By Mary Braswell
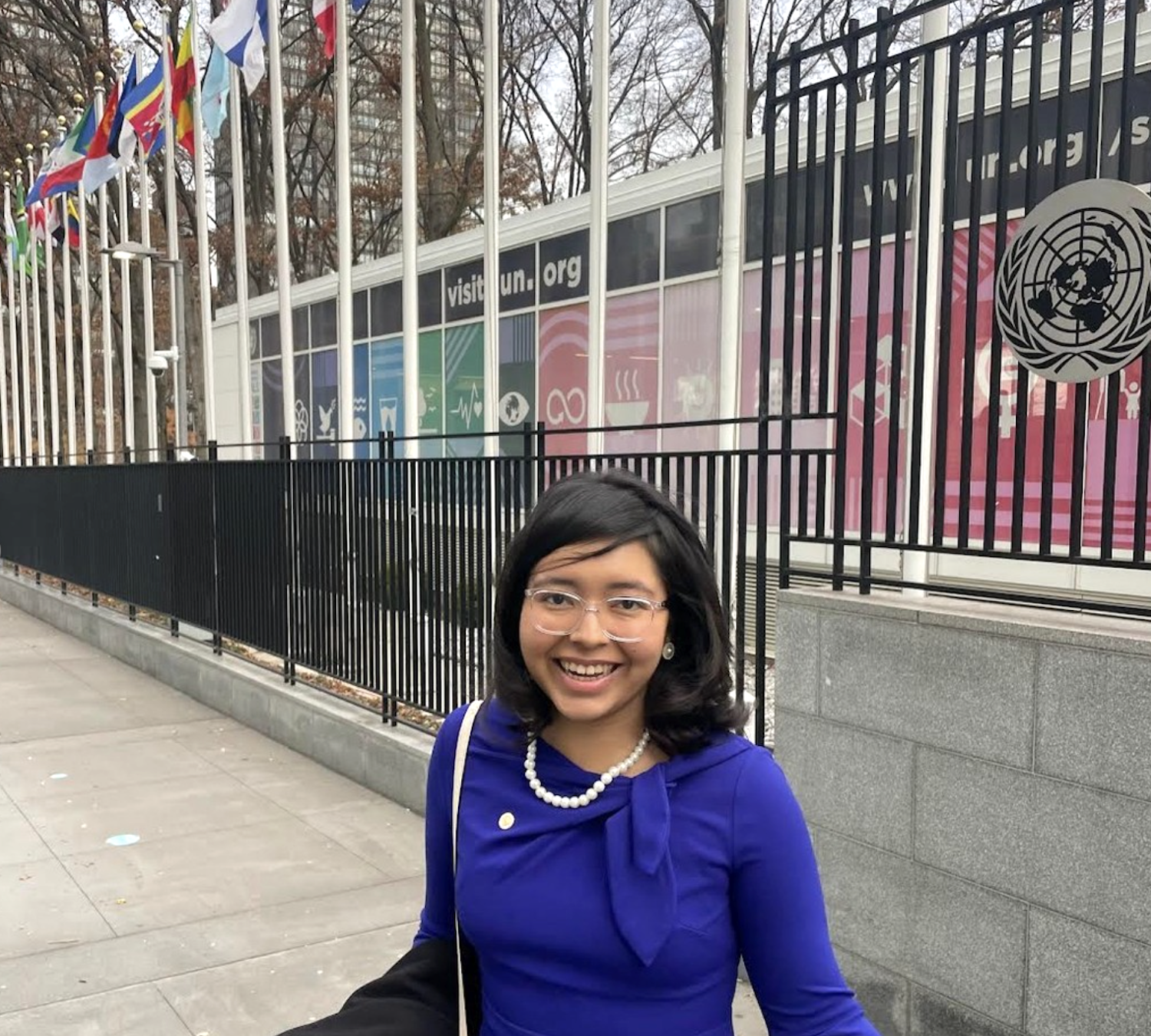
UCLA Luskin undergrad Fiona Lu entered the world of political activism while still in high school, moved by the realization that students like her could effect real change — with the right tools and strategies. Her vision is already paying off with legislative success, including the recent passage of a California law expanding access to menstrual products.
“Your experience as a community member is all you need to be a policy advocate,” says Lu. “You don’t need to have a prestigious degree — what you see in your community matters.”
