[ From the Luskin Forum Online ]
Dean Gary Segura is fond of saying that the UCLA Luskin School of Public Affairs is about human well-being.
“We study ways to make individuals, families, communities and polities function better, for the improvement and quality of lives of all those affected,” Segura told the Class of 2017 at Commencement last June.
 Those students, now Luskin alumni, spent 2016-17 working on a variety of projects related to urgent human needs, such as:
Those students, now Luskin alumni, spent 2016-17 working on a variety of projects related to urgent human needs, such as:
- greenhouse gas reduction
- interventions with at-risk youth
- prison population reduction
- homelessness
- HIV prevention
- meningitis epidemic control
- regulation of new and intrusive technologies
- safe school environments
- quality mental health services
- river restoration
- access to home ownership
- responsive governance in the developing world
“I’m reminded every day of how lucky I am and how special it is to be a part of the Luskin School of Public Affairs,” Segura told proud parents and family members at the graduation ceremony.
This issue of Luskin Forum is dedicated to just that: taking pride in how this school makes a difference, and why it’s important to remember the myriad accomplishments of our students, faculty, staff
and alumni.
Our UCLA Luskin mission statement says it perfectly: “At the convergence of the fields of social work, urban planning, and policymaking, the UCLA Luskin School of Public Affairs identifies and develops emerging areas of research and teaching, cultivating leaders and change agents who advance solutions to society’s most pressing problems.”
In the words of Dean Segura: “Do good in the world. Make change.”
— GEORGE FOULSHAM

We Are Connecting
Like their planning and policy peers at UCLA Luskin, the School’s Master of Social Welfare students are connecting with the community throughout their two-year professional program. First-year MSW students have the opportunity to engage in high-impact internships and placements that begin even before fall classes start.
New Luskin MSW students bring with them a wide range of experience in the community and at social work-related agencies, where they have served as students, employees and volunteers. From the get-go, they immerse themselves in the work of organizations that assist and provide programs for the homeless, the elderly, disabled adults, children with emotional and learning disabilities, and foster youth.
The wide array of student placements includes a downtown women’s shelter, a psychiatric care facility, school and community groups, and other sites that provide services such as law advocacy or assistance with transitional housing, according to Michelle Talley MSW ’98, field education faculty member.
First-year MSW students are placed at various field sites throughout Los Angeles County and in surrounding counties, Talley said. Placements are based on previous experience, prior knowledge of the role of a social worker and other factors.
Their extensive field work also involves community outreach and advocacy. They participate in staff meetings and offer consultation. They engage in research activities and participate in development programs that include training on professional responsibility and reporting mandates.
Both years of the MSW program integrate the School, alumni and the community as integral parts of the educational process for this professional practice-oriented degree, assuring that graduates become high-impact practitioners.
“The goal is to place students at sites that will create opportunities to enhance their growth as a professional social worker,” Talley said.
— STAN PAUL

We Are Protectors
From the streets of Los Angeles to innovative research on social media, UCLA Luskin faculty members like Ian Holloway are gathering data to inform programs and policies that improve the health and well-being of vulnerable communities.
In addition to his position as assistant professor of social welfare at UCLA Luskin, Holloway is director of the Southern California HIV/AIDS Policy Research Center. There are approximately 5,000 new HIV cases in California each year. Holloway’s ongoing work focuses on HIV prevention and treatment among sexual and gender minority people. “Young gay and bisexual men, especially those from racial and ethnic minority communities, are disproportionately impacted by HIV, and HIV-related comorbidities,” Holloway said.
In 2016-17, Holloway and a group of Luskin students and recent graduates canvassed more than 500 gay and bisexual men to gauge their awareness of a yearlong outbreak of meningitis in Southern California. Holloway and his research group found that less than a third of those interviewed were vaccinated against meningitis despite extensive outreach efforts by the California Department of Public Health.
Holloway’s findings suggested that better vaccination uptake surveillance, tailored education and more sites for immunization throughout Southern California are needed in order to bolster efforts to track meningitis and encourage vaccination among gay and bisexual men.
Other research conducted by Holloway and student assistants includes the LINX LA project, which uses a mobile phone app to encourage treatment engagement among HIV-positive African American young gay and bisexual men through access to legal and social service resources in Los Angeles.
