By Mary Braswell
Nithya Raman was elected to the Los Angeles City Council on a platform focused on tackling the region’s dual crises of homelessness and sky-high housing costs. Sixteen months after taking office, she came to UCLA to provide an update on how the fight is going.
Citing lessons learned from the COVID-19 pandemic, Raman said the key to sheltering unhoused Angelenos is a culture of saying yes to creative living solutions of all types, as long as they offer dignity and privacy — not just a bed in a crowded facility.
“That could be motel or hotel rooms, that could be tiny homes, that could be shared apartments where you have a separate bedroom and a shared kitchen — any place where you have a room with a door,” Raman said. “When you offer someone who is experiencing homelessness the ability to go to a room with a door, the experience is really transformative.”
The successes and shortcomings of pandemic-era housing interventions was one topic in a wide-ranging talk by Raman, who came to UCLA’s Kerckhoff Hall on April 14 as part of the University of California Regents’ Lecturer program.
In a conversation moderated by UCLA Luskin Urban Planning chair Chris Tilly, Raman spoke about Los Angeles’ complicated history of land use, which led to the city’s current struggle to provide its residents with safe and affordable housing.
And as an urban planner by training, she stressed the importance of reliable data — including the results of a countywide homeless count, due to be finalized this summer — to gauge the impact of programs and investments and map a path forward.
“What I’m seeing is something really different from what I saw when I was out of City Hall, which is a moment when people are actually getting indoors,” said Raman, who represents L.A.’s District 4, stretching from Los Feliz to Reseda.
“But we don’t have the data to show, did they actually move in enough numbers so that we chipped away at this massive amount of homelessness that we faced in our district? Or did we not do enough during this period of the pandemic?
“I really want to make sure that we’re moving forward with that data in hand and with a sense of real possibility for the city of L.A.”
Raman’s lecture was part of UCLA Luskin Urban Planning’s commemoration of its 50-year anniversary. Her audience included several UCLA Luskin alumni, plus undergraduate and graduate students who may aspire to careers in public service.
Ensuring that Los Angeles’ housing stock continues to grow to meet demand requires saying yes to many approaches all at once, she said.
Cities or nonprofits could lease entire buildings and rent each apartment to voucher holders. Lifting the requirement to include parking in a new development could lead to the construction of smaller, less expensive living spaces attractive to transit riders such as students and young professionals. And developers should be pressed to include more affordable units in high-end properties, she said.
“One of the ways in which we’ve increased affordable housing is actually by creating density bonus programs for market-rate development,” Raman said. “And yet, I hear you. It is galling to see homelessness on our streets and luxury apartments going up, right next to each other.”
Repeating a phrase used throughout the lecture, Raman said the city should push harder. Push to require more of developers who receive lucrative incentives. Push to streamline a permitting process that has put a drag on the construction of housing. And push to ensure that residents aren’t priced out of their own neighborhoods.
“You can build more while still being totally dedicated to protecting tenants who are currently in their housing. And we can do that if we try,” she said.
Raman, the first challenger in 17 years to unseat an incumbent L.A. City Council member, described her experiences working as an outsider to effect change from within the halls of government.
“It’s the daily struggle,” she said. “How do you operate within a system — many aspects of which you find fundamentally unjust — while still moving that system towards change?”
She spoke of choosing her battles, sometimes speaking out forcefully but other times opting for quiet diplomacy to push her top legislative priorities.
“The more people who come in that share a set of values around what L.A. can be and should look like, I think the less you’ll have to make those kinds of choices.”
With their overwhelming support for taxes and bond measures to pay for the fight against homelessness, the people of Los Angeles have proclaimed a “widespread sentiment of ‘yes,’ ” she said.
“We all actually want it. I feel like that’s what every single conversation I have with people shows,” Raman said. “We can build it, we can build it right. We can do this, we can do it right. We can treat people with dignity and help them to get indoors.
“Everyone says, ‘Hell, yes, that’s what I want.’ ”
View photos and video of the lecture.
