By Stan Paul
For a quarter of a century, prospective Bruins, their parents and other visitors passing UCLA’s Public Affairs Building heard a familiar refrain that was an enduring highlight of any campus guided tour: “Mike Dukakis teaches here.”
Dukakis, now 88, has officially retired from his role as a visiting professor of public policy at UCLA. He is no longer making the annual cross-country trek with his wife, Kitty, from the East Coast to Westwood for each winter quarter. But his years of dedication and service remain a living legacy.
“Michael Dukakis is a foundational figure in the history of the Luskin School — a giant in the history of public policy leadership in the U.S.,” said Dean Gary Segura about the former three-term Massachusetts governor and 1988 Democratic presidential nominee.
“Mike has never stopped working to solve problems at the state and local level in Massachusetts and beyond,” Segura added. “All the while, Mike has been a dedicated teacher and mentor, particularly to our undergraduates. We will miss his sage wisdom and kindness in the halls of UCLA Luskin.”
And every winter quarter for more than two decades, prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, Dukakis could be found in those halls early, specifically in his sixth-floor office, before most people arrived on campus — already at work, his office door open, preparing for class, answering emails, engaging in a phone conversation with media or on behalf of a student, or already chatting with a colleague or student.
Dukakis recalled being surprised when he first came to UCLA that the public affairs school was brand new.
“I kind of assumed that a place like UCLA would be deeply into this stuff, and they obviously weren’t,” he said during a recent interview. “That happily changed and changed dramatically.”
When he first arrived, UCLA was entering into a period of growth and development. “It’s really been remarkable in so many ways, and it was great to be a part of that,” Dukakis said.
“My experience here was very special, no question about it,” he said. “And you know, we’ve made wonderful friendships and great colleagues, and I hear from my former students all the time.”

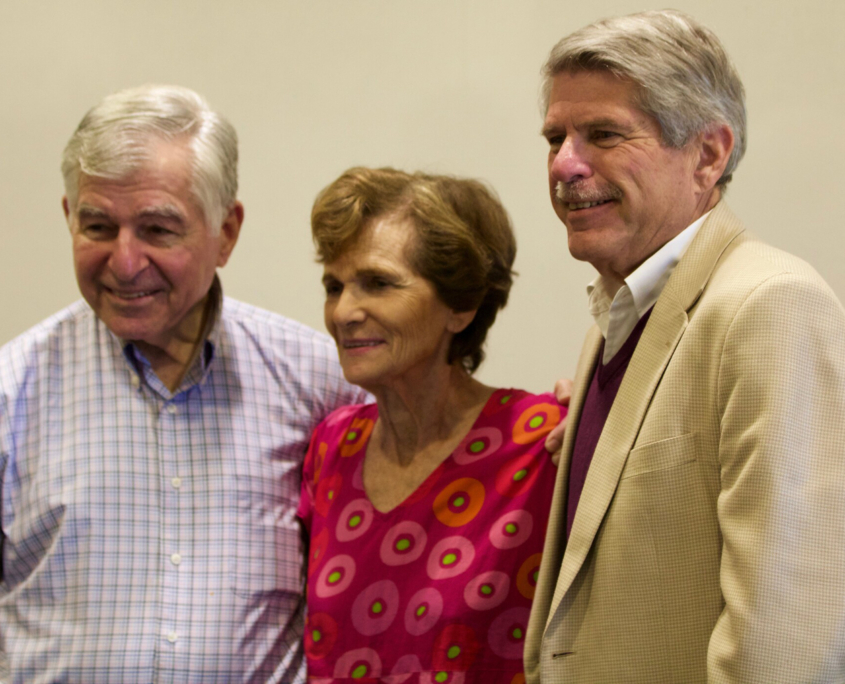
March 2018: UCLA Chancellor Emeritus Albert Carnesale comments during a lunch gathering with Michael and Kitty Dukakis.
“I’ve never seen anybody, any faculty member anywhere, spend more time out of class meeting with students.” —Albert Carnesale, speaking about Dukakis
UCLA Chancellor Emeritus Albert Carnesale has shared office space near Dukakis on the sixth floor of the building since stepping down from UCLA’s top leadership post in 2006.