Next up? Using a new and innovative approach, Holloway and a group of tech-savvy UCLA researchers will use data-mining of social networking sites to learn more about drug use and sexual risk behavior. The project, funded by the National Institutes of Health, aims to use social networking data to inform intervention development. “This would include ‘just-in-time’ technology-delivered interventions aimed at preventing negative health outcomes and promoting healthy behaviors,” Holloway explained.
— STAN PAUL
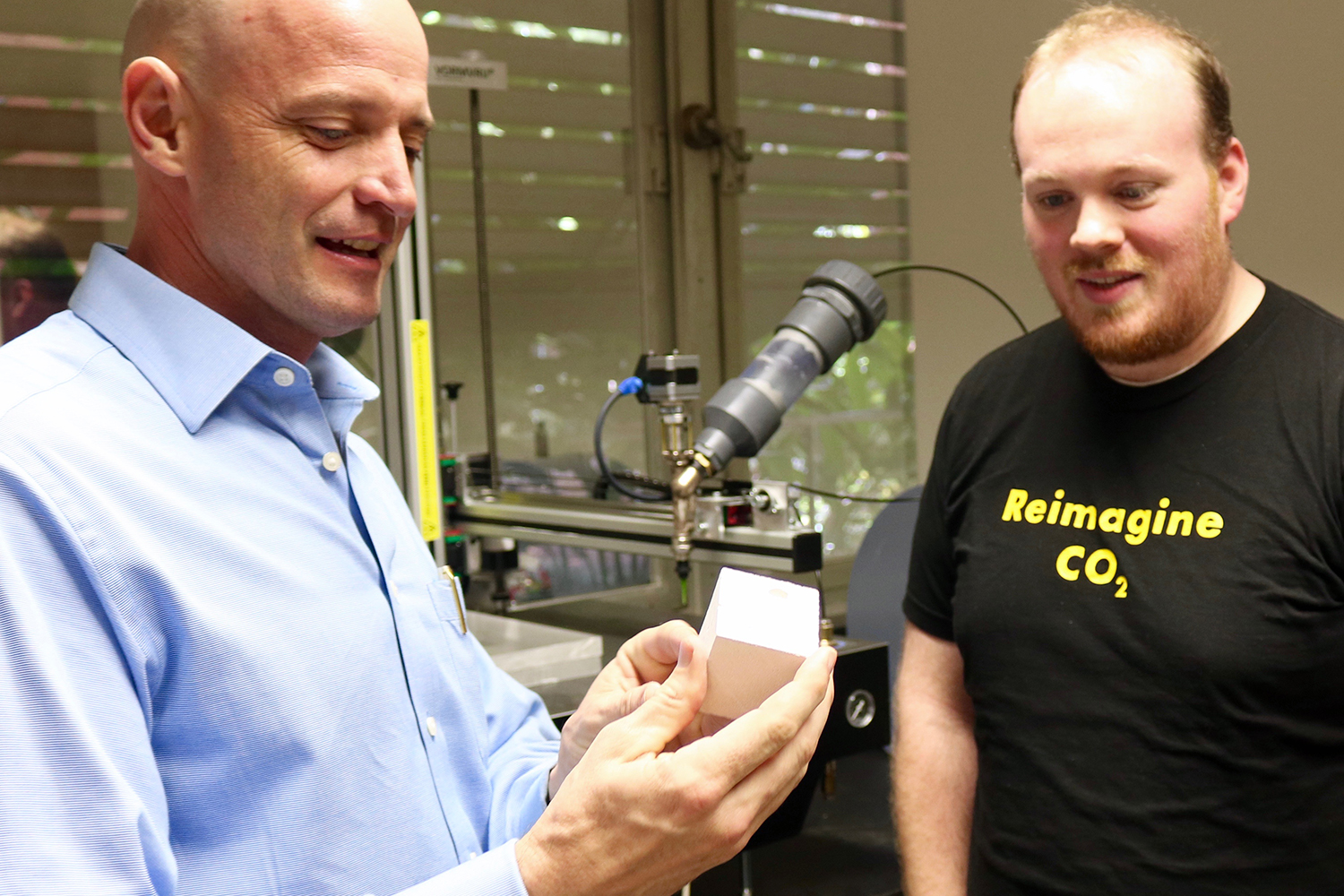

We Are Innovating
Whether it be guiding equitable revitalization of the L.A. River, helping Californians cut down on their electricity use, or advancing a new way to repurpose carbon dioxide into a greener form of concrete, the Luskin Center for Innovation is a trailblazer among UCLA’s many sustainability leaders.