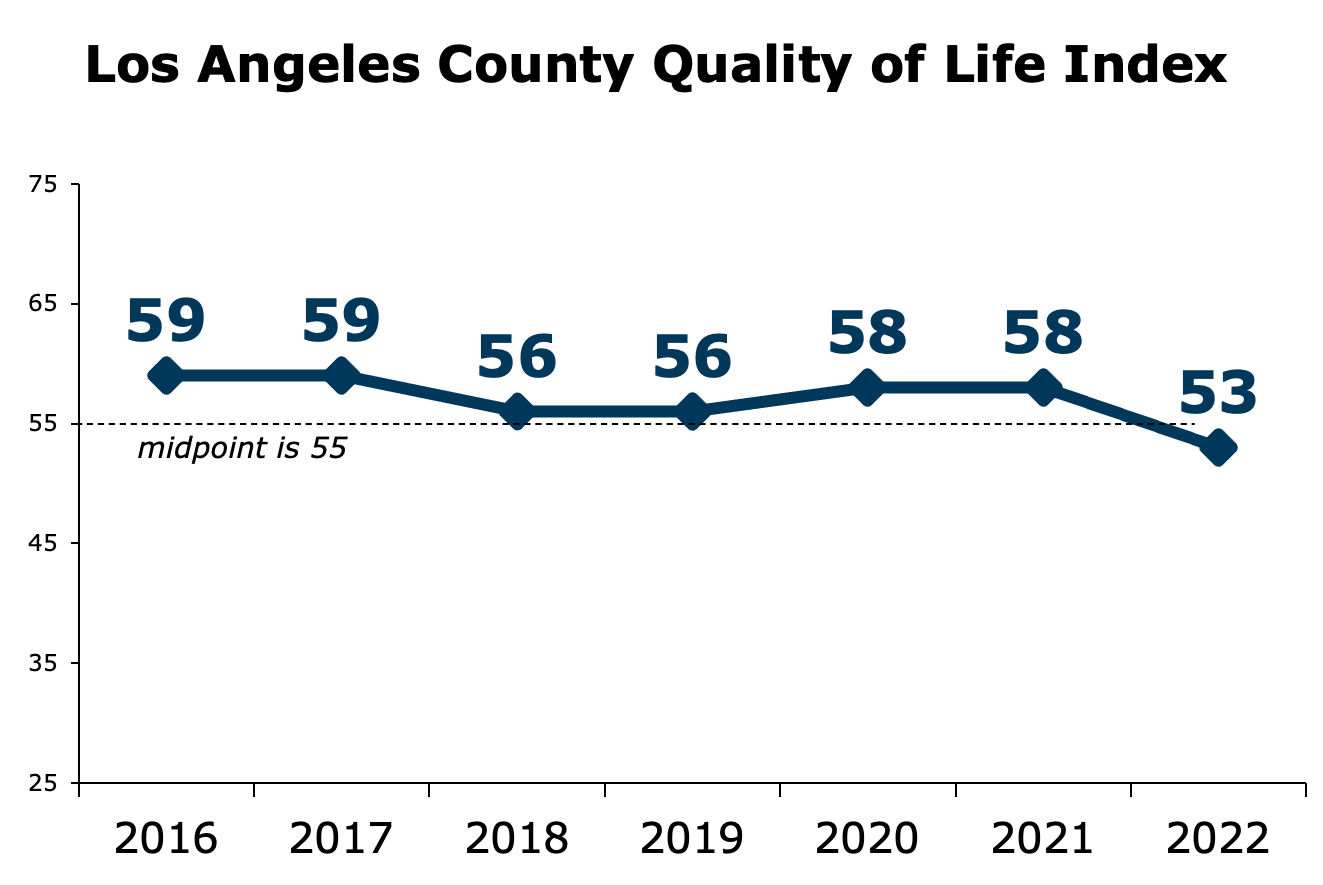
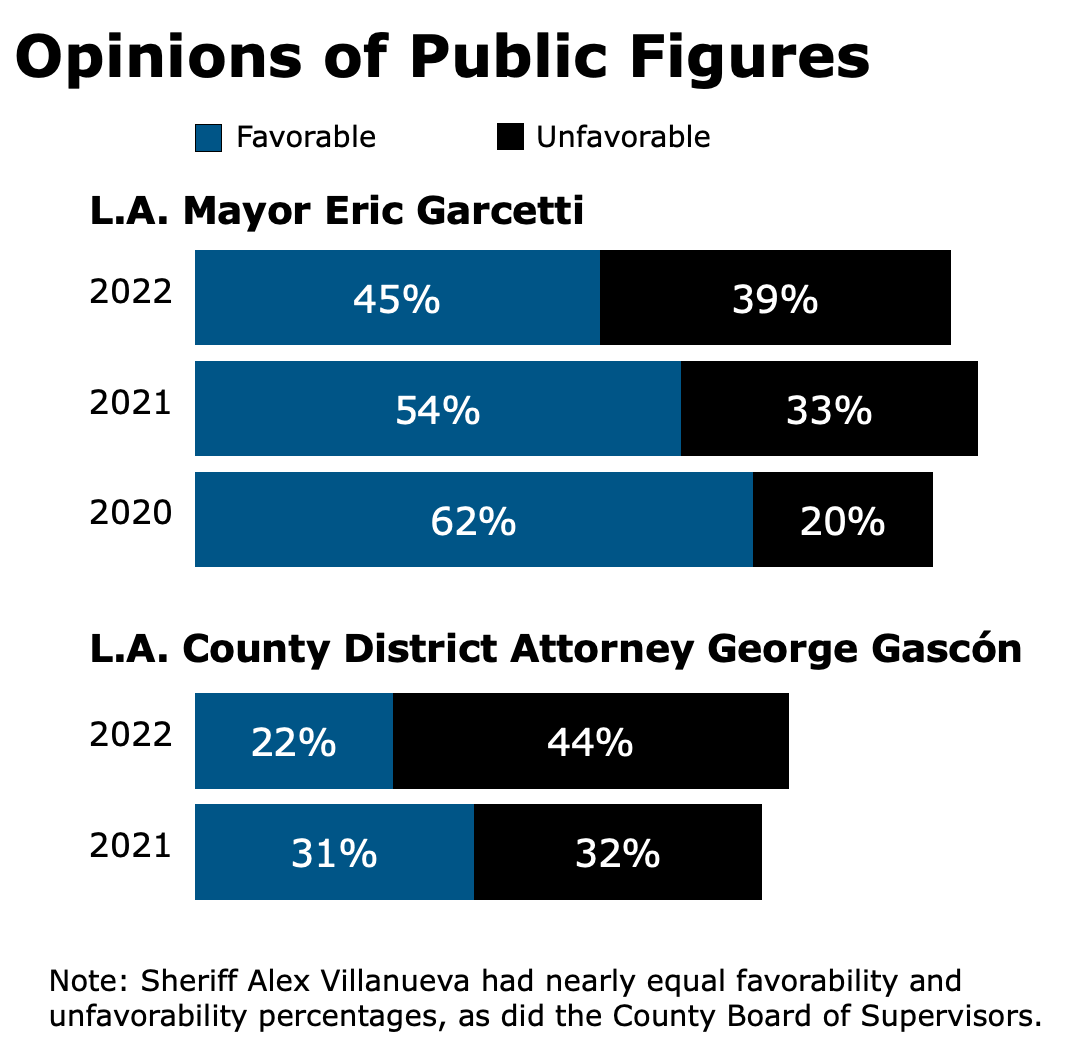
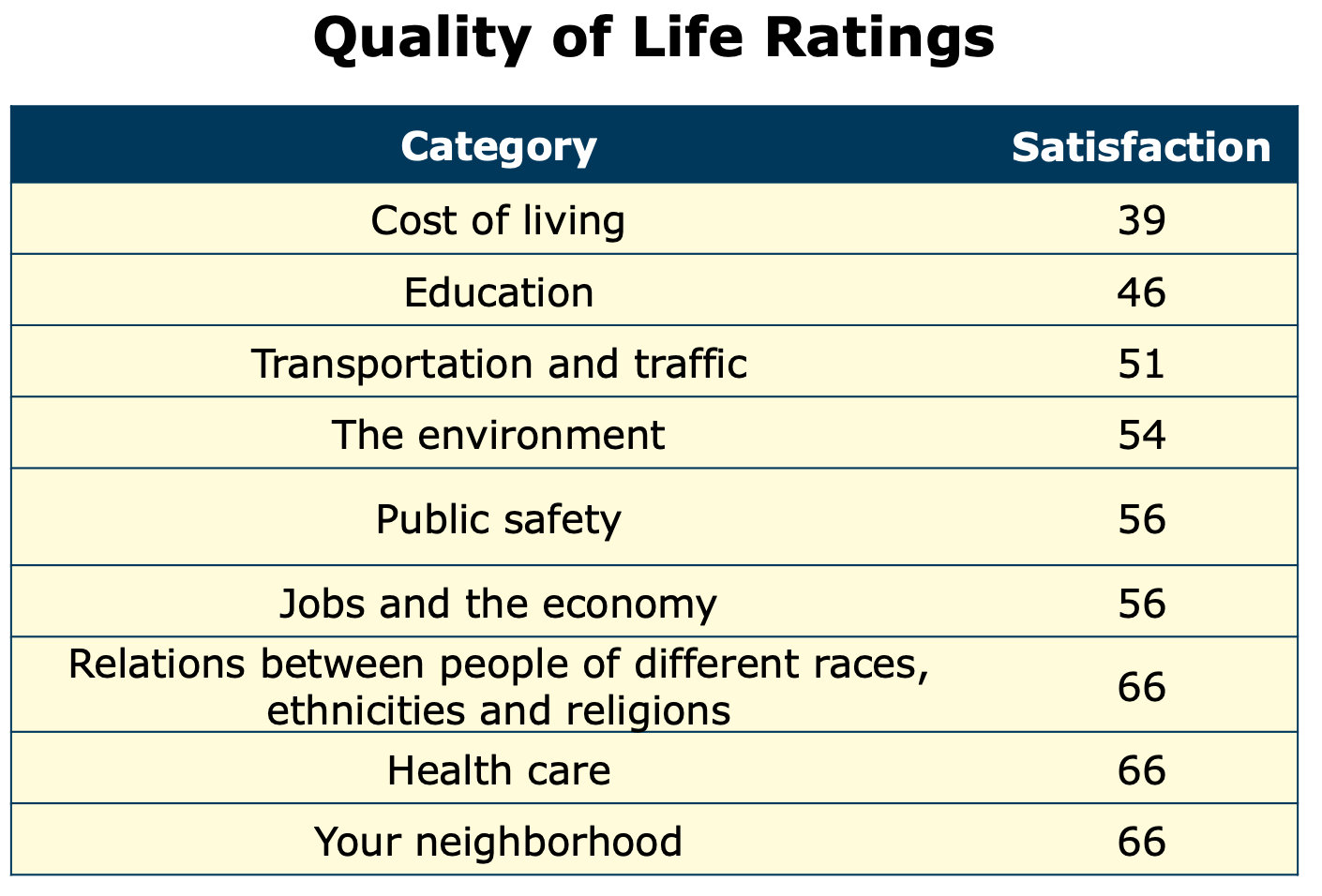 Scores declined in all nine of the survey categories, but the issues that were most responsible for the overall decline were cost of living, education and public safety.