“I’ve never seen anybody, any faculty member anywhere, spend more time out of class meeting with students.” Carnesale said. “When I came in in the morning, there were always one or more students meeting with him.”
Their longtime friendship and professional relationship go back to the 1970s when Dukakis was governor of Massachusetts and Carnesale was at Harvard.
“My friendship with Mike Dukakis long predates either of us coming to UCLA and then continued when we were at UCLA,” said Carnesale, who was appointed UCLA Chancellor in 1997, the year after Dukakis arrived on campus.
Dukakis’ most-lasting impact on students may have been his ability to show why it is important and satisfying to serve the public good.
“And the best way to do that was — not the only way, but the best way to do that, the most direct way — was through public service,” Carnesale said. “He really does exemplify that.”

March 2018: Michael and Kitty Dukakis pose with Zev Yaroslavsky, their longtime friend and faculty colleague.
“He’s a decent honorable man who never compromised his integrity as as a public official…” —Zev Yaroslavsky
Zev Yaroslavsky, director of the Los Angeles Initiative at UCLA, also has been a sixth-floor hall mate of the former governor. The former five-term Los Angeles County supervisor said he visited Dukakis’ classes on a number of occasions while still in office and then later as a colleague at UCLA.
“He’s a decent honorable man who never compromised his integrity as a public official and he teaches the same way, and I think it’s a loss to us not to have him here,” Yaroslavsky said.
People who know Dukakis are quick to point out his honesty despite his political celebrity and his innate ability to connect with people. He possesses a down-to-earth, unassuming nature. Dukakis’ preferred modes of transportation are public transit and walking, and many staff, faculty and students recall seeing him traverse campus in his iconic khakis and flannel shirt, perhaps stopping to pick up some errant litter and deposit it in a recycling bin before resuming his determined pace.
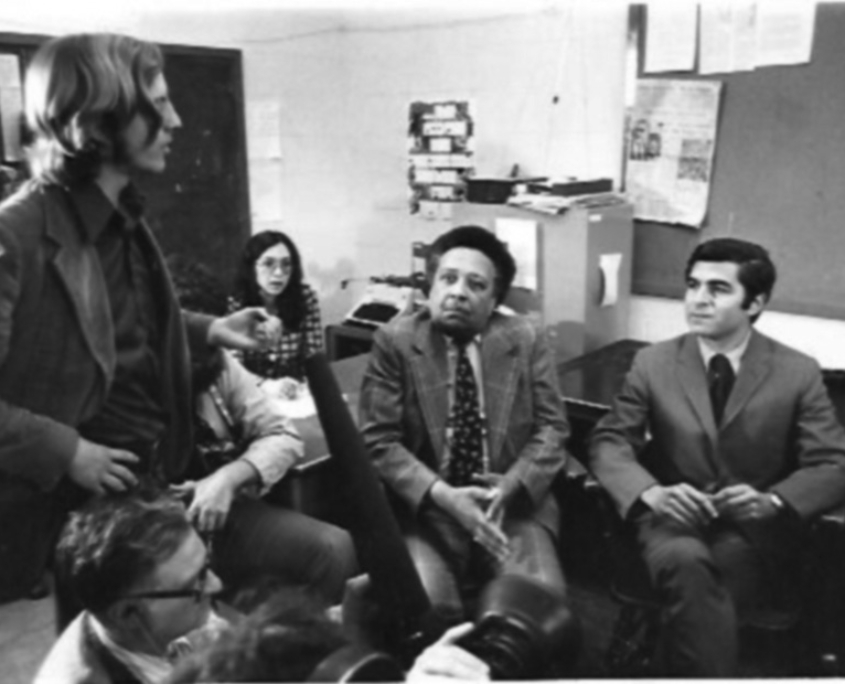

1975: Former UCLA Luskin lecturer and staff member Bill Parent, standing, talks with then-governor Michael Dukakis, right, during a meeting with University of Massachusetts students in Dukakis’ first year as governor. Photo from the UMass Daily Collegian
“I’ve loved the experience. I’ve loved the fact that these kids were interested in getting deeply and actively involved in public affairs.” —Michael Dukakis
Bill Parent, former longtime staff member and lecturer at Luskin, recalled Dukakis’ preference for public transportation. He once offered to drive him downtown to the annual UCLA Luskin Day at City Hall event.