And that’s just for starters.
Since its inception in 2009, the Luskin Center’s research has influenced local, state and national policy. This includes a new rooftop solar program for Los Angeles, the redesign of California’s clean vehicle rebate program, and current efforts to develop a drinking water low-income assistance program in California. Other research informs the state’s world-renowned actions to combat climate change while maximizing local employment, air quality and health benefits.
A think tank housed within the UCLA Luskin School of Public Affairs, the center is organized around initiatives that translate world-class research into real-world policy solutions. Current initiatives include advanced transportation, clean energy, climate action, digital technologies, sustainable water and urban greening — all linked by the theme of informing effective and equitable policies.
The center brings together faculty and staff from a variety of academic disciplines across campus to conduct research in partnership with civic leaders who use the knowledge to inform policy and organizational innovations. Civic leaders include policymakers, nonprofit organizations, and business associations. Students at UCLA Luskin have the opportunity to work with the Luskin Center to gain hands-on research experience and work closely with these decision-makers.
Meyer Luskin, the visionary and benefactor behind the Luskin Center, says, “Sustaining the environment is the greatest inheritance one can leave to children, and the most enduring gift to the community and nation.”
— KELSEY JESSUP
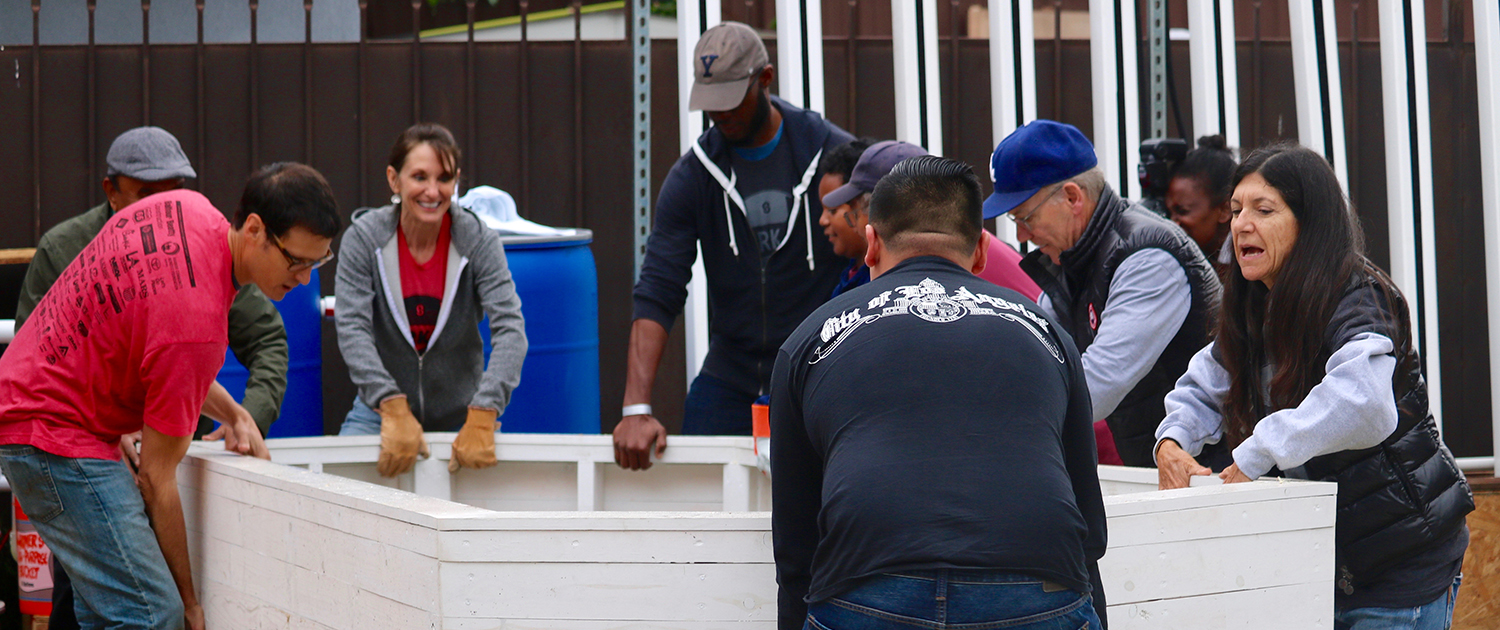

We Are Inspiring
Each year, UCLA Luskin students are embedded in internships and research projects offered through all three departments. That’s a given. Not as well known is how the school also creates partnerships that benefit students and the communities in which they work.
