By Les Dunseith
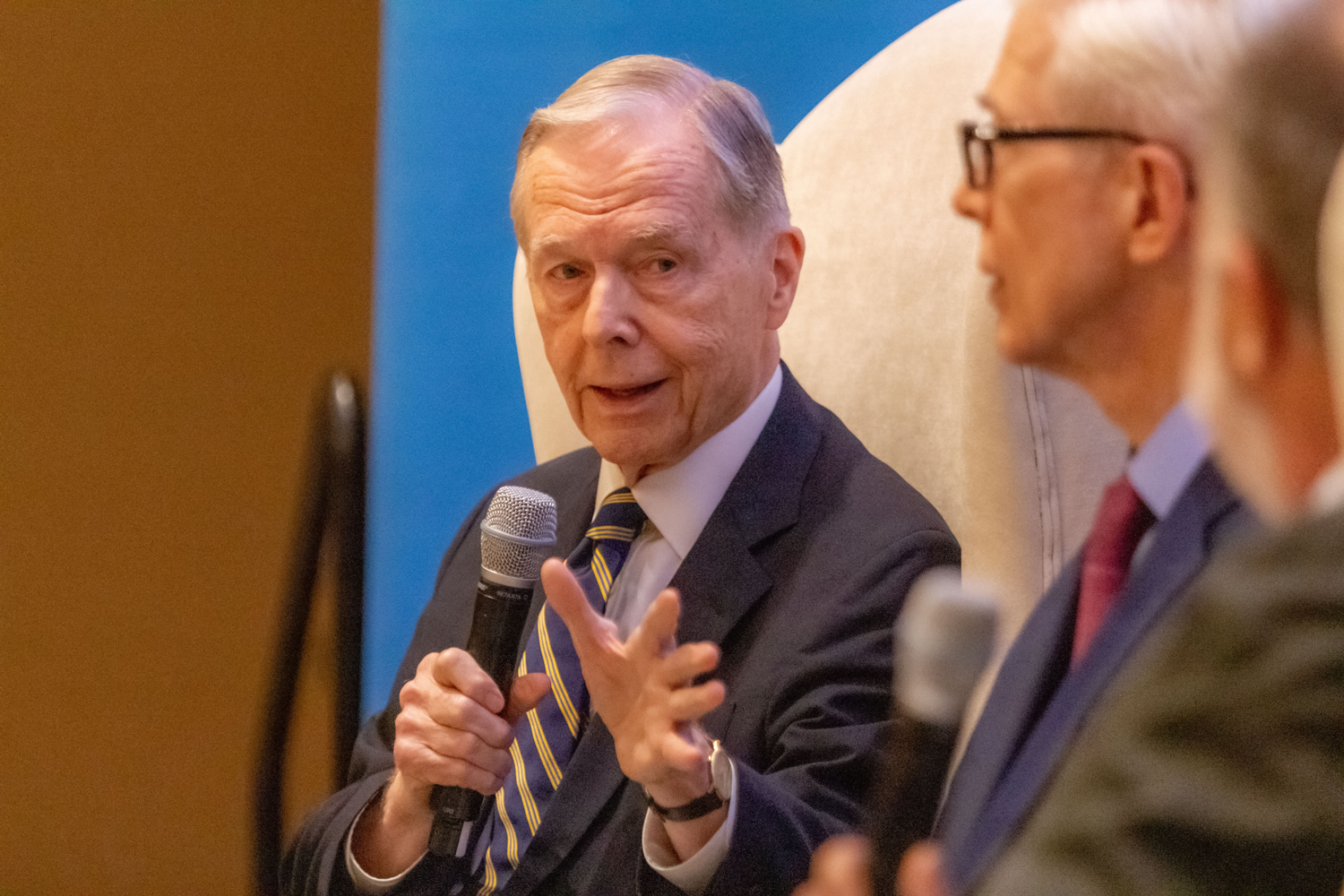
Former California governors Pete Wilson and Gray Davis headlined the closing session of Luskin Summit 2022: Research in Action on April 22, often tackling political issues from starkly different perspectives.
In a session moderated by UCLA Blueprint Editor-in-Chief Jim Newton and titled “The State of California,” the former governors explored topics such as the economy and inflation, housing, environmental issues and rising crime during a discussion that mostly reflected a tone of respectful disagreement.