“ ‘Let’s take the bus,’ ” he said, which I thought was insane,” Parent said. “But there we were on the 720, headed for the Red Line, bouncing along in the very back seat.”
Anastasia Loukaitou-Sideris, distinguished professor of urban planning and former chair of Urban Planning, recalls her first encounter with Dukakis.
“The elections were over and he was a huge name and I had never met him personally. I remember going to make a Xerox copy, and I bumped into Mike, who was making his own copies. For me, this was amazing.”
Dukakis also is well-known for his ability to quickly find a common link and bond with anyone after asking just a few questions. Loukaitou-Sideris said their initial conversation quickly turned into a discussion of their common Greek origins followed by an invitation for the Dukakises to join her family and friends for dinner.
“His answer was immediately ‘yes,’” said Loukaitou-Sideris, adding, “the guests of honor” were the first to arrive. “There’s Mike and Kitty holding a bread that Mike had baked.” Loukaitou-Sideris describes him as the “most accessible person on Earth.”
“You know, the fame and what he has done— amazing things as governor — never went into his head. He connects to people and to anyone,” she said including undergraduate students clamoring to take his class because he has a unique ability to connect some of the larger theoretical ideas to things in practice.
“His contribution to a public policy school all these years has been immense because students wanted to come to study policy because Mike Dukakis was there.”
When not at UCLA, he also taught at Northeastern University, not far from his home in Brookline, Mass., for many years.
“People came often because of his reputation, but he was much more than that,” Loukaitou-Sideris said. “He is a person always trying to find ways to help. And he had a tremendous amount of contacts. And if he knew that you were trying to do something, he would always find the right person to connect you to as well.”
Students definitely made connections and launched careers, recalled Michael Stoll, professor of public policy and urban planning and also a former chair of UCLA Luskin Public Policy.
“The generosity of his support for students included writing more letters of recommendation and securing more internships for students than anyone could ever imagine.”
In addition, Dukakis spearheaded an internship program to provide UCLA Luskin master’s students with first-hand public service experience in government with a specific focus on California.
Michael Fleming, a longtime lecturer in Social Welfare at Luskin and executive director of the Los Angeles-based David Bohnett Foundation, recalls that Dukakis also was instrumental in making a direct connection for UCLA Luskin students to Los Angeles City Hall and the mayor’s office.
At a meeting at Bohnett’s home in the early 2000s that included Fleming, then-Dean Barbara Nelson and others, the idea for connecting UCLA Luskin students with Los Angeles City Hall and the mayor’s office was conceived. Dukakis astutely sized up the opportunity to bring students, and backing, together to address a need, Fleming said.
The David Bohnett Fellowship program was launched in 2007 as a hands-on working experience in the mayor’s office for exceptionally promising UCLA Luskin public policy, social welfare and urban planning graduate students.
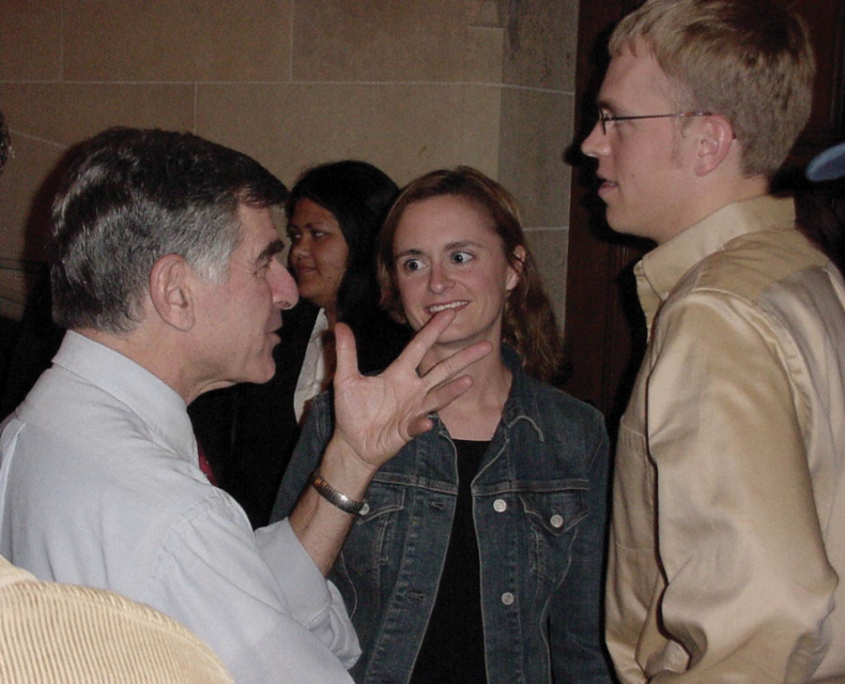

April 2003: Michael Dukakis was a visiting professor at UCLA Luskin for over two decades.