Take, for example, the Watts Leadership Institute (WLI). The brainchild of Social Welfare adjunct professor Jorja Leap MSW ’80 and her research partner, Karrah Lompa MSW ’13, the WLI is engaged in a 10-year mission to bring about positive change in a community hungry for leadership coaching.
Leap and Lompa are working with the first cohort of community members, providing guidance on everything from learning how to establish successful nonprofits to applying those skills in their community garden. After several years of training and coaching, the cohort will provide guidance for future leaders in Watts.
At the same time, Leap is using the project as a way to provide community-based educational experiences for Luskin’s Social Welfare students.
“This kind of a public-private partnership, along with the research attached to it — and the building of the Watts community — really represent the best of how all of these different factors can come together,” said Leap, who has been working in Watts since conducting research there when she was a Social Welfare graduate student in the 1970s. “It represents part of UCLA’s continuing and growing commitment to communities like Watts that need our involvement, our engagement, our organizing, our research.”
The WLI has received funding from the California Wellness Foundation and from GRoW @ Annenberg, a philanthropic initiative led by Gregory Annenberg Weingarten, as well as office space and in-kind support from Los Angeles City Councilman Joe Buscaino.
“What Watts Leadership did was to help us come together, to put our resources together, and be an example for the rest of the nonprofit and leadership community in Watts,” cohort member Pahola Ybarra said. “It’s been an amazing effort to help us grow, and to help us get out of our own way. It encourages us to reach for as much as we can and do as much as we can in the community.”
— GEORGE FOULSHAM

We Are Woke
On Nov. 9, 2016, after many felt their world spin out of control, the Institute on Inequality and Democracy at UCLA Luskin decided to create a space for students, faculty and staff to critically analyze the forms of exclusion, including white nationalism, so pervasive throughout the election that had just ended.
Post-election, the Institute, whose tagline is “Organizing knowledge to challenge inequality,” expanded its mission to challenge state-sponsored violence against targeted bodies and communities by immediately issuing a call for Jan. 18, 2017: Teach.Organize.Resist.
The campaign, known as #J18, included universities and colleges across the nation and internationally that organized nearly 100 courses, performances, sit-ins, and lectures to demonstrate that places of teaching and learning would not bear silent witness to oppression and hate. After a day of programming at UCLA, #J18 ended with “From the Frontlines of Justice,” a multi-performance event held in Ackerman Grand Ballroom. Highlights are online at teachorganizeresist.luskin.ucla.edu
Ananya Roy, professor of urban planning, social welfare and geography and the director of the Institute, remarked: “I encourage students to think of their role as scholars and to consider the power of research and knowledge.”
To strengthen the link between scholarship and collective action even further, the Institute launched its first Activist-in-Residence program in 2017. In the words of the inaugural fellow, Funmilola Fagbamila, arts and culture director of Black Lives Matter LA and adjunct professor of Pan-African Studies at Cal State LA, the definition of “woke” doesn’t end at knowledge. “To achieve the ‘woke’ label, you must be willing to analyze the conditions in your community. Lastly, you must act.”
Through academic research, and in alliance with social justice movements, the Institute creates scholarship, art and collective action to tackle divides and dispossessions in global Los Angeles and in cities around the world.