The governors spoke during a half-day event at the Luskin Conference Center at UCLA to close out this year’s Luskin Summit, which is a series of research-informed, cross-sector explorations of the major issues facing Los Angeles and California. The day’s agenda also included the unveiling of the annual Quality of Life Index led by Zev Yaroslavsky, a well-known former elected official in Los Angeles who, like Newton, is now a faculty member associated with the UCLA Luskin School of Public Affairs.
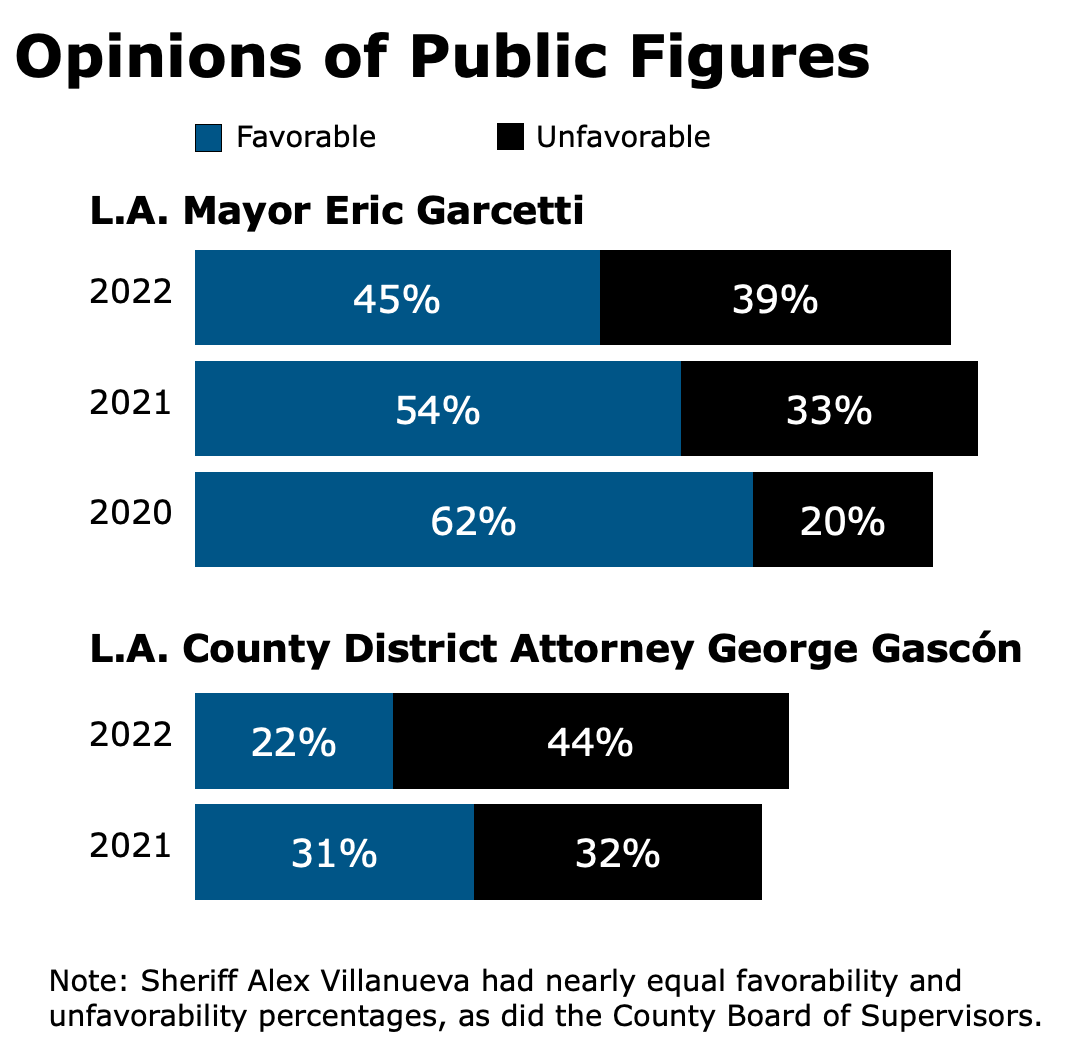
Yaroslavsky’s session, which was moderated by news anchor Phillip Palmer of ABC7, explained why the rating in his survey of Los Angeles County residents fell to its lowest point in seven years of existence. A majority of respondents said they are dissatisfied with the overall quality of their lives as reflected in nine categories, including cost of living, education, the environment and public safety. And those topics were also front of mind during the governors’ discussion.