“He was full of stories about his experiences and lessons learned and was never shy about sharing his wisdom.” —Nelson Esparza MPP ’15
Numerous former students were inspired by Dukakis to pursue public service or seek public office — from local city boards to state elected posts to the U.S. Congress. Among those alumni are Nanette Barragán ’00, who represents the 44th Congressional district in South Los Angeles, and Jimmy Gomez ’99, who represents the 34th Congressional district in Los Angeles.
Another former Dukakis student is Nelson Esparza MPP ’15, who has won elections to the Fresno County School Board and the Fresno City Council in his hometown.
“By the time I was in the MPP program, I was strongly considering returning home to represent my local community,” the former Dukakis internship fellow recalled. “Naturally, the governor and I engaged in many conversations about the practical side of leadership, policymaking and the sacred responsibility of representing a community at any level of government.”
Esparza continued: “He was full of stories about his experiences and lessons learned and was never shy about sharing his wisdom.”
Dukakis sometimes recited the names of elected officials who passed through his classroom over the years. “I’ve always thought it was kind of cool to have joined that group,” Esparza said. “In some ways, you might say that I learned more from the governor outside of the classroom.”
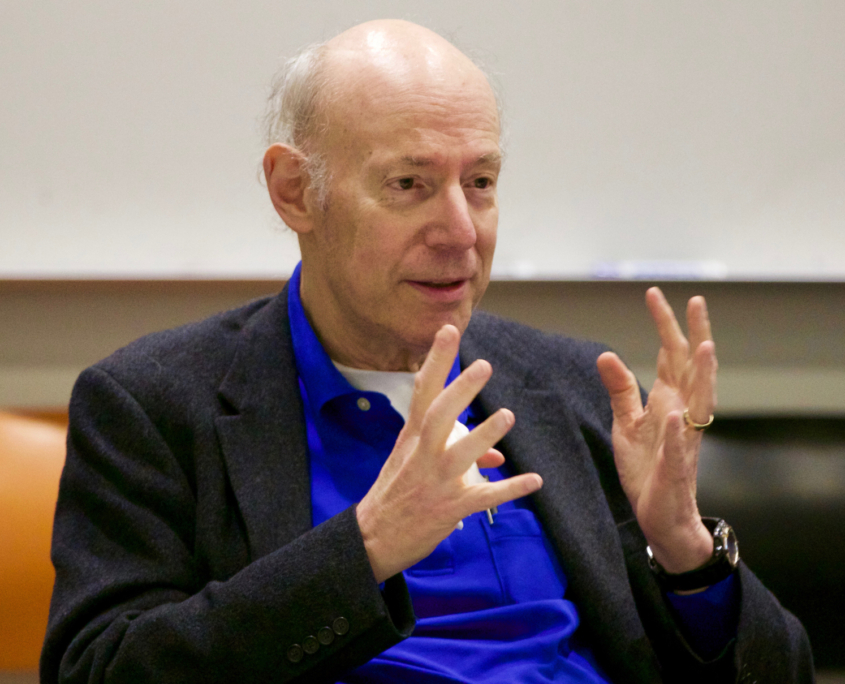

March 2018: Professor Emeritus Dan Mitchell co-taught a course at UCLA Luskin with Michael Dukakis for many years.
“As a professor, Mike was one of the most conscientious instructors our undergraduates were likely to encounter.” —Dan Mitchell
Co-teaching with Dukakis during his entire tenure at UCLA in the often-filled-to-capacity undergraduate course California Policy Issues was Dan Mitchell, emeritus professor of public policy and management.