“We do so to insist on the academic freedom to examine regimes of power and structures of intolerance,” Roy explained. “We do so to forge imaginations of abolitionism, civil disobedience and human freedom. We do so, as James Baldwin reminded us, to shake the dungeon and leave behind our chains.”
— CRISTINA BARRERA
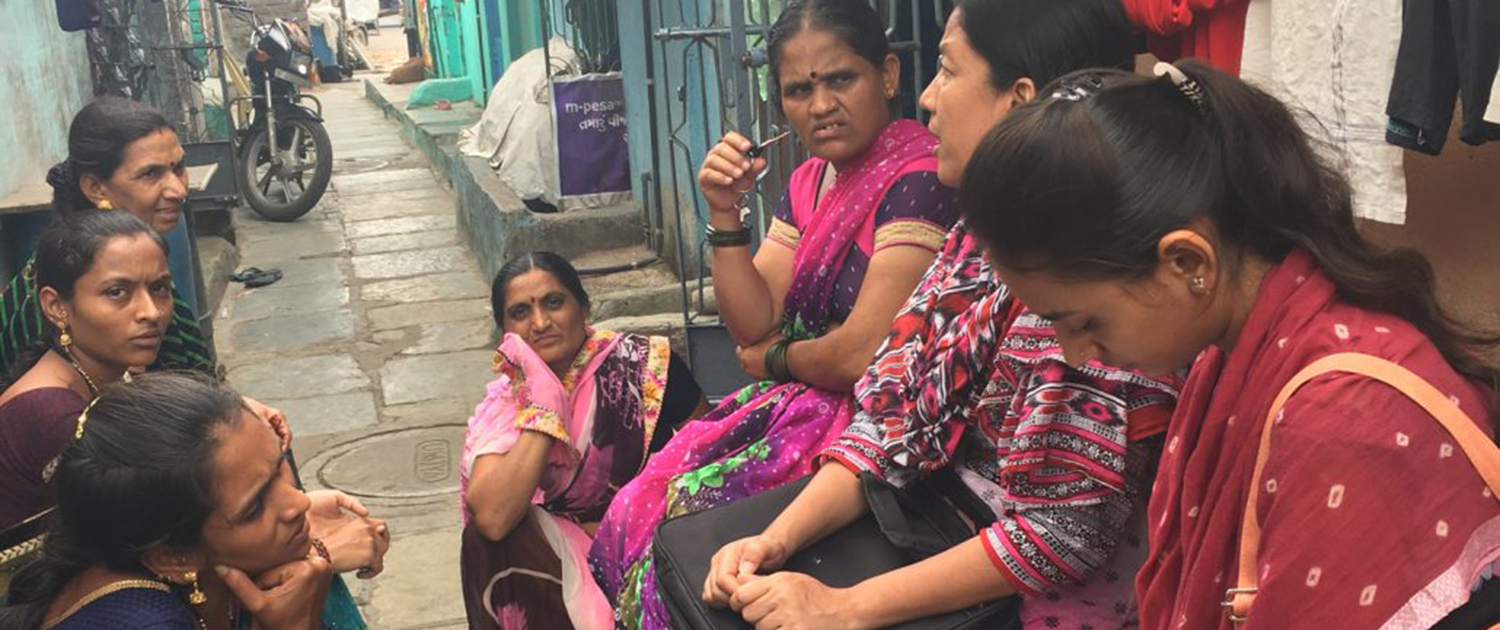
We Are Global
The impact of the Luskin School resonates far beyond the borders of Los Angeles and California. It’s a brand with international flavor. It’s not unusual to find Luskin students and faculty in Mexico, Uganda, India or Japan.
Luskin’s popular Global Public Affairs program offers students the chance to obtain intellectual and professional preparation to become future experts within the realm of international public affairs.
Each year GPA students travel around the globe, immersing themselves in the culture — and problems — of their host countries, and blogging about it for the GPA website. In the past year, students have lived in Mexico City; Paris; Kampala, Uganda; Bonn, Germany; Santo Domingo, Dominican Republic; and Tokyo, among other locales.