Wilson, a Republican who was California governor from 1991 to 1999, took note of the current $80 billion revenue surplus in California, saying that if current lawmakers can’t solve the state’s shortcomings, it won’t be for lack of funds.
“The state is rolling in money. That’s not the problem,” he said when asked by Newton to speculate on the public’s downbeat mood. “The way it is spent is what’s causing a lot of the dissatisfaction. There are people who are very much concerned about crime because they’ve seen a dramatic shift, a really discernible shift. And they’re concerned about their children’s education, and they should be.”
Davis, a Democrat who was governor of California from 1999 to 2003, took a different tack on Californians’ current mood in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic.
“There’s a lot of good news globally, nationally and in California as it relates to people working again, and lower unemployment rates,” he said. “The bad news is that people have been through a very tough time. This has been two-and-a-half years where we’ve been told we can’t do this, we can’t do that. … People don’t like to be told what they can’t do.”
Solving society’s problems will require innovation, Davis said, and California is the right place. The number of U.S. patents that originated in California in recent years, he said, is roughly four times the number originating in the state that comes in second, Texas.
“If you want to invent something, this is the place to do it, in California,” he said. “We invent, we design, we create.”
Davis took note of the setting, a public research university in a state that is widely respected for its institutions of higher education. Mentioning that UCLA Chancellor Gene Block was in attendance, Davis continued, “There is nothing better about California than its 10 UC campuses. Nobody in the country has anything close to this.”
Block provided the introduction for the session, noting that Los Angeles faces substantial challenges relating to public safety, the ongoing pandemic and a shortage of affordable housing.
“These issues are bearing down on people all across the state. We’re not alone,” Block said. “Addressing them is going to require scholars, businesspeople, community leaders to really work together and devise and enact solutions.”
Noting the presence of the two former governors, Block continued. “Wisdom is gained by experience, and we have a vast amount of that here.”
Newton, a former reporter and editor at the Los Angeles Times whose books include a recent biography of two-time governor Jerry Brown, asked Wilson and Davis to talk about their approaches to public safety.
Davis acknowledged crime rates are on the rise, although not to “where they were in the ’90s when Pete Wilson and I were a governor.”
One solution, he said, lies in effective law enforcement.
“Police have to be part of the equation,” said Davis, acknowledging past abuses by some officers. “Anyone who saw the video of the George Floyd murder knows it was appalling, not acceptable, and should never happen again. But there are some common-sense reforms that I think most law enforcement agree with.”
He called for a balanced approach. “The police have to behave in a respectful way, treat people with dignity, in a way that commands respect.”
Wilson echoed the sentiment. “It’s called community policing. And it makes great sense, as does treating people respectfully when you stop them as a police officer.”
In his view, however, effective law enforcement is too often undermined by a lenient criminal justice system, especially regarding violent crime.
“I think I was the first governor in the country to sign — what was also subsequently in the same year, an initiative measure — that was called three strikes. And what it did was to focus on recidivism, on the people who were career violent criminals. … It’s not fair to play with people’s lives by letting people out on the street who are known violent criminals.”
Davis countered by pointing to a shortcoming of taking a hard-line approach to crime — overcrowded prisons that tend to perpetuate societal and racial inequities. Incarceration without rehabilitation doesn’t work either.
“Getting people to transition from prison back to productive life requires an extraordinary amount of help,” he said.
Perhaps no public policy issue better represents the divide between the haves and have-nots in California than the housing crisis. At a time when many homeowners are sitting on a fortune in housing equity, millions of people in the state struggle to pay rent. Some end up homeless.
“The California legislature has to get serious about making housing more affordable,” Davis said.
He pointed to legislation pending in Sacramento that would allocate $25 billion to an agency that could help potential homebuyers with a down payment and closing costs. Another effort in the private sector is offering 10% of a home’s down payment in exchange for 25% of the homeowner’s future equity.
“I’m not saying it’s perfect, but that’s on the right track,” Davis said.