“As a professor, Mike was one of the most conscientious instructors our undergraduates were likely to encounter. All student work was read and evaluated by the instructors, not the TA. Even in a large class, there were always separate meetings with small groups of students.”
Mitchell said Dukakis was a tough evaluator. “At the end of the day, either the final product met the standard, or it didn’t,” he said. Each year, Dukakis delivered a short lecture that came to be known as the excellent writer statement, emphasizing the need to develop that ability.
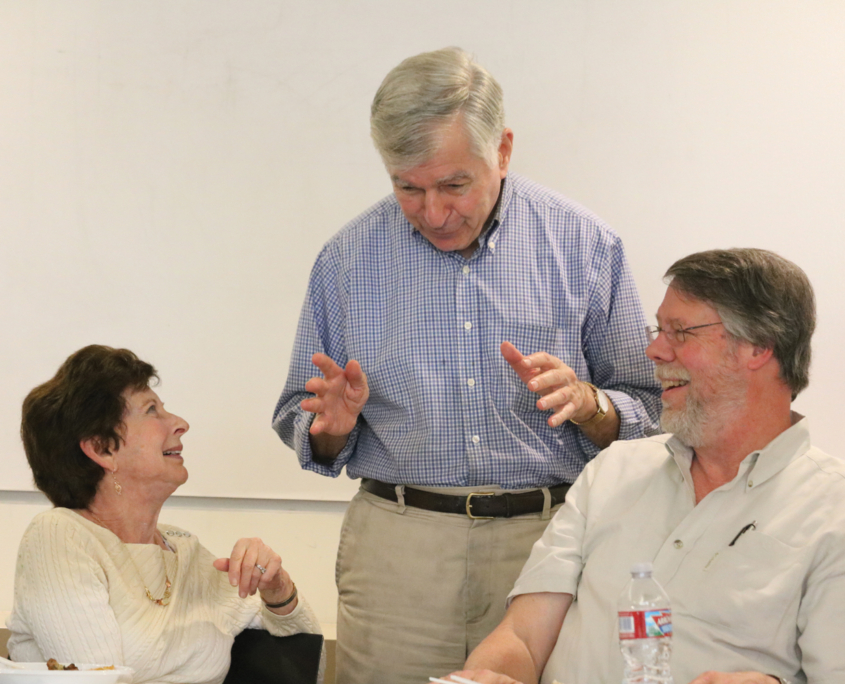

March 2017: Renee Luskin and Mark Peterson enjoy a laugh with Michael Dukakis
“He wasn’t just any experienced government official. We hit the jackpot.” —Mark Peterson
Longtime Luskin faculty and staff mirrored those comments.
“Mike, there from close to the beginning of the School, for many years was the only actual practitioner — real policymaker — on the faculty of a program whose mission is to train policymaking professionals,” said UCLA Professor of Public Policy, Political Science and Law Mark Peterson. “But he wasn’t just any experienced government official. We hit the jackpot,” said the former chair of UCLA Luskin Public Policy.
“Moreover, he dove into his teaching full bore, excelled at it, and added significantly to the curricula of both the MPP graduate program and the then-undergraduate minor, now a major at UCLA.”