The GPA program is led by two members of the Urban Planning faculty. Michael Storper, distinguished professor of regional and international urban planning, is the director of GPA. He’s also a professor of economic sociology at the Institute of Political Studies in Paris and professor of economic geography at the London School of Economics. Stephen Commins UP PhD ’88, a lecturer in Urban Planning, is a former senior development specialist at the World Bank and director of policy and planning at World Vision International. UCLA Luskin’s international influence also includes:
- Urban Planning faculty like Paavo Monkkonen MPP ’05, whose students made multiple visits to Tijuana, Mexico, where they provided guidance to city and government officials about the best ways to deal with a housing crisis.
- Policy professors like Manisha Shah, associate professor of public policy, who has traveled around the world — to India, Mexico, Tanzania and Indonesia — to conduct research into microeconomics, health and development.
- Faculty leaders like Donald Shoup and Anastasia Loukaitou-Sideris who are among the many UCLA Luskin faculty in great demand as speakers at conferences around the world.
- Our international students — who add a global perspective to the student body and to Luskin educational efforts.
“A focus on problems that cross borders and involve international interdependence, also identifies where international forces affect domestic policies,” Commins said. “Students can learn from comparing experiences of different countries in how they face planning, policy and social welfare challenges and apply the experiences to their own studies and professional practice.”
— GEORGE FOULSHAM
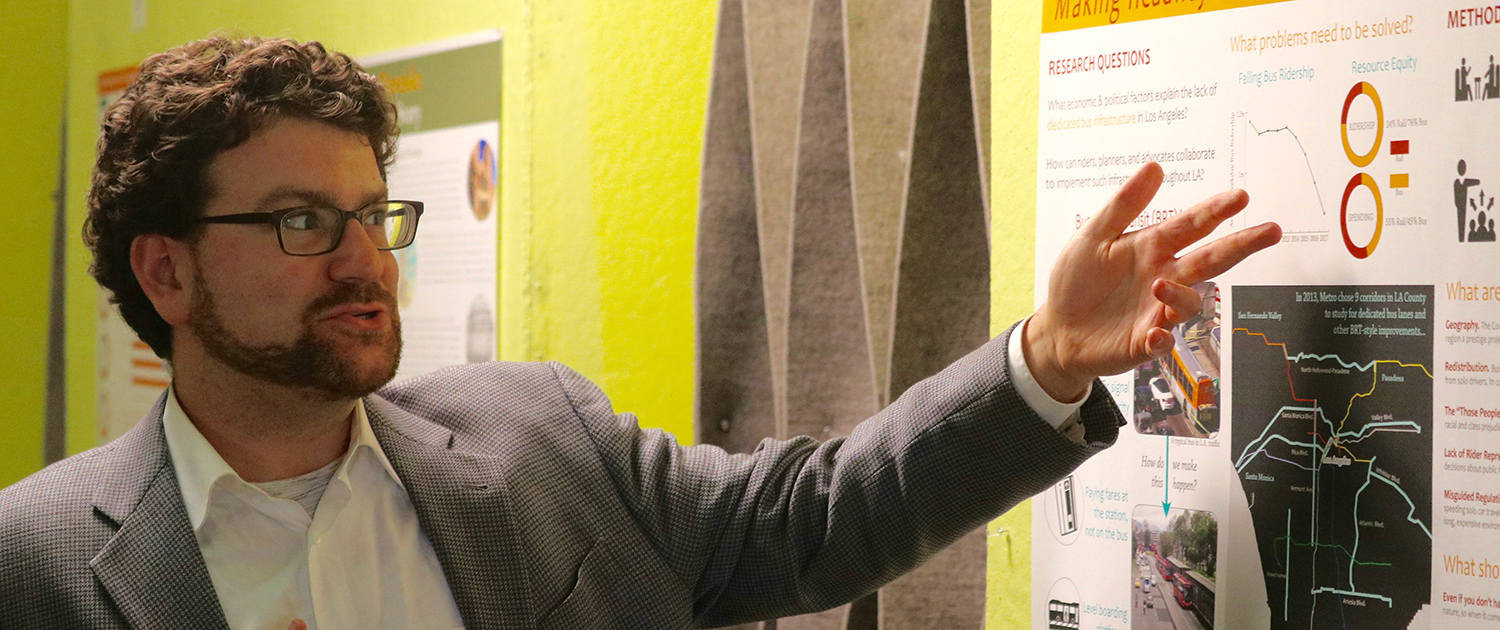

We Are Problem Solvers
Graduate students at UCLA Luskin don’t wait to step beyond the classroom to address California’s pressing challenges. Master of Public Policy (MPP) and Master of Urban and Regional Planning (MURP) students spend their time on campus deeply immersed in local, state, national and global issues. At the Luskin School, it’s part of the program.