Wilson pointed to the California Environmental Quality Act, known as CEQA, passed in 1970 and signed by then-governor Ronald Reagan, as a major hurdle to building more affordable housing in the state.
“The best single thing that could happen is for CEQA to be reformed because that has held up the construction of homes,” said Wilson, who decried the long wait that developers often face to clear the environmental protection review process. “It has hugely added to the delay in providing housing. And that has cost a fortune in terms of the ultimate buyer.”
But the legislation still has value, Newton said. “It is protective of the environment. No?”
Davis jumped into the discussion.
“Look, the original idea was: If Caltrans was building a freeway, the public should comment on it, and it should be thoroughly debated before it occurs,” he said.
Today, circumstances have changed, and the focus has turned to building homes for the state’s large population. Environmental reviews and public hearings about land use take time, but there are ways to shorten the process.
“The good news is we are making some progress,” Davis said. “When it comes to the homeless — anything for the building of shelter for the homeless and for all the services attended to in mental health and social services — all those buildings should be exempt [from CEQA].”
Newton also asked the governors to weigh in on another hot button topic, giving some of the state’s budget surplus back to Californians.
“Absolutely. I mean, gas prices are near a record high,” Davis said.
“Well, I think that it’s not bad, but it’s like dipping into [the country’s] petroleum reserve, it’s not the answer,” Wilson said.
Newton pressed forward, seeking to clarify that both former governors think the current governor, Gavin Newsom, should send a portion of the California surplus back to the state’s residents.
“We have a big surplus. It should be used for one-time expenditures like this,” Davis said.
“If it’s a one-time, modest solution, that will help,” Wilson said.
“You do agree,” Newton said, smiling. “I was surprised.”
Soon after, Newton thanked the former elected officials for their years of government service and their willingness to participate in a public discussion of political issues seen from their different vantage points.