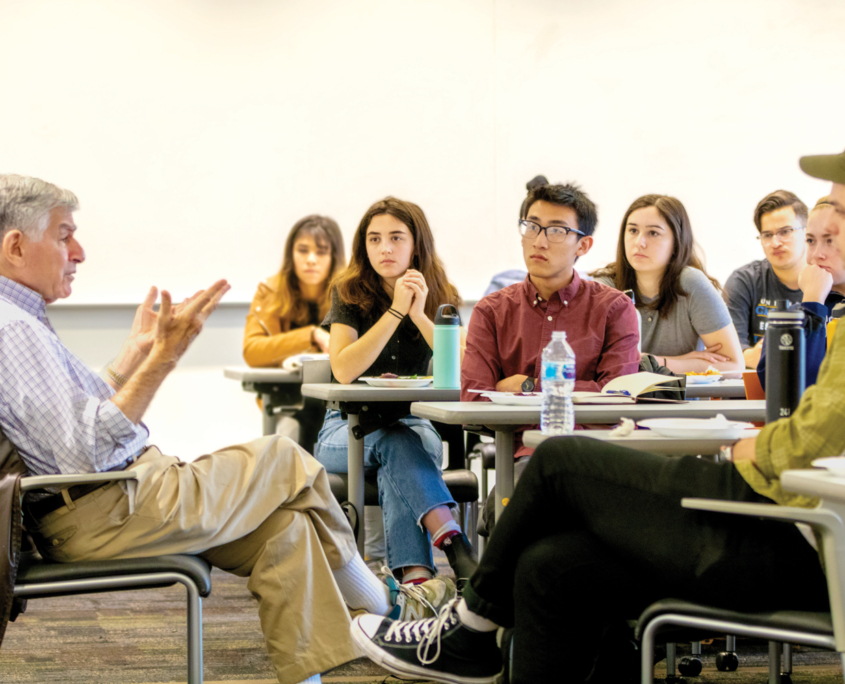

January 2019: Visiting Professor Michael Dukakis speaks with a group of undergraduate students at UCLA.
“When we invited him to speak to the first students of the new public affairs B.A. in 2019, he told all of them to run for office or get involved in politics — it was a call to action.” —Jocelyn Guihama
Jocelyn Guihama, a 2003 MPP graduate and former student of Dukakis, agrees. She now serves as director of administration and experiential learning for the School’s public affairs major.
“Prof. Dukakis’ tireless advocacy for public service has inspired generations of Luskin students, Guihama said. “When I was an MPP student in the early days of the program, I told him that I was planning to work in the nonprofit sector, and he immediately told me that I needed to channel that energy into the public sector.
“That message hasn’t changed,” she said.
“When we invited him to speak to the first students of the new public affairs B.A. in 2019, he told all of them to run for office or get involved in politics — it was a call to action.”
Guihama said that Dukakis’ former students in the major are already getting involved and connecting with elected officials.
Longtime UCLA Luskin faculty colleague Fernando Torres-Gil said Dukakis has exemplified life after politics, building a memorable post-politician career as an educator.
Torres-Gil, professor of social welfare and public policy, is also director of the Center for Policy Research on Aging. He said he knew Dukakis from his time serving as his deputy issues director in the 1988 campaign.
“I saw first-hand his deep integrity and commitment to public service and a focus on doing so honorably, a term rarely seen among most political players,” Torres-Gil said. “It was such a thrill to know that he and I would be at UCLA and the Luskin School and to maintain our friendship and continued participation in civic life.
“Professor Dukakis, by all measures, has been a master teacher and one of the most popular and effective instructors,” Torres-Gil said.
He noted that Dukakis also represented UCLA to donors and stakeholders, connecting the Luskin School with the wider policy and political arenas.
“We will miss Professor Dukakis greatly, but he has set the gold standard for professional practice faculty and for honorable contributions after public service.”
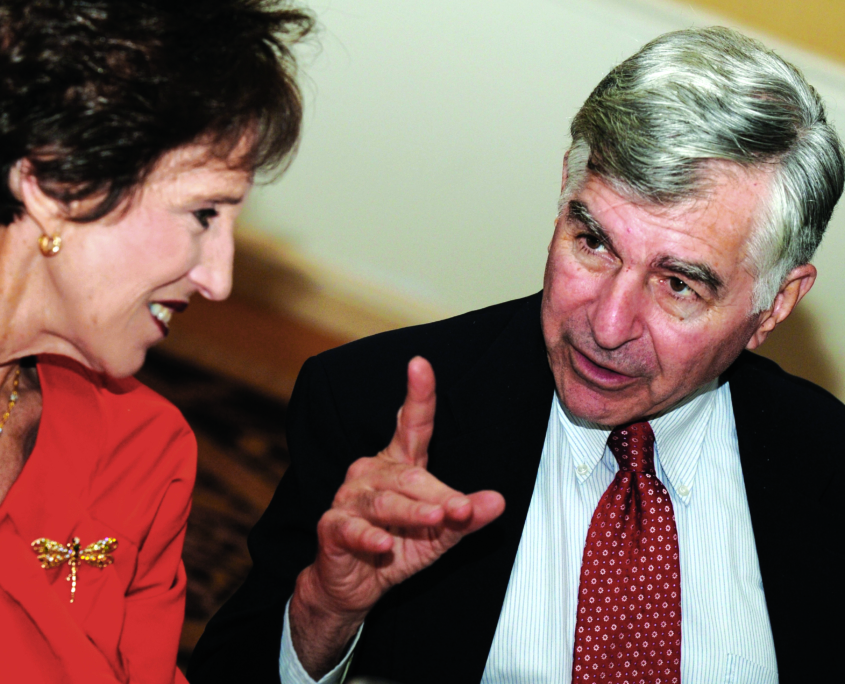

March 2010: Michael Dukakis often spoke with community groups and UCLA supporters during his time on campus.
