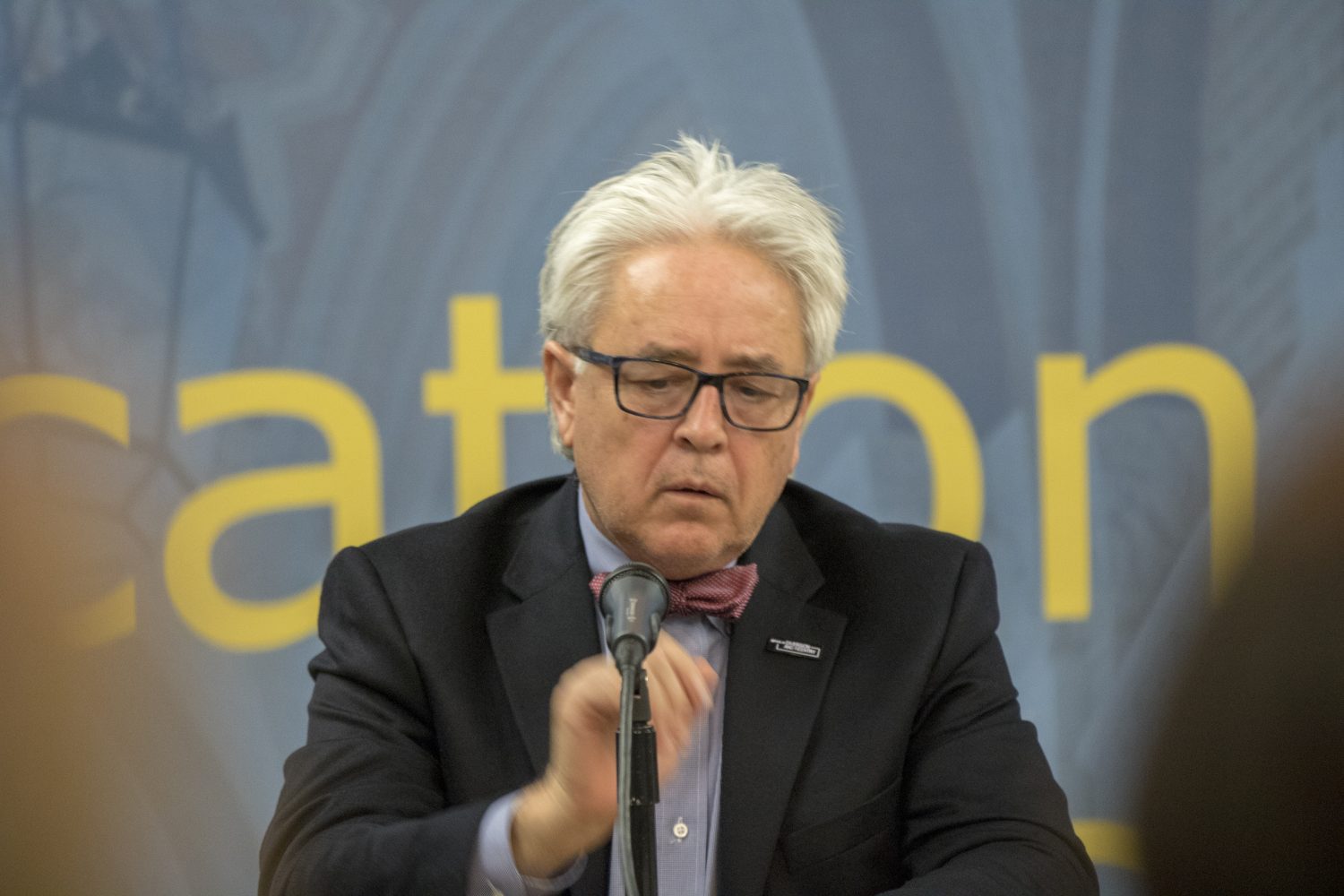
The panelists included retired Superior Court Judge Peter Espinoza, the director of the Los Angeles County Office of Diversion and Reentry, who has played a leadership role in recent efforts to reframe how L.A. County handles youth when they first get into trouble with the law. He described the significance of the County Board of Supervisors’ recent motion creating a new Office of Youth Diversion and Development, which will be overseen by Espinoza within his office.