Scores declined in all nine of the survey categories, but the issues that were most responsible for the overall decline were cost of living, education and public safety.











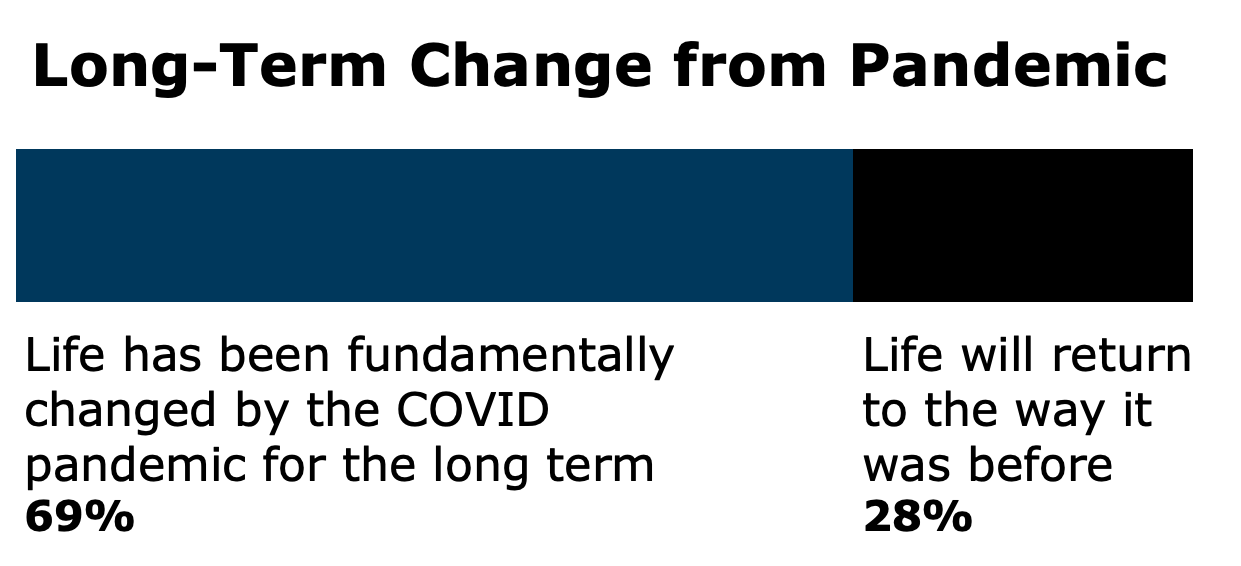 Most respondents, 69%, said life has been fundamentally changed by the COVID-19 pandemic. Only 28% said that life would return to the way it was before.
Most respondents, 69%, said life has been fundamentally changed by the COVID-19 pandemic. Only 28% said that life would return to the way it was before.