“We will miss Professor Dukakis greatly, but he has set the gold standard for professional practice faculty and for honorable contributions after public service.” —Fernando Torres-Gil
Outside of teaching, Dukakis was often a speaker at events in Southern California during the winter quarter. Some events were linked to UCLA and others not, Mitchell said, adding that he preferred not to say “no” when an invitation occurred, even the times and places were less than convenient.
Kitty Dukakis also traveled each year to Westwood, and she was involved and active in speaking engagements with the former governor, who said she “was no passive spectator … wouldn’t have been any other way.”
“And because of her interest in mental health and related kinds of things, she had an opportunity to do some good things herself,” Dukakis said.
Public Policy lecturer Jim Newton, an award-winning journalist and former editor of the editorial page of the LA Times, also shared the sixth floor of the Public Affairs Building with Dukakis for the past several years. Newton knows a bit about governors, having written historical books on two of them — Jerry Brown and Earl Warren.
“It’s sort of my stock in trade,” said Newton, now editor of UCLA Blueprint magazine, which has included profiles and interviews with Dukakis.
“I know we had a number of conversations about UCLA and its engagement in the community, and so my interest and the governor’s overlapped in a lot of ways,” which included a common interest in government and politics, Newton said.
“One of the things that has impressed me throughout my acquaintance or friendship with the governor is how available he is and how much of an integrated part of the overall UCLA community here. There’s nothing aloof or unapproachable about him,” Newton said.
“I’ve spent my life with people in politics. There’s a lot of people I admire as a result of that. I got to know and admire and have respect for a lot of them who are not super-nice people. They’re ambitious, and they’re smart, and they’re interesting,” Newton said. But they sometimes can be “kind of difficult or prickly.”
“[Dukakis] is not that person. Not here, he is the opposite of that. Just as warm and as modest, and as humble and approachable as a person can be,” Newton said.
“So, I have a world of respect for him. Both in terms of his achievement, but also just in terms of the way he holds himself out and makes himself available and helps people to learn and understand.”
March 2015: Friends and family were on hand when UCLA Luskin celebrated the Michael S. Dukakis Internship program and his 20 years of teaching at UCLA.
“You know, the fame and what he has done— amazing things as governor — never went into his head. He connects to people and to anyone.” —Anastasia Loukaitou-Sideris
Dukakis finished his 25th and final winter quarter at UCLA Luskin in 2020 by, what else, grading papers. His return home to Massachusetts was then delayed a few weeks by a bout of pneumonia, and his travel options then and now have been impacted by COVID-19 restrictions.
When asked what his impact has been, he responded in his typical way, humble and redirecting toward students: “I’m hoping it’s positive. I’ve loved the experience. I’ve loved the fact that these kids were interested in getting deeply and actively involved in public affairs.”
Dukakis said he can’t count how many students he convinced to take advantage of UCLA’s program in Washington, D.C., which he said could lead to internships at the municipal level, the state level and other career opportunities.
Any regrets about relocating from coast to coast every year for more than two decades?
“No, never regretted it for a minute. It’s really been remarkable in so many ways, and it was great to be a part of that.” He elaborated, “I’ve worked both with a great faculty and with a wonderful group of students, so you know, for me and for us — for Kitty and I — it was a great experience and I’m sorry it had to end.
“There’s nothing more satisfying than being in a position where you can introduce and convince young people to go into the public sector, surely, and then to see them thrive,” he said, reflecting on his decades-long experience at UCLA. “Luskin is doing it all the time.”