“That action culminated almost a year of work where disparate justice partners, community organizations and law enforcement came together to try to hammer out what became an 80-page road map for youth diversion in Los Angeles County,” Espinoza explained.
The new model will “divert youths at first point of contact with law enforcement and not at the point of arrest,” Espinoza noted.
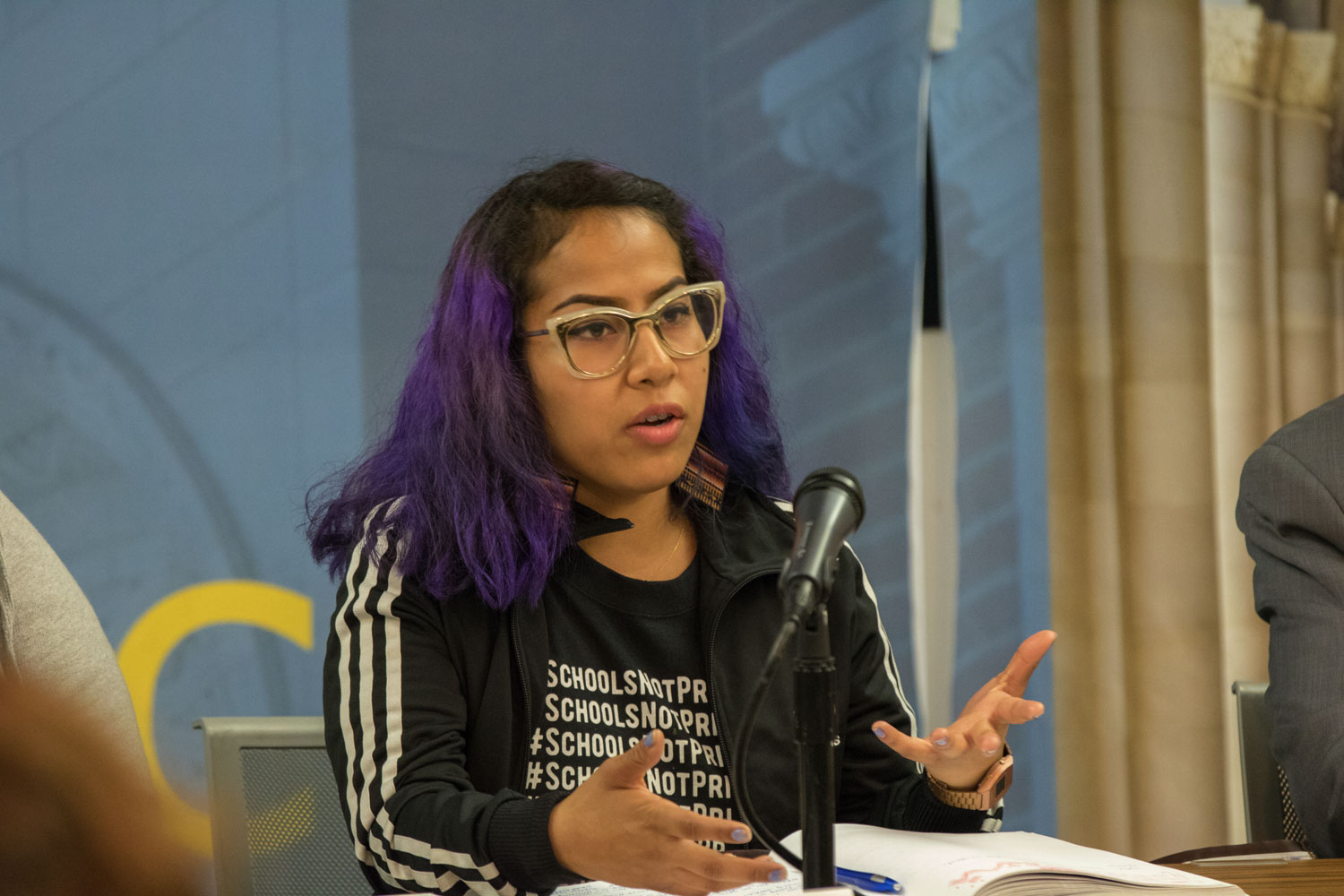
Panelists Gloria Gonzales and Kim McGill are organizers with the Youth Justice Coalition, one of the community-based groups that will be providing some of the services for the new diversion program. Both have personally had experiences with juvenile justice systems in the past. Out of their commitment to systems change, they have also been part of this effort and expressed cautious optimism.
“It’s at the point where this is the best start to building a relationship between the community-based organizations and the police and law enforcement agencies,” Gonzales said. “But I also know that is going to be a really, really hard new model to establish.”
“We have a really strong plan,” McGill said about the effort, which she participated in creating. “But how do we make a dream real in L.A. County?”
Panelist Sean Kennedy, the former director of the federal public defender’s office who now serves as director of the Loyola Law School Center for Juvenile Law and Policy, observed: “I think this is a great start. But, in the past, diversion is often too limited. Too many great kids are excluded.”
Although Leap and the four panelists all said they view the new approach as being a positive development, similar efforts in the past have fallen short in part because of outmoded attitudes that emphasized punishment of youth without dealing with the root causes of their actions.
“Diversion, in my view, isn’t about accountability – although I guess that is a part of it,” Kennedy said. “It’s really about addressing unaddressed trauma, seeking to heal damaged kids, and — and I think this is too often overlooked — education advocacy to deal with problems in the schools where they often first arise.”
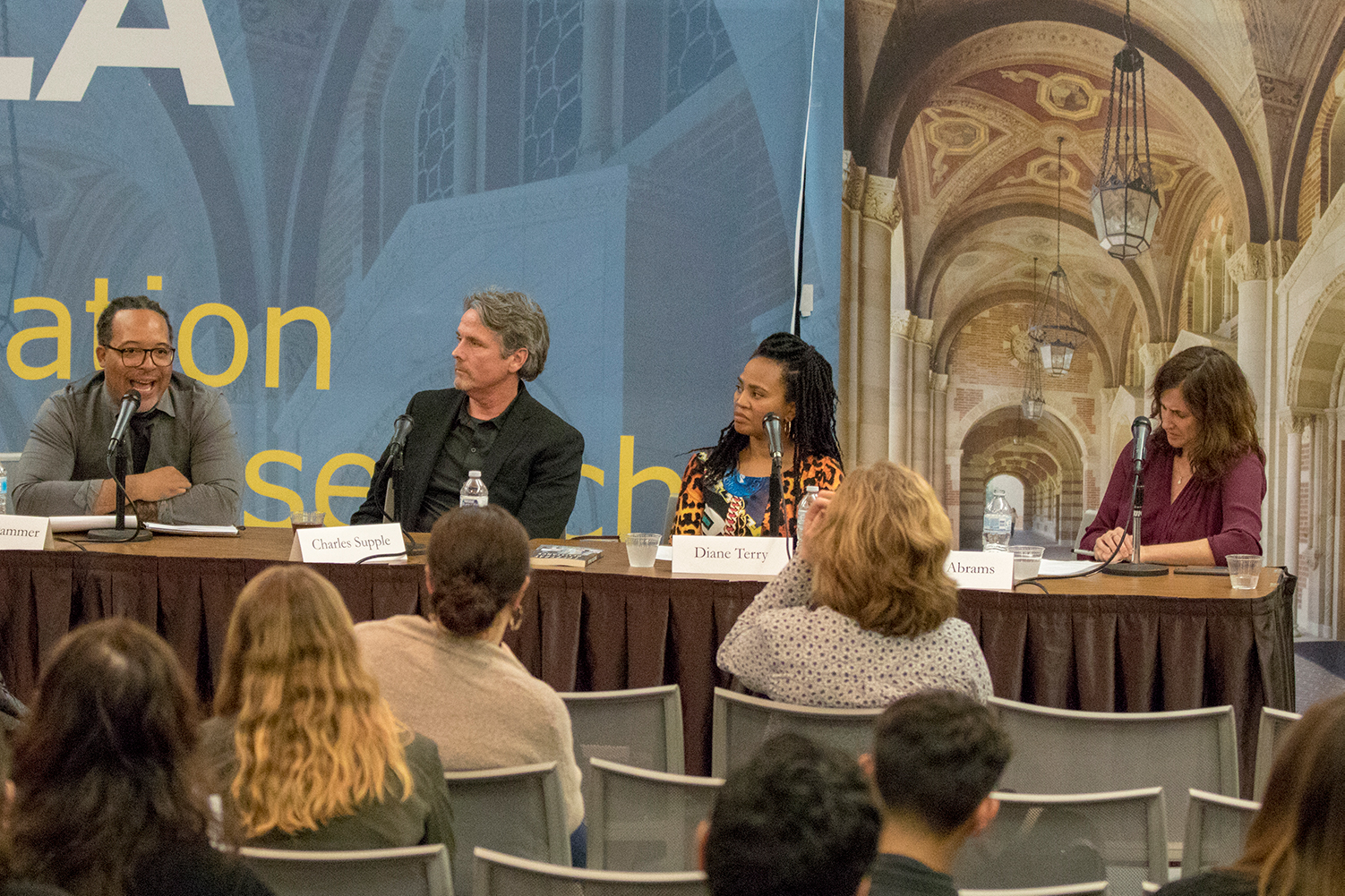
Abrams moderated a second panel that focused on the concept of desistance, which relates to efforts by individuals to cease — or at least moderate — the attitudes, behaviors and habits that contributed to criminal justice involvement. Desistance is often defined as the gradual process of establishing a new, crime-free lifestyle.
Terry offered examples from her book with Abrams to illustrate that desistance is far more complicated than simply forcing someone to abide by the law.
“Desistance is a process,” Terry said. “It does not happen linearly; it’s fluid. But it starts with the changes that the young people themselves are trying to make.”
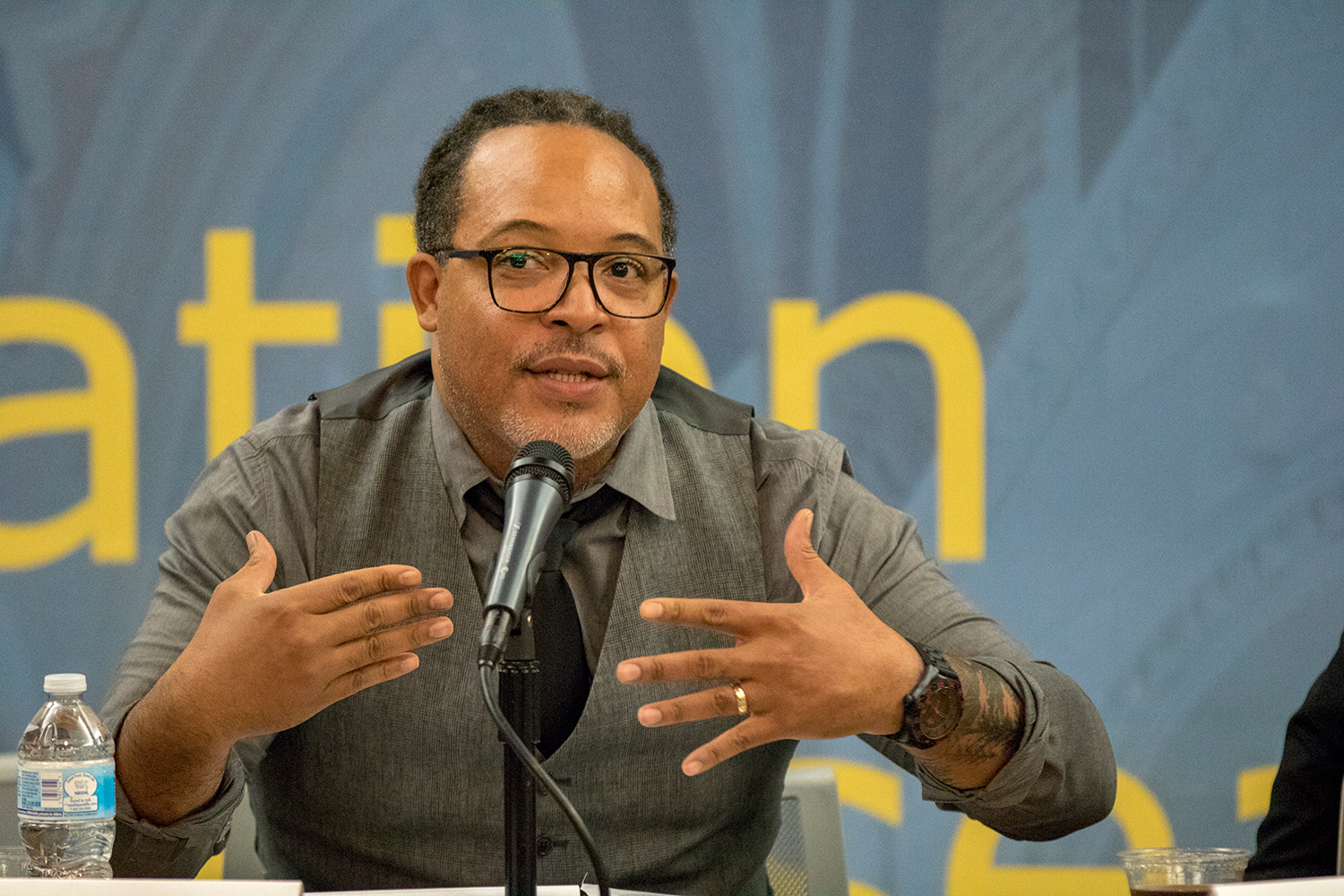
Panelist Harry Grammer is founder and president of New Earth, which provides arts, educational and vocational programs to empower youth ages 13-25 to transform their lives and move toward positive, healthier life choices. He applauded the contributions of academics to the transformative justice movement, but cautioned the many students in attendance against viewing young people only as they fit into groups or populations for statistical purposes.
“This is important if you are going to be doing research or evaluations on anyone,” Grammer said. “If you don’t understand their culture, where they come from, the foods that they eat, who they love in their lives, then there is no way to build a true rapport.”
Chuck Supple, director of the Division of Juvenile Justice for the California Department of Corrections, flew in from the Sacramento area to participate in the panel discussion and express his support for research and policy that changes the ways that society deals with young people who have gotten into trouble.
“We hope to be able to play a part in helping to develop new skills to reduce risk while they are in DJJ, but, more importantly, to be able to build strengths that are going to transcend into the community,” Supple told an audience of about 50 people at UCLA’s James West Alumni Center.
“It’s not just doing no harm, but going back into the community and playing important roles in terms of employment, education and community involvement. It’s helping them to change the very conditions that led to them coming to us in the first place,” he said.
The evening closed with an emphasis on the factors that will play out in the implementation of both the diversion plan and ongoing desistance.
“It’s critical to think about the key themes that emerged from both panels – the importance of paying attention to individual youth as well as the need for lasting systems change,” Leap said. “These two poles are connected, always, by the crucial role played by the community – the nonprofit organizations, the families and the residents – who are all involved and part of the change that is underway.”