Luskin students log countless hours learning lessons from leading-edge faculty and researchers. Here they seek solutions related to ongoing problems like housing, transportation or sustainability. They look into topics of vital importance to Southern California like electric recharging stations, barriers to bicycling in and around the city, or accessibility to water and food.
“At Luskin, we give students a diverse set of tools (both quantitative and qualitative) that will help guide them through the APP process and ultimately to go out into the real world and conduct policy analysis on issues close to their hearts,” said Manisha Shah, associate professor of public policy and faculty coordinator for the Applied Policy Project program completed by MPP graduates.
Recent work has connected students with county and city offices such as the Mayor of Los Angeles and the Los Angeles Department of Transportation. Regional agencies such as the Southern California Association of Governments (SCAG) frequently serve as clients. Recent APP projects included healthy food choices for elementary school students and employment opportunities for youths. Students also tackle educational issues right here at UCLA or work with the University of California’s Office of the President.
Many student projects benefit local and regional clients and the communities they serve, but they also reach out to communities far way. A recent planning capstone evaluated the short-term rental market in a Northern California city, for example. And a recent policy project analyzed governance at
the local level in the Ukraine.
— STAN PAUL
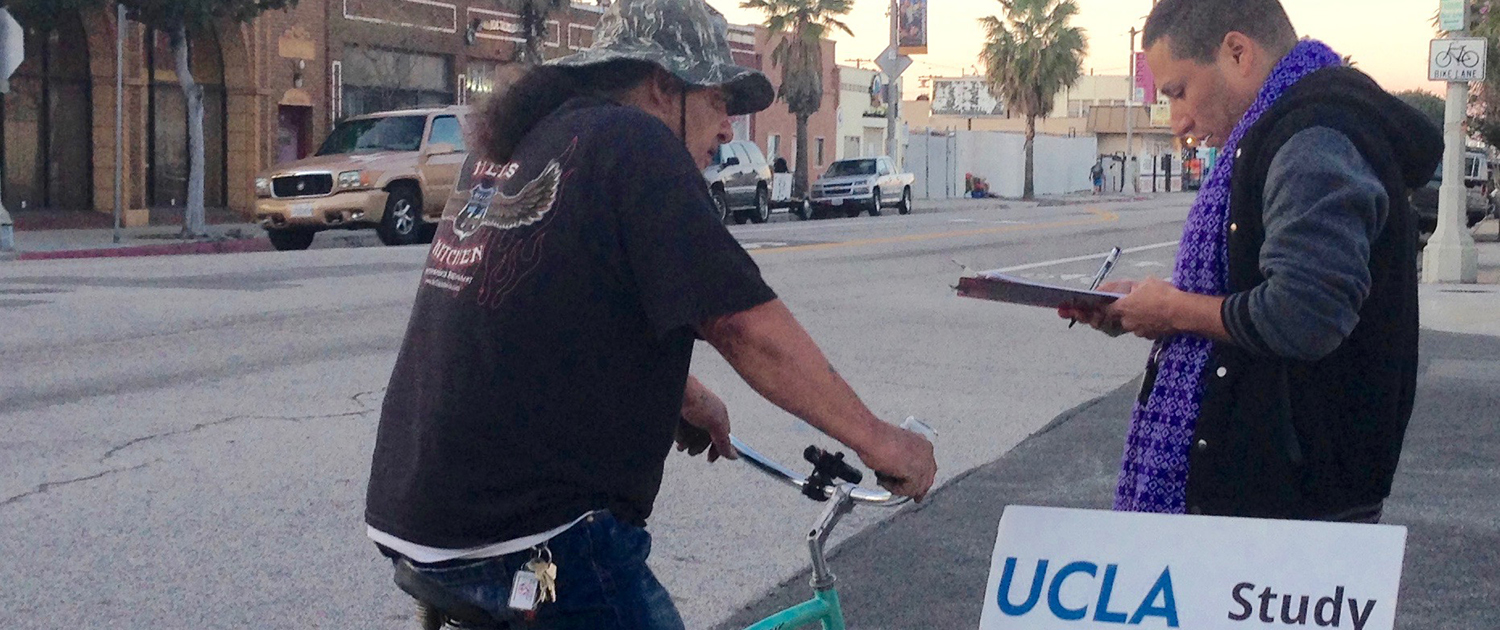

We Are Trailblazing
There’s no better place to study how people get around than Southern California — and for the past 25 years, UCLA has been home to one of the country’s preeminent transportation research centers.