“We all will disagree on things,” Newton said to the in-person audience and those watching online. “I think it’s too commonplace these days to assume that disagreement is [just cause] to be enemies. And it’s heartening to have the both of you here to show otherwise.”
Watch a recording of the session:
See additional photos from both April 22 sessions on Flickr:












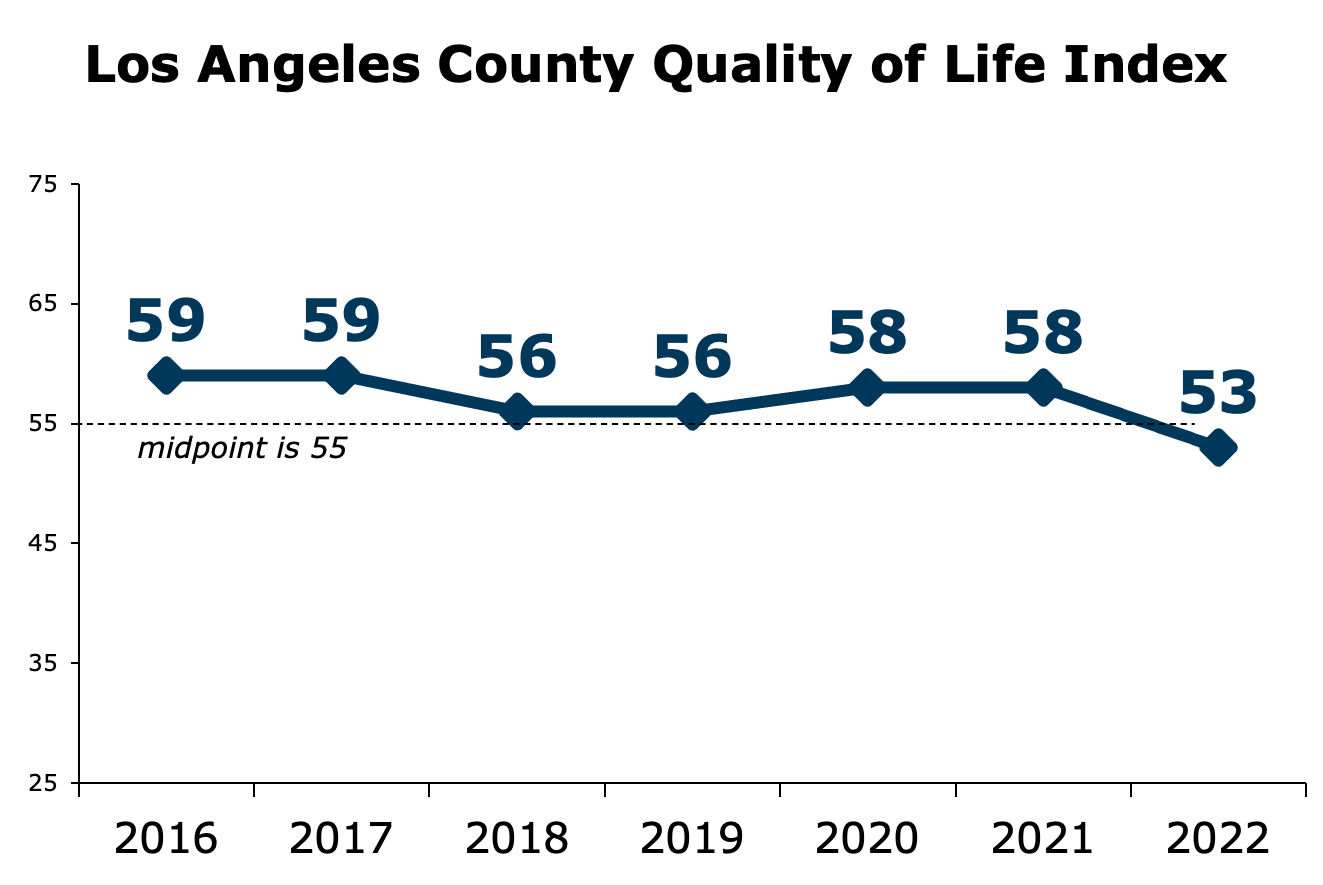
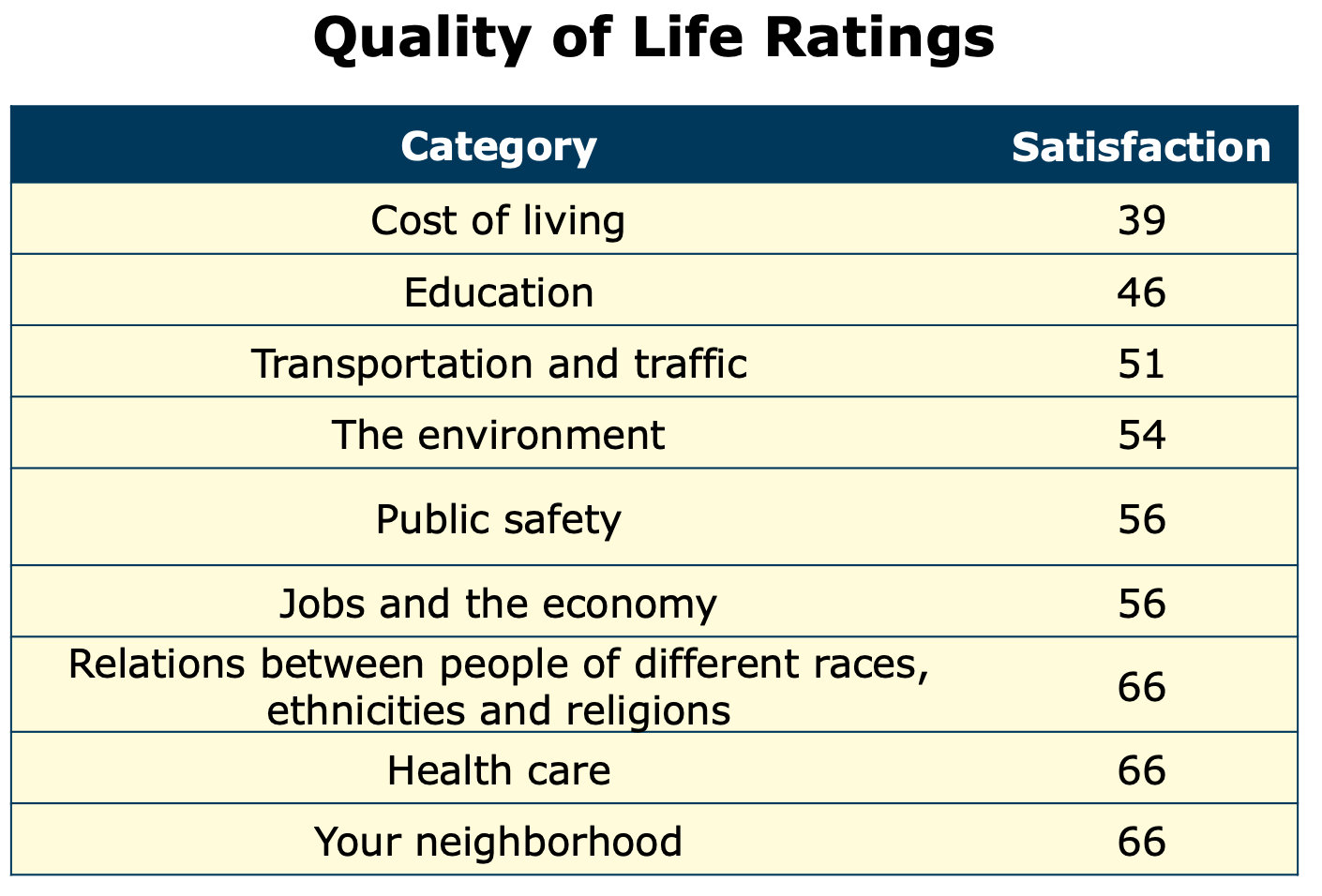 Scores declined in all nine of the survey categories, but the issues that were most responsible for the overall decline were cost of living, education and public safety.
Scores declined in all nine of the survey categories, but the issues that were most responsible for the overall decline were cost of living, education and public safety.











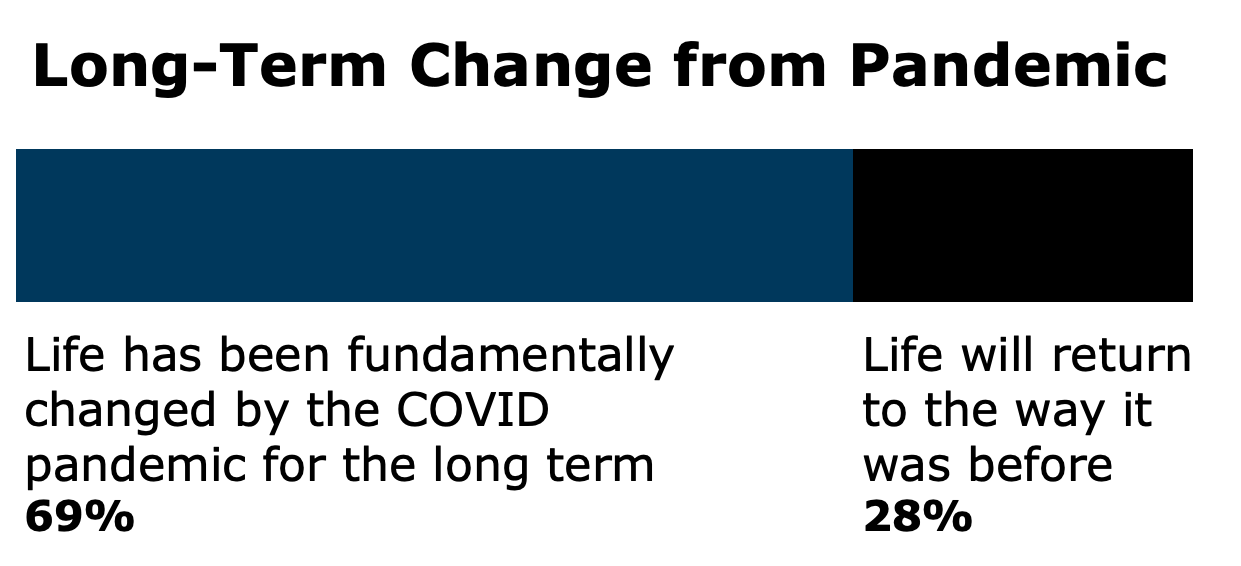 Most respondents, 69%, said life has been fundamentally changed by the COVID-19 pandemic. Only 28% said that life would return to the way it was before.
Most respondents, 69%, said life has been fundamentally changed by the COVID-19 pandemic. Only 28% said that life would return to the way it was before.