With the dual goals of advancing economic justice and training other young people to maximize their political impact, Lu co-founded the advocacy organization What We All Deserve in November 2023. The group’s outreach to California lawmakers included two UCLA Luskin alumni, Assemblyman Isaac Bryan MPP ’22 and Sen. Caroline Menjivar MSW ’22, who authored and co-authored AB 1810.
The new law ensures that the state’s incarcerated population has unimpeded access to menstrual products, addressing what Bryan called a “gross abuse of power” in jails, prisons and juvenile facilities, where period products were at times withheld in an atmosphere of coercion, humiliation or harassment.
“It’s an issue at the intersection of gender rights, reproductive rights, but also poverty,” says Lu, a second-year student with plans to major in Public Affairs and Labor Studies and minor in Asian American Studies.

Lu, right, and Esther Lau, co-founders of the What We All Deserve advocacy group. Photo by Monet Oganesian
AB 1810 is one of two What We All Deserve-supported bills that have been enacted, and two more are in the pipeline. In recognition of its impact, the group was recently awarded a $25,000 grant from an Allstate Foundation initiative to support youth empowerment.
Lu says her activism is shaped in part by the help that she, her mother and her 7-year-old brother have received through government assistance programs.
“I was a free lunch kid. And I still benefit from a lot of support systems the state of California and the federal government provide, like the Pell Grant and the Cal Grant,” Lu says.
“These support systems are so, so crucial, not just for people who are impoverished but also for people who might be going through a period of unemployment. Your economic circumstances can affect your physical and mental health and the type of life you think can be possible for you.”
Before launching her own advocacy venture, Lu was active in student-powered organizations such as Gen-Up and California High School Democrats, where she learned tangible ways to turn policy priorities into action. Key among those is building alliances with elected officials.
Last year, when What We All Deserve was working on the proposal that would become AB 1810, Lu reached out to Bryan.
“He has a such a robust background in criminal justice advocacy, and we were really glad that he was able to champion this idea,” she said.
Her first contact with Menjivar came years before, when Lu was a junior in high school. Menjivar had just been elected to represent a San Fernando Valley district in the state Senate, and Lu felt she would be the perfect author of another bill, still pending, that would make menstrual products affordable for low-income Californians.
“Sen. Menjivar is a social worker, and she knows how much access to basic needs affects your health and your overall well-being,” says Lu. “So I contacted her office and said, ‘We have this really cool policy idea. I would love it if we could meet with you.’ And she said yes.
“We really want to let young people know that sometimes it’s just that easy.”
Menjivar said that, as a state senator, she has prioritized authoring youth-serving and youth-led bills, and Lu is one of her strongest legislative collaborators.
“Not only a pleasure to work with, Fiona also has a pivotal voice that’s deeply knowledgeable on the issues young people face today,” says Menjivar.
“She is a determined leader in grassroots advocacy, including building the youth coalitions that are so important to our future, and I’ve absolutely loved every opportunity we’ve had to work together.”
Through What We All Deserve, Lu and co-founder Esther Lau are sharing these strategies for forging effective alliances with youth across California and now Texas and New York.
“A lot of times, young people think they have to have policy expertise or technical data or something super hardcore to speak to the people we elect,” Lu says. “But they’re supposed to represent your voices, and you’re supposed to feel comfortable talking to them. So that’s a big part of what we’re trying to demystify.”
Lu applied to UCLA as a Public Affairs pre-major because of its emphasis on social change.
“It’s a really unique program. We’ve already established that there is inequality in the U.S., in California, in our own communities. But in these classes, we’re asking, how can we work toward rectifying that? And how can we find policy solutions that are grounded in community values?”
She honed her advocacy skills during UCLA’s summer internship program in Washington, D.C. And at the invitation of Social Welfare Professor Laura Wray-Lake, Lu addressed an international youth conference hosted by UCLA Luskin last spring and beamed to an audience of 720,000 people worldwide.
Lu says her work is motivated in large part by the brother she is helping to raise.
“Watching my brother grow up has helped me really ground my anti-poverty work in this idea that children deserve this,” she says. “All children are not born in the same circumstances. But all of them deserve to thrive.”
This story appears in the 2025 issue of Luskin Forum magazine, coming soon in print and online.