The UCLA Institute for Transportation Studies (ITS) at UCLA Luskin combines cutting-edge research with meaningful, influential civic engagement to lead to policy results in California and beyond. From the impacts of traffic congestion to fairness around rideshare hailing to the civic consequences of paying for parking, ITS scholars produce work that ties directly to current transportation planning practices and policymaking at the local, state and national levels. ITS is noted for connecting transportation and equity, and for emphasizing the effect of transportation decisions on people’s lives.
“We take our policy mandate seriously,” said Brian Taylor UP PhD ’90, director of ITS and professor of urban planning.
Through close partnership with dozens of outside organizations that include government agencies, private transportation companies, nonprofit foundations and advocacy groups, ITS faculty, staff and students translate the latest knowledge on transportation into proposed real-world policies around movement and growth. ITS’ biannual digital magazine is widely read throughout the transportation community, highlighting important new research in a clear, constructive manner for practitioners.
Luskin students working at ITS collaborate closely with faculty members, receive generous scholarship funding for their own trailblazing projects, and have garnered an inordinate number of prestigious grants and awards over the years. Regular interactive events and publications showcase student findings to the academic community and the public at UCLA and around the country.
The next quarter-century will bring significant changes to how we travel, with daunting societal impacts. As it has since 1992, ITS research and policy action will help guide the way toward solutions.
— WILL LIVESLEY-O’NEILL

We Are Family
Attend any gathering at UCLA Luskin and you may feel like you stumbled into someone’s family reunion.
There will be a toddler or two, chasing a balloon or dancing as a faculty, staff or student parent hovers nearby. You’ll notice plenty of happy young faces — graduate students tend to be in their 20s — but look closer, and you’ll see older folks too. Mid-career professionals returning to add a degree. Staff and faculty, some grayed and others not. Perhaps alumni who earned degrees during the days of typewriters or even pencil and paper, not smartphones.
But family is more than differences in age. It’s continuity. Legacy. Progress over time, as one generation blazes a trail and then passes the torch of knowledge along to another to mark its own, slightly different path. It’s every professor who imparts a tidbit of knowledge only to be surprised, and humbled, when a protégé nurtures that information into something new and wonderful and impactful.
A lifetime of learning walks the Public Affairs Building each day — legends who become mentors, colleagues, even friends. Marty Wachs. Joan Ling. Mark Peterson. Michael Dukakis. Ananya Roy. Gerry Laviña. And so many more. People who have done everything in their careers that students could ever dream of doing themselves and yet still seem to care most about what their students learn now that will improve the world tomorrow.
Family provides inspiration. At Luskin, it’s instructors who know how to say, “You can do better,” in a way that makes students understand that, yes, they really can.
Families help those who need it. It’s every person on the Donor Honor Roll whose name is there not because their wealth exceeds their needs but because money is a way to honor someone who once expanded their worldview. Or lifted their spirits. Or answered a question late one night as a deadline loomed.
After 40 years at UCLA Luskin, Donald Shoup knows all about the Luskin family. In 2017, he won another big award, honoring his contributions as an educator. He put it in perspective: “If we have any influence — if there is going to be anything to remember after we are gone — I think it will be the successful careers of our students who will be changing the world for the better.”
— LES DUNSEITH

 Those students, now Luskin alumni, spent 2016-17 working on a variety of projects related to urgent human needs, such as:
Those students, now Luskin alumni, spent 2016-17 working on a variety of projects related to urgent human needs, such as: