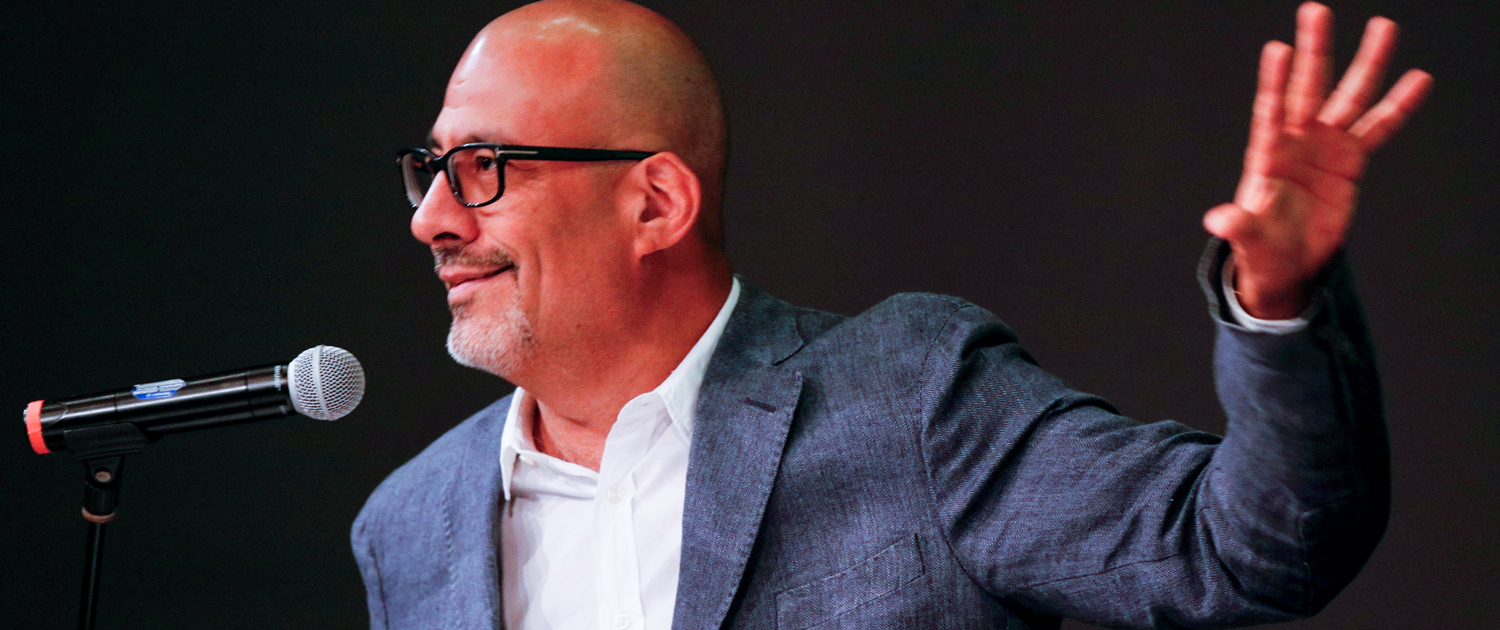
Examining the Unspoken Truth of Sexually Exploited Youth Author and researcher Alexandra Lutnick keynotes UCLA Luskin School conference on the hidden problem of youth caught up in the sex trade in the U.S
“The stories I tell no way describe the torture I felt
Years of destruction I knew nothing else
Trusted my mind, body, and soul
In the hands of another human being to control”from the poem “Mind, Body and Soul,” by Ummra Hang, a second-year master of social welfare student at UCLA Luskin
By Stan Paul
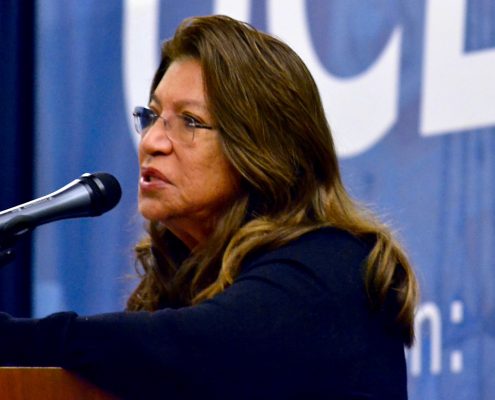
Ummra Hang’s reading of her powerful poem was one of many highlights of a UCLA Luskin School of Public Affairs conference examining sexually exploited children. The event, held May 6, 2017, brought together students, faculty, policy experts, law enforcement and service agency personnel — as well as survivors of abuse and commercial sexual exploitation — to focus on a complicated and emotionally charged problem.
The conference, which included appearances by several alumni from the Luskin School, highlighted how commercial sexual exploitation is not just happening in other countries. It is believed to involve more than 100,000 young people throughout the United States — especially in densely populated California cities such as San Francisco, San Diego and Los Angeles. The conference also served as the final project for — and was conducted by — Luskin master of social welfare research students in the University Consortium for Child and Families (UCCF) program, the culmination of their year-long research projects and part of a three-quarter course led by professor of social welfare Rosina Becerra. UCCF is a federally funded program and partnership between the County of Los Angeles Department of Children and Families and six masters of social work programs in Los Angeles, including UCLA.
Assisting the students in putting on the conference were Consuelo Bingham Mira, a lecturer in social welfare and coordinator of evaluation and research for the Public Child Welfare (PCW) California Social Welfare Education Counsel (CalSWEC) program and social welfare field faculty Michelle Talley.
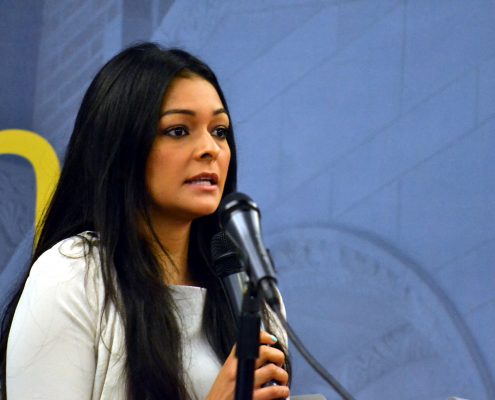
Although the problem is difficult to measure, research shows that sexual abuse and exploitation is not limited to young girls. It affects males, females and across the spectrum of genders and sexualities for a variety of reasons, said keynote speaker Alexandra Lutnick, a researcher and expert on human trafficking, the sex industry, substance abuse and criminalization.
“Our lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, queer, questioning, intersex — all face high rates of incarceration, family rejection, homelessness and child welfare involvement,” said Lutnick, author of the book “Domestic Minor Sex Trafficking: Beyond Victims and Villains.” “Any one of those on their own puts someone at an increased risk of trading sex. And, when we look at the intersectionality of those, we realize the ways in which gender discrimination, discrimination based on sexual orientation, housing insecurity, institutionalized homophobia and transphobia all conspire to make this group of young people more vulnerable to being involved in selling sex.”
Lutnick explained that a complicated issue such as this refutes prevailing narratives.
“We don’t know how many are involved — it’s a hidden population,” she said. “There’s no registry,” and therefore no ability to gather data about the ages of youth entering the sex trade.
Lutnick discussed the role that physical or emotional neglect plays in bringing youth into the sex trade. With emotional neglect, a young person may not find support from the adults in the immediate family, so he or she may seek that support elsewhere.
“That could be coupling with somebody in an intimate partnership,” Lutnick said. “And then that person is asking, coercing or forcing them to sell sex. It could be looking for validation from people who are paying them for sex.”
Adding to this complex story is the role of child abuse, said Lutnick. “Inevitably that’s going to come up in any conversation about young people being involved in the sex trade. For some this means they’re being abused at home and to get away from the abuse they run away and then we’re back into the narrative of the role of homelessness.”
For others, she said, “their involvement in the sex trade is a continuation of the way in which their parents and guardians have been abusing them for many, many years. And it’s just one of the ways that’s now happening,” she said.
Panelist Gabriella Lewis, a supervising case manager with CAST, a Los Angeles-based nonprofit anti-trafficking organization, said that the problem is more common than most people realize. “Anyone can be a victim and anyone can be a trafficker,” Calderon said. “Safety is constantly an issue with this population.”
Solutions are challenging, Lutnick said, and they remain obstructed by nebulous dichotomies such as victim and villain.
The idea of, “Oh, we just need to rescue the good kids and punish the bad people,” flies in the face of the reality on the streets, Lutnick said. “We can’t arrest our way out of this. We can’t legislate our way out of it and we need to direct attention to the root factors that contribute to young people either deciding to that the sex trade is their best or their worst option or finding themselves in situations where someone is specifically taking advantage of the vulnerabilities that they have.”
There is some positive news in California, Lutnick said. The state Senate passed a bill in the past year that decriminalizes youth involvement in the sex trade — progress that was many years in the making.
“Even though you’ve got a federal definition, they’re regulated at the state level,” Lutnick said. “So unless states change their penal codes, young people are still being arrested.”
Lutnick also had some advice for lawmakers and policymakers.
“When we have these proposed outcomes — lawsuits or legislation — what are the questions we need to ask ourselves?” she asked. “Is it going to result in the hoped-for outcome? What are the potential negative impacts? Does it address key vulnerabilities such as poverty, racism homophobia, transphobia? And, if not, maybe we need to work a little harder to do that deeper level work — that macro level work — to come up with solutions that aren’t going to create harm for anybody.”
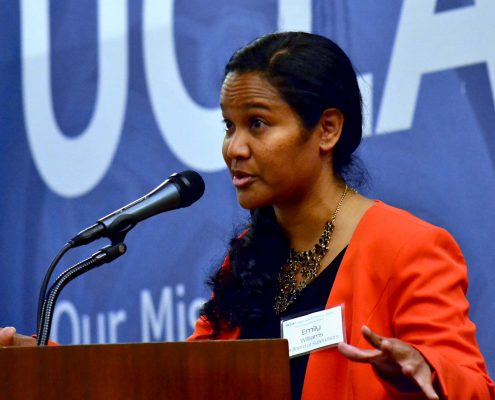
Two Luskin graduates — Emily Williams MPP ’98, assistant senior deputy for Human Services, Child Welfare, and Education for Los Angeles County Supervisor Mark Ridley-Thomas; and Sarah Godoy MSW ’15, a policy associate for the National Center for the Youth Law’s Child Trafficking Team — were among the expert panelists. Both were part of the juvenile justice/law enforcement panel that included LAPD detective Dana Harris, who specializes in the investigation of human trafficking, and Maria Griglio, a deputy county counsel representing the Department of Children and Family Services.
Recognizing that young people over the age of 18 involved in prostitution may have been a victim of exploitation long before that, Williams talked about the L.A. County Supervisors’ ongoing efforts to end commercial exploitation of children as well as the expansion and implementation of support services to those who are 18-24 years of age.
“We understand they need to be served just as much as children do,” said Williams, who serves as a policy liaison to a number of service agencies including the Department of Children and Family Services, the Department of Public Social Services, Child Support Services and the Los Angeles County Office of Education.
Panelist Monique Calderon, who was part of the “healing to action” panel, shared her own story of getting into “the life” in the sex industry after graduating from college, and how difficult it was to get out.
Conference organizers were pleased with the results of the daylong discussions.
“The conference exceeded my expectations,” UCLA Luskin social welfare field faculty member Michelle Talley MSW ’98 said after the event. “Every panelist enhanced the conference as each one imparted their knowledge and expertise about human trafficking and engaged the audience.”
Every student who participated went above and beyond to ensure the success of the conference, she said. “The conference was a start of an invigorating discussion of sex trafficking of youth in hopes to end trafficking as we know it today,” Talley said.
“This successful conference is just one of the examples of the many activities that the students are able to do in our MSW program,” added Becerra, who also acknowledged generous support for the conference by members of the Los Angeles County Board of Supervisors Mark Ridley-Thomas, Sheila Kuehl and Hilda Solis, as well as by private donors.