By Stan Paul
Newly graduated Social Welfare master’s degree recipient Deshika Perera’s research project extended across the United States and as far north as Alaska.
Evan Kreuger helped create a nationwide database as a basis for his research into LGBT health and health outcomes to culminate his Master of Social Welfare (MSW) studies at the UCLA Luskin School of Public Affairs.
Perera and Kreuger are members of the first graduating class of Social Welfare students to complete a capstone research project as a graduation requirement for their MSW degrees. Like their UCLA Luskin counterparts in Urban Planning and Public Policy who must also complete capstones, working individually and in groups to complete research and analysis projects that hone their skills while studying important social issues on behalf of government agencies, nonprofit groups and other clients with a public service focus.
“It’s been fun; it’s been interesting,” said Perera, who worked with Associate Professor Ian Holloway. Her qualitative study examined the relationship between the Violence Against Women Act and nonprofits, focusing on programs that provide services to indigenous survivors of sexual assault and domestic violence on reservations and in remote areas of the U.S.
As a member of the pioneering class for the MSW capstone, Perera said that although the new requirement was rigorous, she enjoyed the flexibility of the program.
“I feel we got to express our own creativity and had more freedom because it was loosely structured,” Perera said, explaining that she and her fellow students got to provide input on their projects and the capstone process. The development of the requirement went both ways. “Because it was new, [faculty] were asking us a lot of questions,” Perera said.
“We strongly believe that this capstone experience combines a lot of the pieces of learning that they’ve been doing, so it really integrates their knowledge of theory, their knowledge of research methods and their knowledge of practice,” said Laura Wray-Lake, associate professor and MSW capstone coordinator. “I think it’s really fun to see research come alive and be infused with real world practice.”
Krueger, who also was completing a Ph.D. in public health at UCLA while concluding his MSW studies, previously worked as a research coordinator for a national survey on LGBT adults through the UCLA School of Law’s Williams Institute. He said he had a substantial amount of data to work with and that he enjoyed the opportunity to combine his research interests.
“I’m really interested in how the social environment influences these public health questions I’m looking at,” said Kreuger who has studied HIV and HIV prevention. “I kind of knew what I wanted to do, but it was a matter of pulling it all together.”
For years, MSW students have completed rigorous coursework and challenging educational field placements during their two-year program of study, and some previous MSW graduates had conducted research in connection with sponsoring agencies. This year’s class included the first MSW recipients to complete a new two-year research sequence, Wray-Lake said.
◊
View more photos from Public Policy’s APP presentations.
Applied Policy Projects
In UCLA Luskin Public Policy, 14 teams presented a year’s worth of exacting research during this year’s Applied Policy Project presentations, the capstone for those seeking a Master of Public Policy (MPP) degree.
Public Policy students master the tools to conduct policy analysis during their first year of study. In the second year, they use those tools to create sophisticated policy analyses to benefit government entities and other clients.
The APP research is presented to faculty, peers and curious first-year students over the course of two days. This May’s presentations reflected a broad spectrum of interests.
Like some peers in Social Welfare, a few MPP teams tackled faraway issues, including a study of environmental protection and sustainable tourism in the South Pacific. Closer to home, student researchers counted people experiencing homelessness, looked at ways to reform the juvenile justice system, sought solutions to food insecurity and outlined ideas to protect reproductive health, among other topics.
“Our students are providing solutions to some of the most important local and global problems out there,” said Professor JR DeShazo, chair of UCLA Luskin Public Policy.
After each presentation, faculty members and others in the audience followed up with questions about data sources, methodologies and explanations for the policy recommendations.
◊
View more photos from Urban Planning’s capstone presentations.
Careers, Capstones and Conversations
Recently graduated UCLA Luskin urban planners displayed their culminating projects in April at the annual Careers, Capstones and Conversations networking event, following up with final written reports for sponsoring clients.
Many planning students work individually, but a cohort of 16 Master of Urban and Regional Planning (MURP) students worked together to complete a comprehensive research project related to a $23 million grant recently received by the San Fernando Valley community of Pacoima. The project was the culmination of almost six months of analysis in which the MURP students helped the nonprofit Pacoima Beautiful, other community partners and government agencies prepare a plan seeking to avoid displacement of residents as a result of a pending major redevelopment effort.
“I think our project creates a really amazing starting point for further research, and it provided concrete recommendations for the organizations to think about,” said Jessica Bremner, a doctoral student in urban planning who served as a teaching assistant for the class that conducted the research. Professor Vinit Mukhija, chair of UCLA Luskin Urban Planning, was the course instructor.
◊
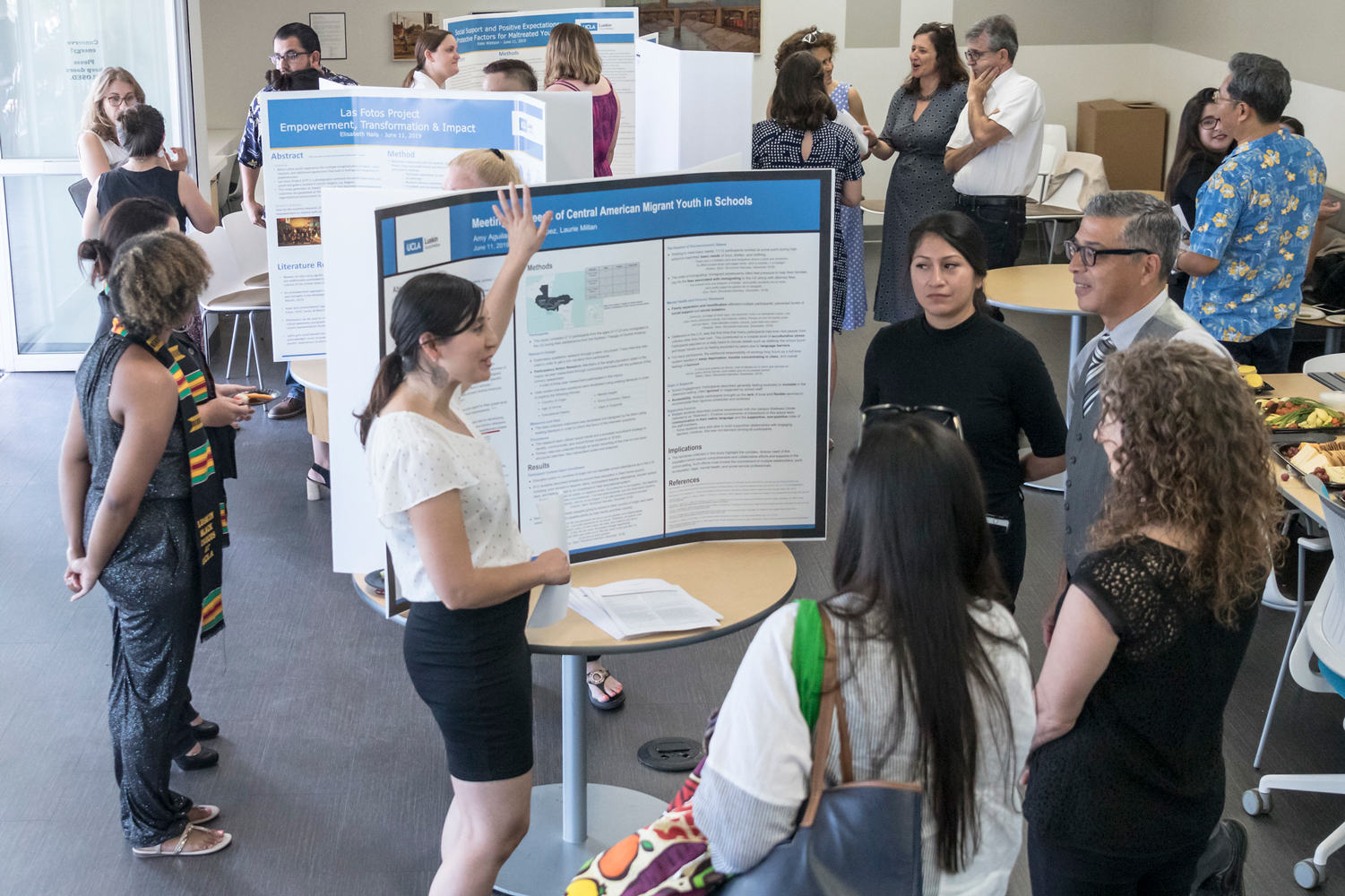
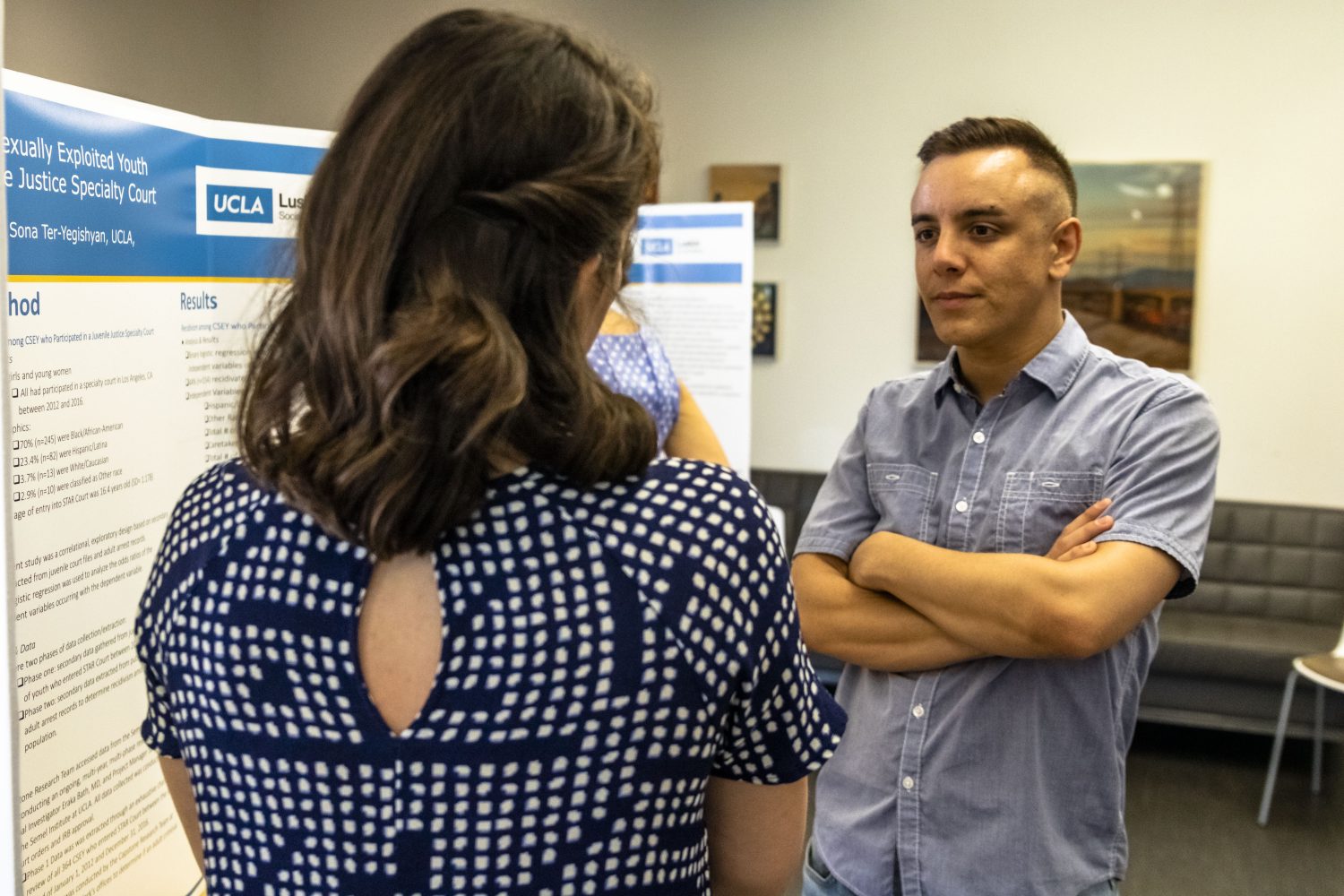
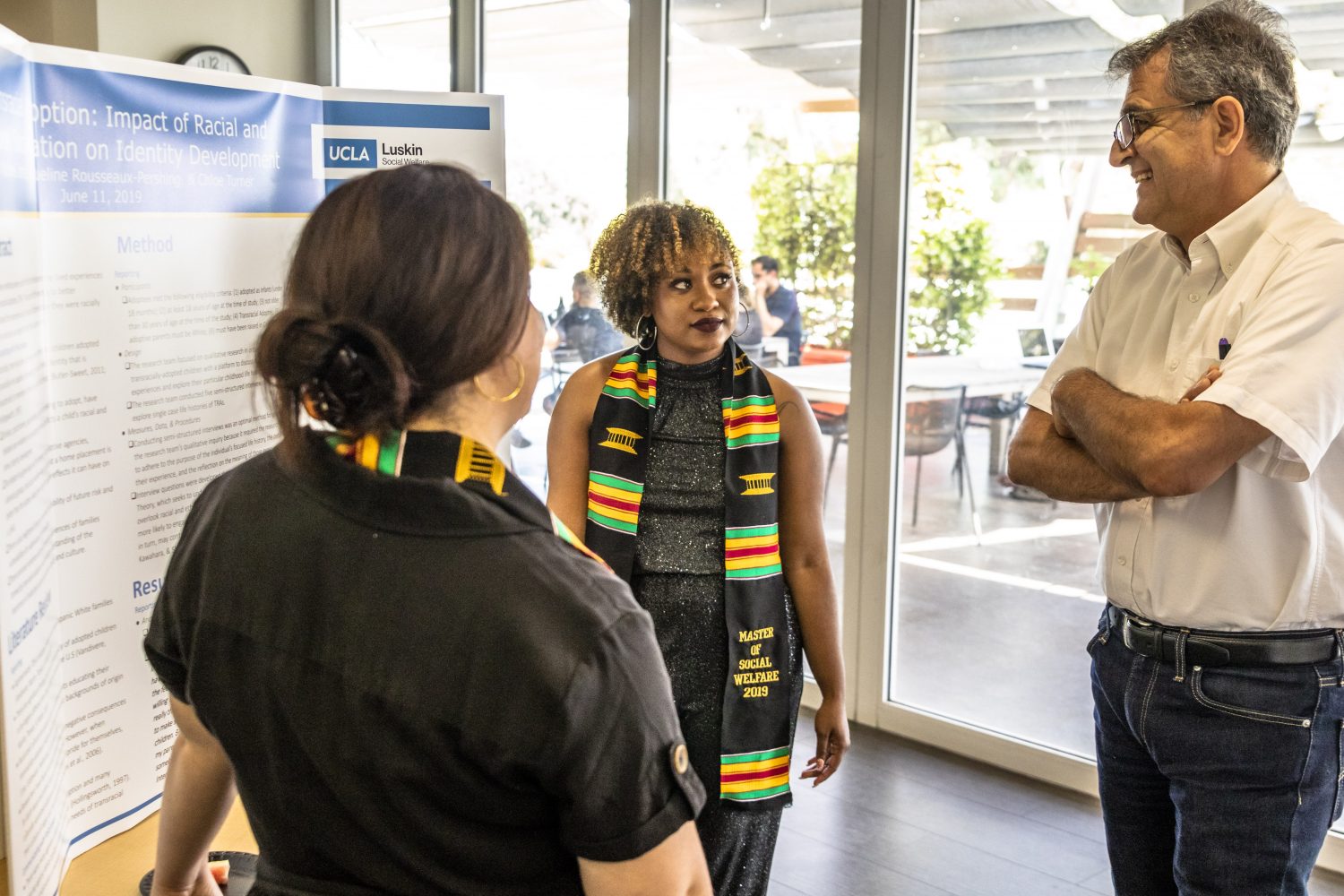
View more photos from Social Welfare’s capstone presentations.
MSWs Test Research Methods
In Social Welfare, the projects represented a variety of interests and subject matter, said Wray-Lake, pointing out that each student’s approach — quantitative and/or qualitative — helps distinguish individual areas of inquiry. Some students used existing data sets to analyze social problems, she said, whereas others gathered their own data through personal interviews and focus groups. Instructors provided mentoring and training during the research process.
“They each have their own challenges,” said Wray-Lake, noting that several capstones were completed in partnership with a community agency, which often lack the staff or funding for research.
“Agencies are very hungry for research,” she said. “They collect lot of data and they have a lot of research needs, so this is a place where our students can be really useful and have real community impact with the capstones.”
Professor of Social Welfare Todd Franke, who serves as a lead instructor for the capstone projects, said his students worked on issues that impact child welfare. Others studied the relationship between child neglect and involvement with the juvenile justice system. Another capstone focused on predictors of educational aspirations among black and Native American students. The well-being of caregivers and social workers served as another study topic.
Assistant Professor Amy Ritterbusch, who also served as a capstone instructor, said her students focused on topics that included education beyond incarceration, the needs of Central American migrant youth in schools, and the unmet needs of homeless individuals in MacArthur Park. One project was cleverly titled as “I’m Still Here and I Can Go On: Coping Practices of Immigrant Domestic Workers.”
“They all did exceptional work,” Ritterbusch said.